Final ID: Su4025
Enhancing the PREVENT Equation with a Polygenic Risk Score: Clinical Utility Evaluation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
The PREVENT risk prediction equations for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) was developed to overcome limitations of prior ACVD equations. Despite the inclusion of additional risk factors, there has been criticism that PREVENT underestimates risk. We explored the impact of adding a polygenic risk score (PRS) to improve clinical utility of PREVENT.
Methods
We used Genetic Epidemiology Resource in Adult Health and Aging (GERA) cohort of 60,544 members of Kaiser Permanente of Northern California between the ages of 30-74 years at baseline in 2007-08 (68% female, 81.2% European, 3.4% African-American, 7.0% Hispanic, 7.6% Asian) . There were 3,026 CHD (stable/ unstable angina, myocardial infarction, coronary revascularization, CHD death) incident events during 14 years of follow-up. A validated 12-SNP polygenic risk score (PRS) optimized for CHD (CARDIO inCode-Score) was used to capture genetic predisposition to CHD (Low=quintile 1; Intermediate=quintiles 2-4; High=quintile 5). We implemented time-to-event survival analysis and clinical utility evaluation of adding PRS to a model containing PREVENT.
Results
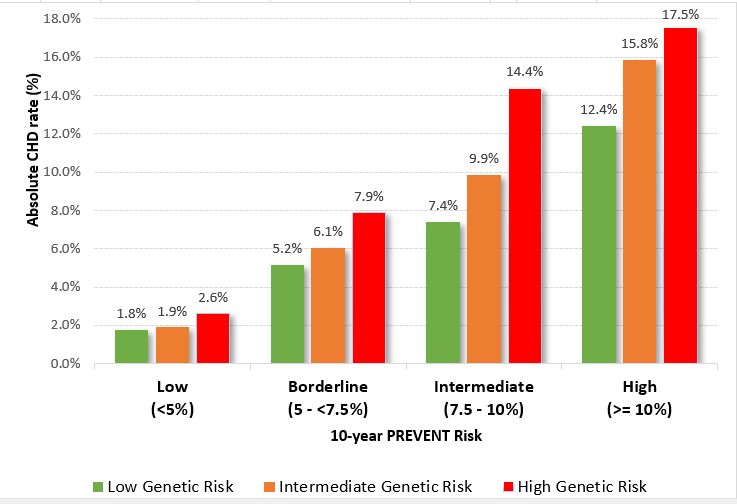
Mean (SD) age of cohort was 59 (9) years. Mean (SD) 10-year PREVENT risk was 4.8% (3.8%). Distribution of PREVENT risk groups was: 61% low (<5%), 18% borderline (5≤7.5%), 11% intermediate (7.5-10%) and 10% high (≥10%). Absolute CHD rates (per 100 persons) according to joint categories of PREVENT and polygenic risk are shown in the Figure. Among subjects with high PRS (n=10,865), 29% were at borderline/intermediate PREVENT risk and, of those, 50.2% were not taking statins at baseline. Notably, individuals with borderline PREVENT/high PRS had significantly higher rate than intermediate PREVENT/low PRS and similar for intermediate PREVENT/high PRS versus high PREVENT/low PRS. In a Cox model with simultaneous entry of categories of PREVENT and polygenic risk adjusting for 10 principal components of genetic ancestry, adding PRS to model containing PREVENT increased Harrell’s C statistic by 0.01 (0.747 to 0.757; p<0.0001). The category based Net Reclassification Improvement was 10.7 (7.6-13.9) in borderline/intermediate PREVENT risk.
Conclusion
A polygenic risk score added significant and clinically meaningful predictive information to the PREVENT equation and may help refine risk assessment, particularly among PREVENT borderline/intermediate individuals where decisions to initiate/intensify therapy is critical.
The PREVENT risk prediction equations for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) was developed to overcome limitations of prior ACVD equations. Despite the inclusion of additional risk factors, there has been criticism that PREVENT underestimates risk. We explored the impact of adding a polygenic risk score (PRS) to improve clinical utility of PREVENT.
Methods
We used Genetic Epidemiology Resource in Adult Health and Aging (GERA) cohort of 60,544 members of Kaiser Permanente of Northern California between the ages of 30-74 years at baseline in 2007-08 (68% female, 81.2% European, 3.4% African-American, 7.0% Hispanic, 7.6% Asian) . There were 3,026 CHD (stable/ unstable angina, myocardial infarction, coronary revascularization, CHD death) incident events during 14 years of follow-up. A validated 12-SNP polygenic risk score (PRS) optimized for CHD (CARDIO inCode-Score) was used to capture genetic predisposition to CHD (Low=quintile 1; Intermediate=quintiles 2-4; High=quintile 5). We implemented time-to-event survival analysis and clinical utility evaluation of adding PRS to a model containing PREVENT.
Results
Mean (SD) age of cohort was 59 (9) years. Mean (SD) 10-year PREVENT risk was 4.8% (3.8%). Distribution of PREVENT risk groups was: 61% low (<5%), 18% borderline (5≤7.5%), 11% intermediate (7.5-10%) and 10% high (≥10%). Absolute CHD rates (per 100 persons) according to joint categories of PREVENT and polygenic risk are shown in the Figure. Among subjects with high PRS (n=10,865), 29% were at borderline/intermediate PREVENT risk and, of those, 50.2% were not taking statins at baseline. Notably, individuals with borderline PREVENT/high PRS had significantly higher rate than intermediate PREVENT/low PRS and similar for intermediate PREVENT/high PRS versus high PREVENT/low PRS. In a Cox model with simultaneous entry of categories of PREVENT and polygenic risk adjusting for 10 principal components of genetic ancestry, adding PRS to model containing PREVENT increased Harrell’s C statistic by 0.01 (0.747 to 0.757; p<0.0001). The category based Net Reclassification Improvement was 10.7 (7.6-13.9) in borderline/intermediate PREVENT risk.
Conclusion
A polygenic risk score added significant and clinically meaningful predictive information to the PREVENT equation and may help refine risk assessment, particularly among PREVENT borderline/intermediate individuals where decisions to initiate/intensify therapy is critical.
More abstracts on this topic:
Diet quality, pathway-specific polygenic risk scores, and risk of type 2 diabetes among US men and women
Mei Zhendong, Liang Liming, Hu Frank, Li Jun, Wang Xingyan, Yun Huan, Sevilla-gonzalez Magdalena, Hu Jie, Bhupathiraju Shilpa, Sun Qi, Stampfer Meir, Willett Walter
A Health Coach-Based Multi-Level Personalized Strategy Lowers LDL-Cholesterol and Enhances Lipid Control in Veterans with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease – The VA Lipid Optimization Reimagined Quality Improvement Project at VA New York Harbor Healthcare SystemChen Tina, Ingerman Diana, Haley Leah, Salovaara Priscilla, Nicholson Andrew, Illenberger Nicholas, Natarajan Sundar