Final ID: Su1014
Artificial Intelligence Enhances Diagnostic Confidence and Significantly Reduces Referral Delays in Acute Cardiac Conditions in Low-Resource Settings
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a leading cause of global mortality, with disparities in healthcare access, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Acute cardiac conditions such as ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and atrial fibrillation require timely diagnosis for better outcomes. Many LMICs lack cardiology specialists, leading to delays in diagnosis and referrals. Artificial intelligence (AI) can address this gap by helping clinicians diagnose these conditions more efficiently.
Research Questions
This study evaluates the adoption of AI tools for diagnosing acute cardiac conditions across healthcare systems. We hypothesize that AI tools improve diagnostic accuracy, clinician confidence, and reduce referral delays, particularly in low-resource settings.
Methods
We conducted a multinational survey from December 2024 to May 2025 with 700 clinicians from the USA, UK, China, India, Pakistan, Yemen, Ethiopia, and Chad. The survey assessed AI tool usage, diagnostic confidence, referral delays, clinician trust in AI, and barriers to AI adoption. Statistical analyses included chi-square tests, ANOVA, and logistic regression.
Results
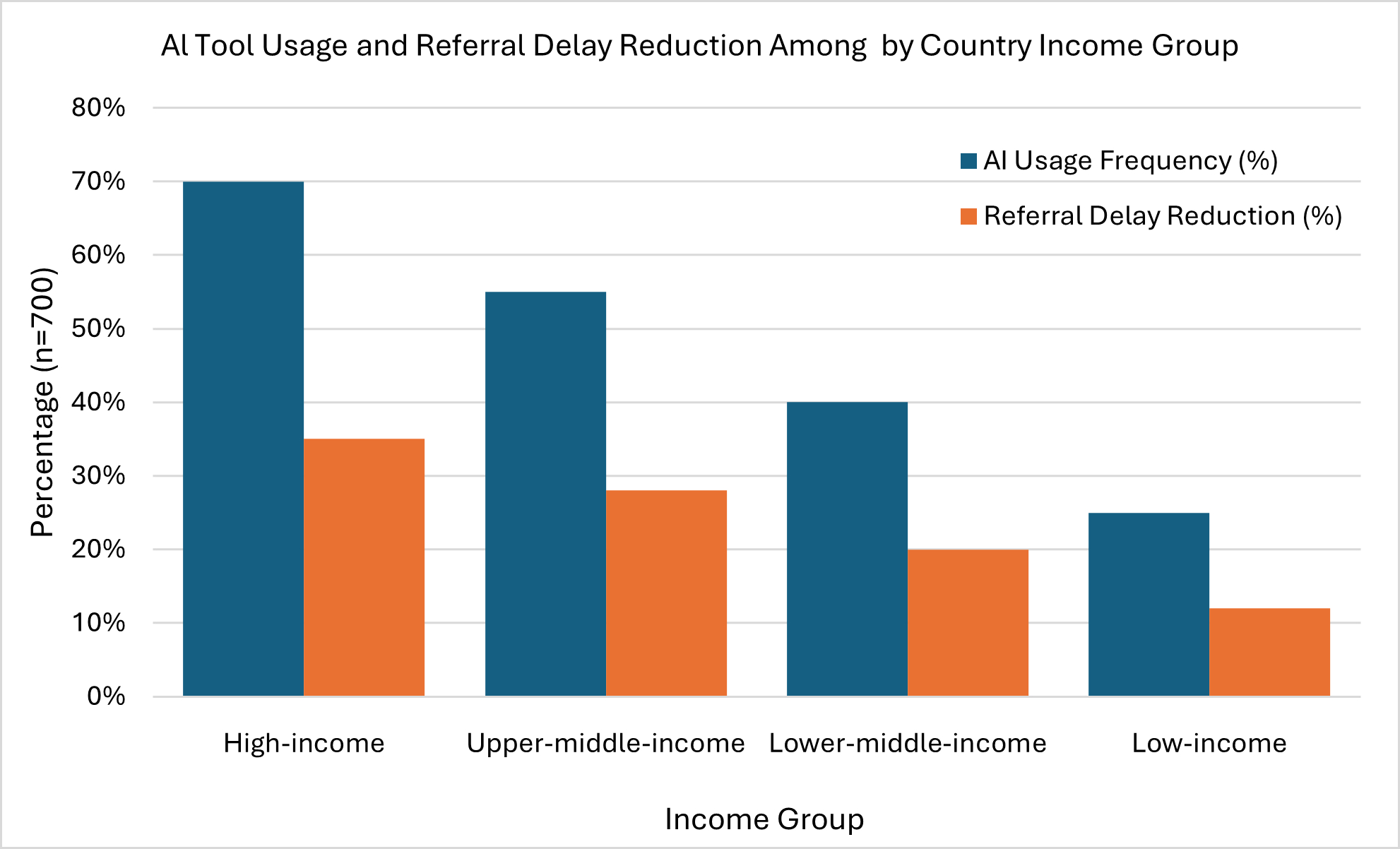
AI Tool Usage: AI usage was higher in middle- and low-income countries (68%) than in high-income countries (45%) (p < 0.001). Figure 1 shows AI usage and referral delay reduction by income group, with a stronger impact in low-income settings.
