Final ID: MP1092
Integrative Epigenomic and Single-Cell Transcriptomic Profiling of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAAs) affect up to 1% of the population. Transcriptional regulation governs vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) phenotypic plasticity, yet upstream epigenomic mechanisms remain poorly defined. Here, we characterize the epigenomic cis-regulatory landscape of sporadic TAAs to uncover regulatory features driving VSMC dysfunction.
Methods:
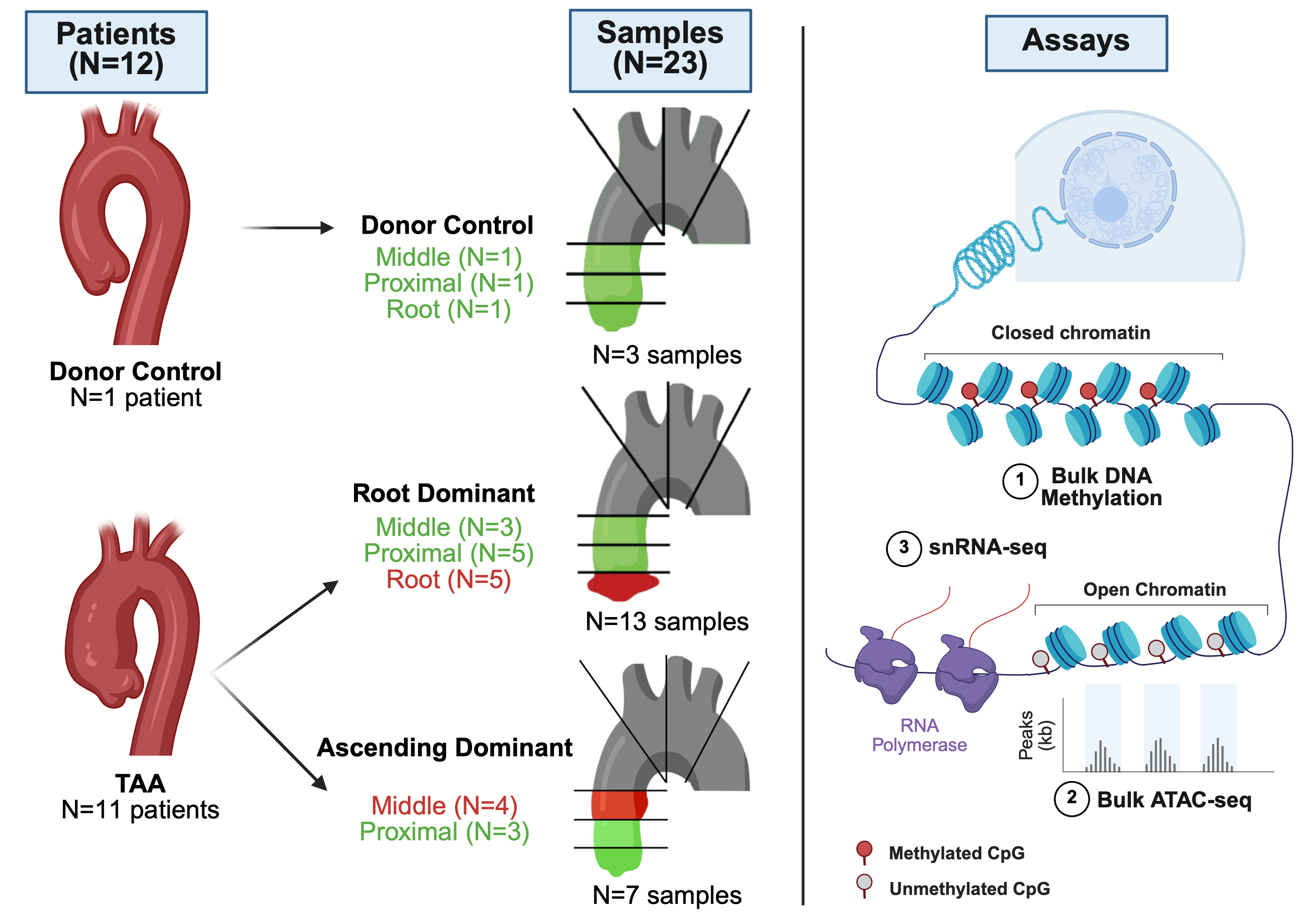
We prospectively collected fresh-frozen aortic tissue from patients with TAA and donor controls across anatomically distinct regions of the thoracic aorta: root, proximal, mid, and distal ascending. Patients were classified into root- or ascending-dominant phenotypes based on maximally dilatied regions. Bulk ATAC-seq was used to profile chromatin accessibility in TAAs, bulk methylation to assess CpG methylation, and snRNA-seq to compare dilated vs. non-dilated segments in ascending-dominant TAAs. DESeq2 identified differentially accessible peaks and methylated regions (q < 0.05, log2FC > 0), while HOMER assessed transcription factor (TF) motif enrichment.
