Final ID: MP2668
Repetitive Ventricular Response During Radiofrequency Ablation of Left Posterior Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia: A Reliable Indicator of Success or Mere Observation?
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
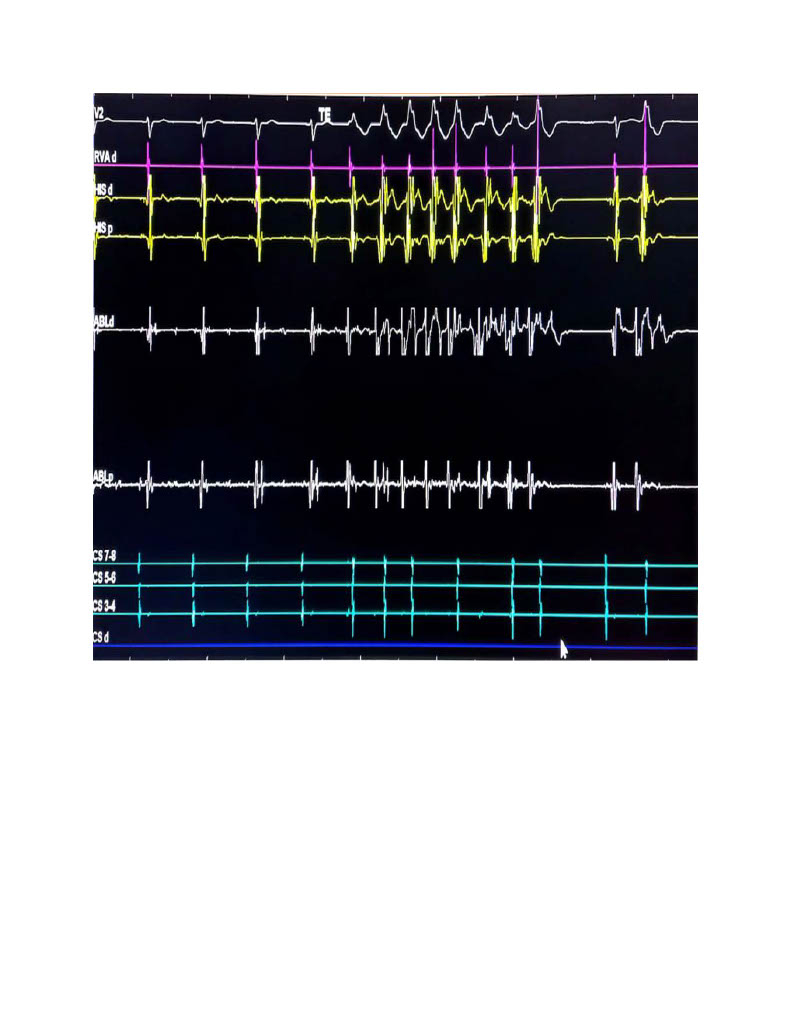
Idiopathic left posterior fascicular ventricular tachycardia (LPF-VT) is commonly treated with radiofrequency ablation (RFA), where non-inducibility of VT post-ablation is the conventional procedural endpoint. However, the occurrence of repetitive ventricular responses (RVR)—defined as ablation-induced, non-sustained ventricular tachycardia (NSVT) with morphology matching the clinical VT—may indicate real-time lesion effectiveness, even during sinus rhythm. This study aimed to assess whether RVR serves as a reliable predictor of successful ablation and long-term outcomes.
Methods:
This retrospective study included 38 consecutive patients (mean age 30 ± 9 years; 84% male) with inducible LPF-VT who underwent RFA during sinus rhythm. Ablation targeted low-amplitude Purkinje-like potentials in the left posterior septum. RVR was defined as ≥3 beats of NSVT provoked by RF energy and matching the clinical VT QRS morphology. Patients were stratified based on the presence or absence of RVR. Procedural success (non-inducibility post-RFA) and VT recurrence during a mean 24-month follow-up were compared.
Results:
RVR was observed in 27 of 38 patients (71%). Acute procedural success was achieved in all patients. VT recurrence was significantly lower in the RVR-positive group (2 of 27; 7.4%) compared to the RVR-negative group (4 of 11; 36.4%). All RVR episodes showed QRS morphology identical to the clinical VT. Two transient complications (one ventricular fibrillation, one polymorphic VT) occurred without long-term sequelae. These findings align with the “thermal mapping” concept, suggesting RVR may reflect effective lesion formation.
Conclusion:
Repetitive ventricular responses during RFA of LPF-VT are associated with improved long-term outcomes and lower recurrence rates. When the induced NSVT matches the clinical VT morphology, RVR may serve as a valuable adjunctive intra-procedural marker of successful ablation. Incorporating RVR as a procedural indicator may enhance ablation guidance in patients with LPF-VT.
Idiopathic left posterior fascicular ventricular tachycardia (LPF-VT) is commonly treated with radiofrequency ablation (RFA), where non-inducibility of VT post-ablation is the conventional procedural endpoint. However, the occurrence of repetitive ventricular responses (RVR)—defined as ablation-induced, non-sustained ventricular tachycardia (NSVT) with morphology matching the clinical VT—may indicate real-time lesion effectiveness, even during sinus rhythm. This study aimed to assess whether RVR serves as a reliable predictor of successful ablation and long-term outcomes.
Methods:
This retrospective study included 38 consecutive patients (mean age 30 ± 9 years; 84% male) with inducible LPF-VT who underwent RFA during sinus rhythm. Ablation targeted low-amplitude Purkinje-like potentials in the left posterior septum. RVR was defined as ≥3 beats of NSVT provoked by RF energy and matching the clinical VT QRS morphology. Patients were stratified based on the presence or absence of RVR. Procedural success (non-inducibility post-RFA) and VT recurrence during a mean 24-month follow-up were compared.
Results:
RVR was observed in 27 of 38 patients (71%). Acute procedural success was achieved in all patients. VT recurrence was significantly lower in the RVR-positive group (2 of 27; 7.4%) compared to the RVR-negative group (4 of 11; 36.4%). All RVR episodes showed QRS morphology identical to the clinical VT. Two transient complications (one ventricular fibrillation, one polymorphic VT) occurred without long-term sequelae. These findings align with the “thermal mapping” concept, suggesting RVR may reflect effective lesion formation.
Conclusion:
Repetitive ventricular responses during RFA of LPF-VT are associated with improved long-term outcomes and lower recurrence rates. When the induced NSVT matches the clinical VT morphology, RVR may serve as a valuable adjunctive intra-procedural marker of successful ablation. Incorporating RVR as a procedural indicator may enhance ablation guidance in patients with LPF-VT.
More abstracts on this topic:
A novel risk score predicts the prevalence of left atrial low-voltage areas and rhythm outcome in patients undergoing long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation ablation
Ooka Hirotaka, Nakao Sho, Kusuda Masaya, Ariyasu Wataru, Kudo Satoshi, Fujii Subaru, Mano Toshiaki, Matsuda Yasuhiro, Masuda Masaharu, Okamoto Shin, Ishihara Takayuki, Nanto Kiyonori, Tsujimura Takuya, Hata Yosuke, Uematsu Hiroyuki
A Comparative Analysis of Esophageal Cooling for Preventing Esophageal Injury Post Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysisIbrahim Momen Mohamed, Al Hennawi Hussam, Tanas Yousef, Abourady Youmna, Sewedan Nourhan, Hashem Ahmed Magdy, Motawea Karam R.