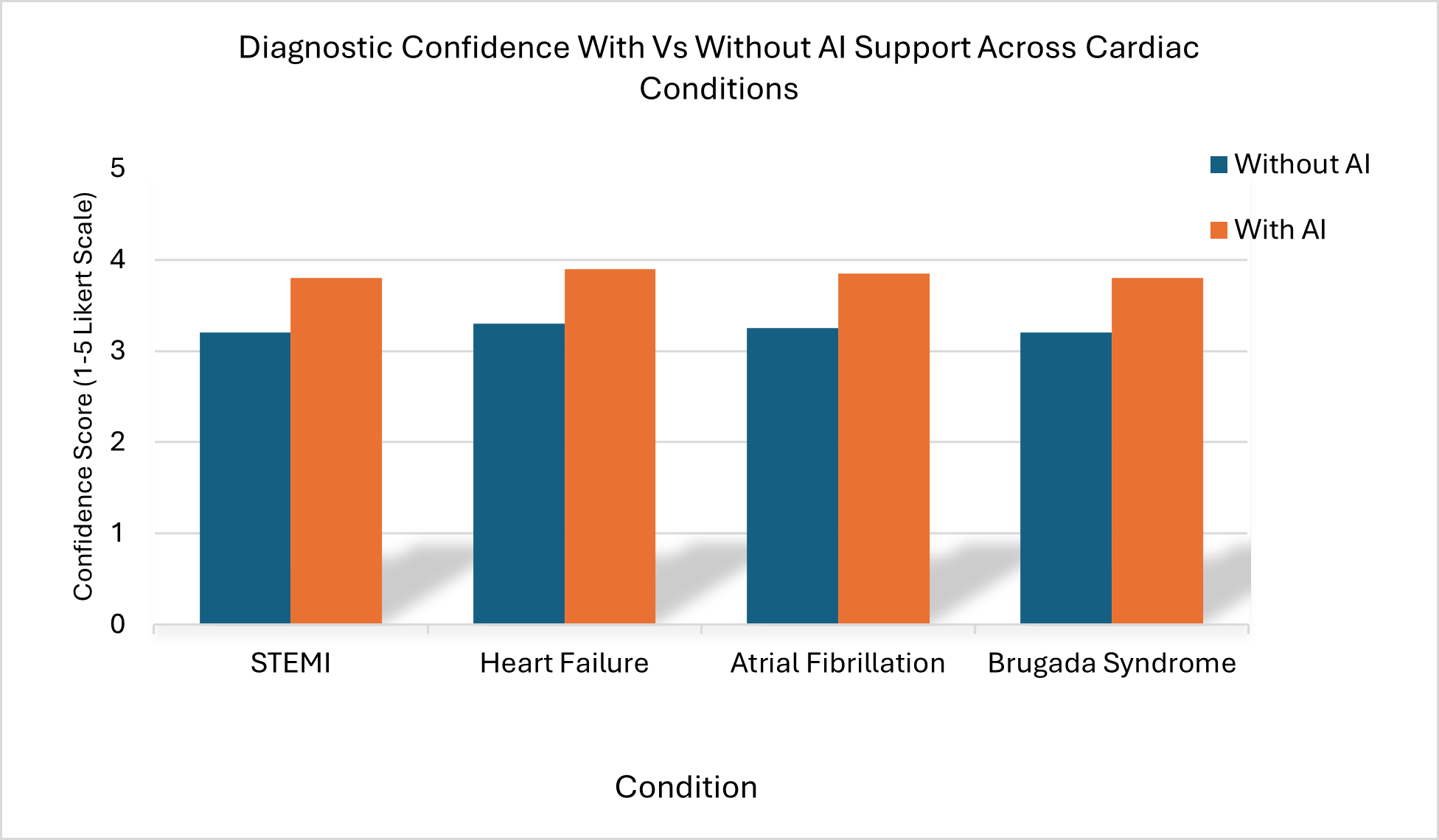
Diagnostic Confidence: AI tools significantly increased diagnostic confidence for STEMI, atrial fibrillation, and heart failure. Mean scores increased from 3.20 to 3.80 for STEMI (p < 0.001), 3.30 to 3.90 for heart failure (p < 0.001), and 3.25 to 3.85 for atrial fibrillation (p < 0.001). Figure 2 shows these increases in diagnostic confidence with AI support.
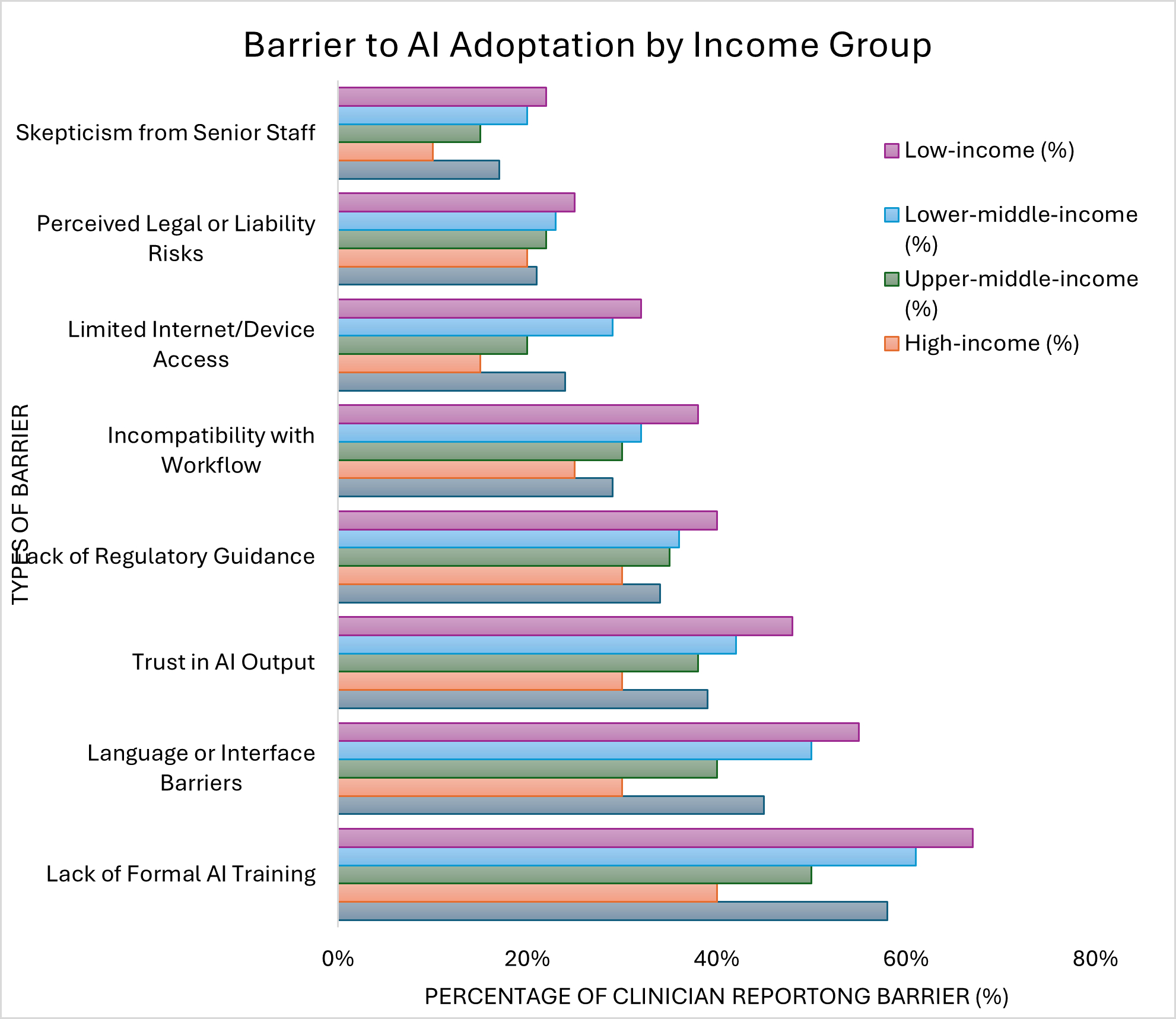
Barriers to AI Adoption: Common barriers included lack of training (58%), language issues (45%), and trust concerns (39%), more common in low-income countries. Figure 3 shows barriers to AI adoption by income group, emphasizing their impact on timely diagnosis and referrals.
Conclusion(s)
AI tools improve the management of acute cardiac conditions, especially in low-resource settings, by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and reducing referral delays. Addressing barriers like insufficient training and language issues is essential for broader AI adoption. Policymakers should focus on integrating AI into healthcare systems, especially in LMICs, to reduce disparities.