Results:
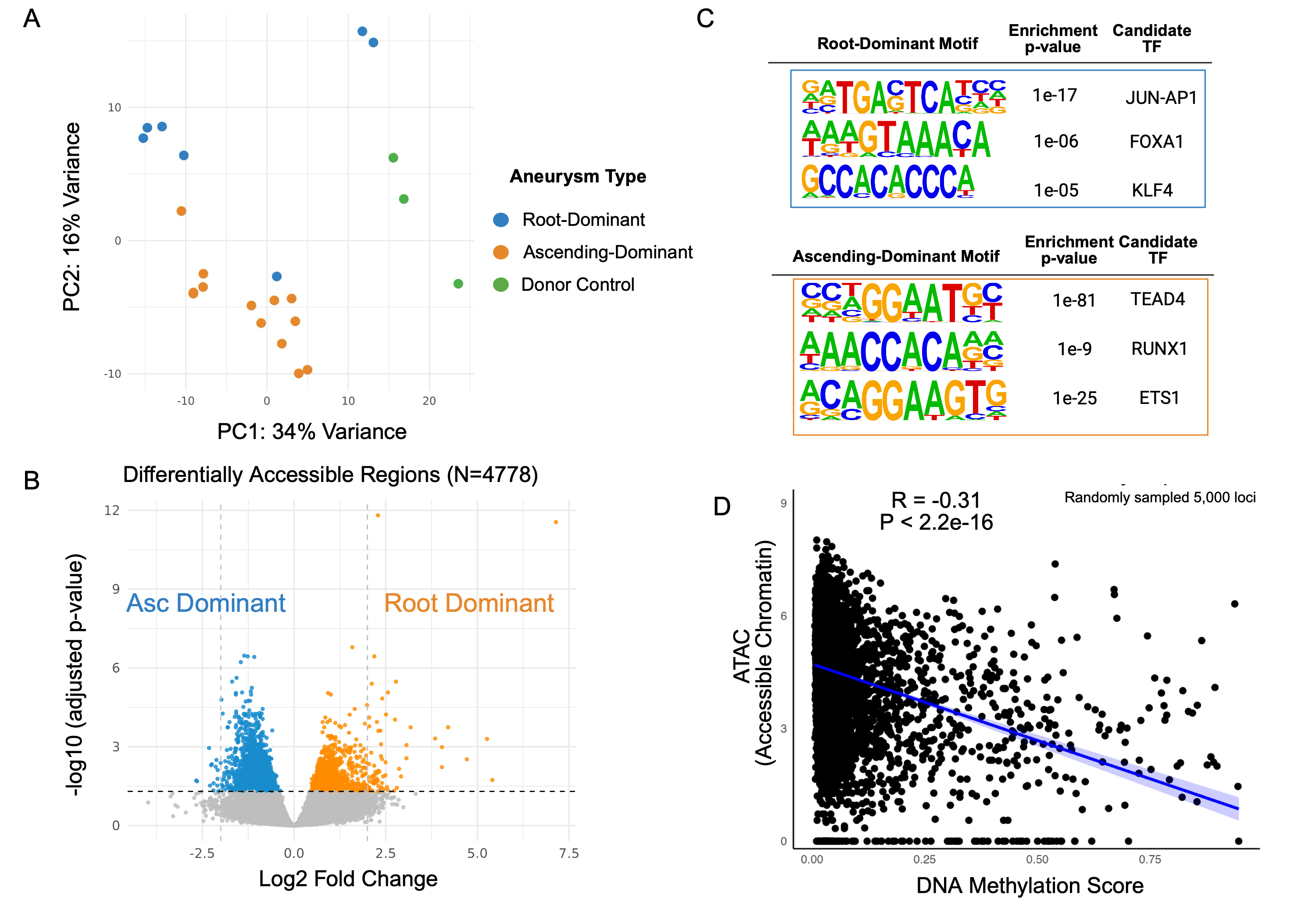
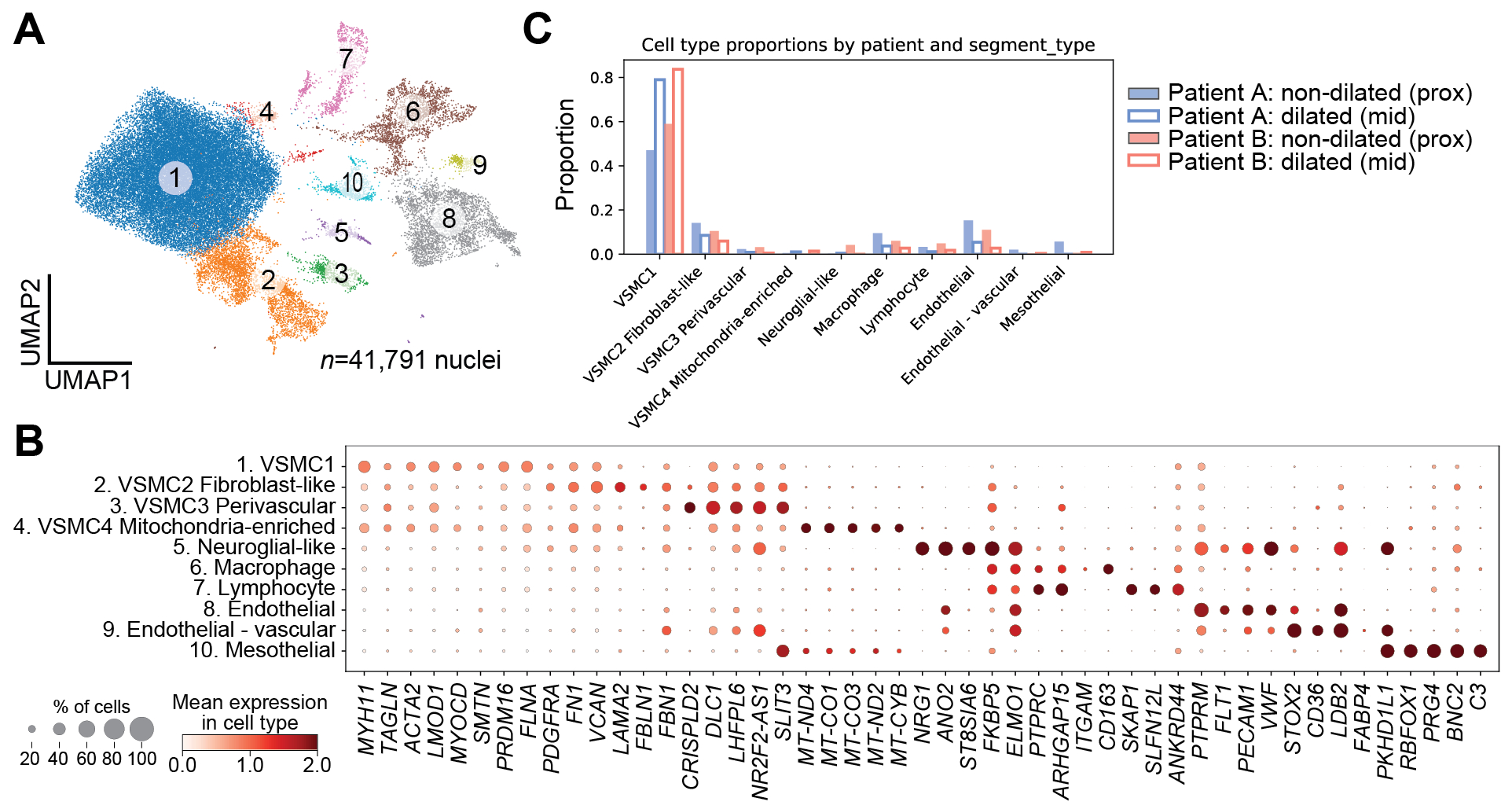
We analyzed 23 segments from 12 individuals (20 segments from 11 TAA patients, 3 segments from 1 donor control). All samples were profiled using ATAC-seq. DNA methylation profiling was performed on 6 samples from 3 patients, and snRNA-seq was conducted on 4 samples from 2 patients. Principal component analysis of 158,420 ATAC-seq peaks clearly separated TAA and control samples, including TAA subtypes. We identified 731 differentially accessible peaks in TAA samples linked to genes implicated in TAA pathogenesis, including KLF4 (log2FC=1.1, q=0.02). Motif analysis revealed enrichment of over 200 TF binding sites that were distinct between TAA phenotypes. Chromatin accessibility and DNA methylation scores were inversely correlated in promoter regions (r = –0.31, p < 2.2e-16), consistent with regulatory activity. From 41,791 nuclei profiled by snRNA-seq, we identified 10 distinct cell clusters, with 4 VSMC clusters comprising the majority (80.9%). TF motifs from differentially accessible peaks had higher expression in VSMCs from dilated samples.
Conclusion:
Our integrative analysis reveals a distinct coupling between chromatin accessibility and gene expression in TAAs, suggesting a stable and unique cis-regulatory architecture in VSMCs. We identify chromatin accessibility changes and transcriptional programs associated with VSMC dysfunction that warrant further exploration.
Thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAAs) affect up to 1% of the population. Transcriptional regulation governs vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) phenotypic plasticity, yet upstream epigenomic mechanisms remain poorly defined. Here, we characterize the epigenomic cis-regulatory landscape of sporadic TAAs to uncover regulatory features driving VSMC dysfunction.
Methods:
We prospectively collected fresh-frozen aortic tissue from patients with TAA and donor controls across anatomically distinct regions of the thoracic aorta: root, proximal, mid, and distal ascending. Patients were classified into root- or ascending-dominant phenotypes based on maximally dilatied regions. Bulk ATAC-seq was used to profile chromatin accessibility in TAAs, bulk methylation to assess CpG methylation, and snRNA-seq to compare dilated vs. non-dilated segments in ascending-dominant TAAs. DESeq2 identified differentially accessible peaks and methylated regions (q < 0.05, log2FC > 0), while HOMER assessed transcription factor (TF) motif enrichment.
Results:
We analyzed 23 segments from 12 individuals (20 segments from 11 TAA patients, 3 segments from 1 donor control). All samples were profiled using ATAC-seq. DNA methylation profiling was performed on 6 samples from 3 patients, and snRNA-seq was conducted on 4 samples from 2 patients. Principal component analysis of 158,420 ATAC-seq peaks clearly separated TAA and control samples, including TAA subtypes. We identified 731 differentially accessible peaks in TAA samples linked to genes implicated in TAA pathogenesis, including KLF4 (log2FC=1.1, q=0.02). Motif analysis revealed enrichment of over 200 TF binding sites that were distinct between TAA phenotypes. Chromatin accessibility and DNA methylation scores were inversely correlated in promoter regions (r = –0.31, p < 2.2e-16), consistent with regulatory activity. From 41,791 nuclei profiled by snRNA-seq, we identified 10 distinct cell clusters, with 4 VSMC clusters comprising the majority (80.9%). TF motifs from differentially accessible peaks had higher expression in VSMCs from dilated samples.
Conclusion:
Our integrative analysis reveals a distinct coupling between chromatin accessibility and gene expression in TAAs, suggesting a stable and unique cis-regulatory architecture in VSMCs. We identify chromatin accessibility changes and transcriptional programs associated with VSMC dysfunction that warrant further exploration.
More abstracts on this topic:
18F-NaF and 18F-FDG and calcification predict the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms and is attenuated by drug therapy
Nakahara Takehiro, Miyazawa Raita, Iwabuchi Yu, Tonda Kai, Narula Nupoor, Strauss Harry, Narula Jagat, Jinzaki Masahiro
Altered Cardiac Cell Populations in Hypoplastic Left Heart SyndromeMorton Sarah, Seidman Christine, Brown Kemar, Wei Eric, Gorham Joshua, Mcdonough Barbara, Beyer Martin, Neyazi Meraj, Layton Olivia, Seidman Jonathan