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a leading cause of global mortality, with disparities in healthcare access, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Acute cardiac conditions such as ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and atrial fibrillation require timely diagnosis for better outcomes. Many LMICs lack cardiology specialists, leading to delays in diagnosis and referrals. Artificial intelligence (AI) can address this gap by helping clinicians diagnose these conditions more efficiently.
Research Questions
This study evaluates the adoption of AI tools for diagnosing acute cardiac conditions across healthcare systems. We hypothesize that AI tools improve diagnostic accuracy, clinician confidence, and reduce referral delays, particularly in low-resource settings.
Methods
We conducted a multinational survey from December 2024 to May 2025 with 700 clinicians from the USA, UK, China, India, Pakistan, Yemen, Ethiopia, and Chad. The survey assessed AI tool usage, diagnostic confidence, referral delays, clinician trust in AI, and barriers to AI adoption. Statistical analyses included chi-square tests, ANOVA, and logistic regression.
Results
AI Tool Usage: AI usage was higher in middle- and low-income countries (68%) than in high-income countries (45%) (p < 0.001). Figure 1 shows AI usage and referral delay reduction by income group, with a stronger impact in low-income settings.
Diagnostic Confidence: AI tools significantly increased diagnostic confidence for STEMI, atrial fibrillation, and heart failure. Mean scores increased from 3.20 to 3.80 for STEMI (p < 0.001), 3.30 to 3.90 for heart failure (p < 0.001), and 3.25 to 3.85 for atrial fibrillation (p < 0.001). Figure 2 shows these increases in diagnostic confidence with AI support.
Barriers to AI Adoption: Common barriers included lack of training (58%), language issues (45%), and trust concerns (39%), more common in low-income countries. Figure 3 shows barriers to AI adoption by income group, emphasizing their impact on timely diagnosis and referrals.
Conclusion(s)
AI tools improve the management of acute cardiac conditions, especially in low-resource settings, by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and reducing referral delays. Addressing barriers like insufficient training and language issues is essential for broader AI adoption. Policymakers should focus on integrating AI into healthcare systems, especially in LMICs, to reduce disparities.
More abstracts on this topic:
Challenging Case: Acute Type A Aortic Dissection with Multi-Organ Malperfusion
Agarwal Rishab, Bradshaw Alleabelle, Lawton Jennifer
A Novel Animal Model for Pulmonary Hypertension: Lung Endothelial Specific Deletion of Egln1 in MiceLiu Bin, Yi Dan, Ramirez Karina, Fallon Michael, Dai Zhiyu