Final ID: MP2199
Beyond Heritability: Multimodal AI Integrating Imaging and Genetics Enables Population-Scale Precision Coronary Artery Disease Risk Prediction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Identifying asymptomatic individuals and treating them based on underlying risk is a key challenge in preventing coronary artery disease (CAD). Genetic risk scores and plaque quantification from cardiac imaging have emerged as powerful tools to expand conventional risk stratification. However, these modalities have not been combined in a single predictive model.
Objectives: First, to evaluate whether a multimodal AI model integrating imaging, genetic, and lipid-based risk improves prediction of 10-year incident CAD beyond clinical models. Second, to assess whether genetic risk adds predictive value after accounting for imaging. Third, to determine whether non-cardiac imaging modalities contribute independent information.
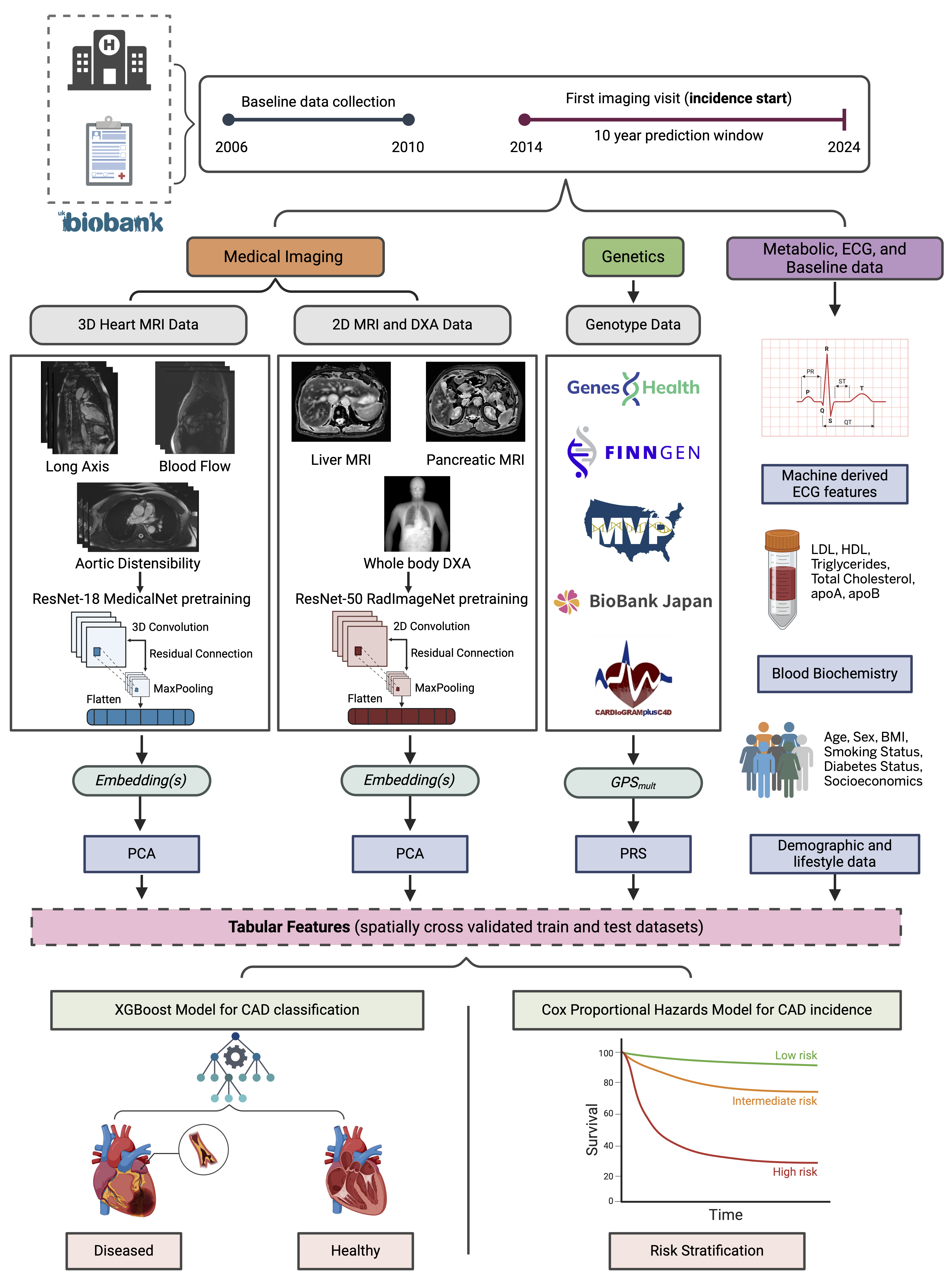
Methods: We analyzed data from over 60,000 UK Biobank participants with ~4,000 CAD events after imaging. Vision models were fine-tuned on cardiac, liver, and pancreas MRI and DXA scans. Imaging embeddings were reduced using principal component analysis and integrated with a multi-ancestry PRS (trained on >2M individuals), metabolic and ECG traits, and baseline variables in a unified Cox proportional hazards model. Model performance was assessed using pseudo R2 (leave-one-out) and commonality analysis.
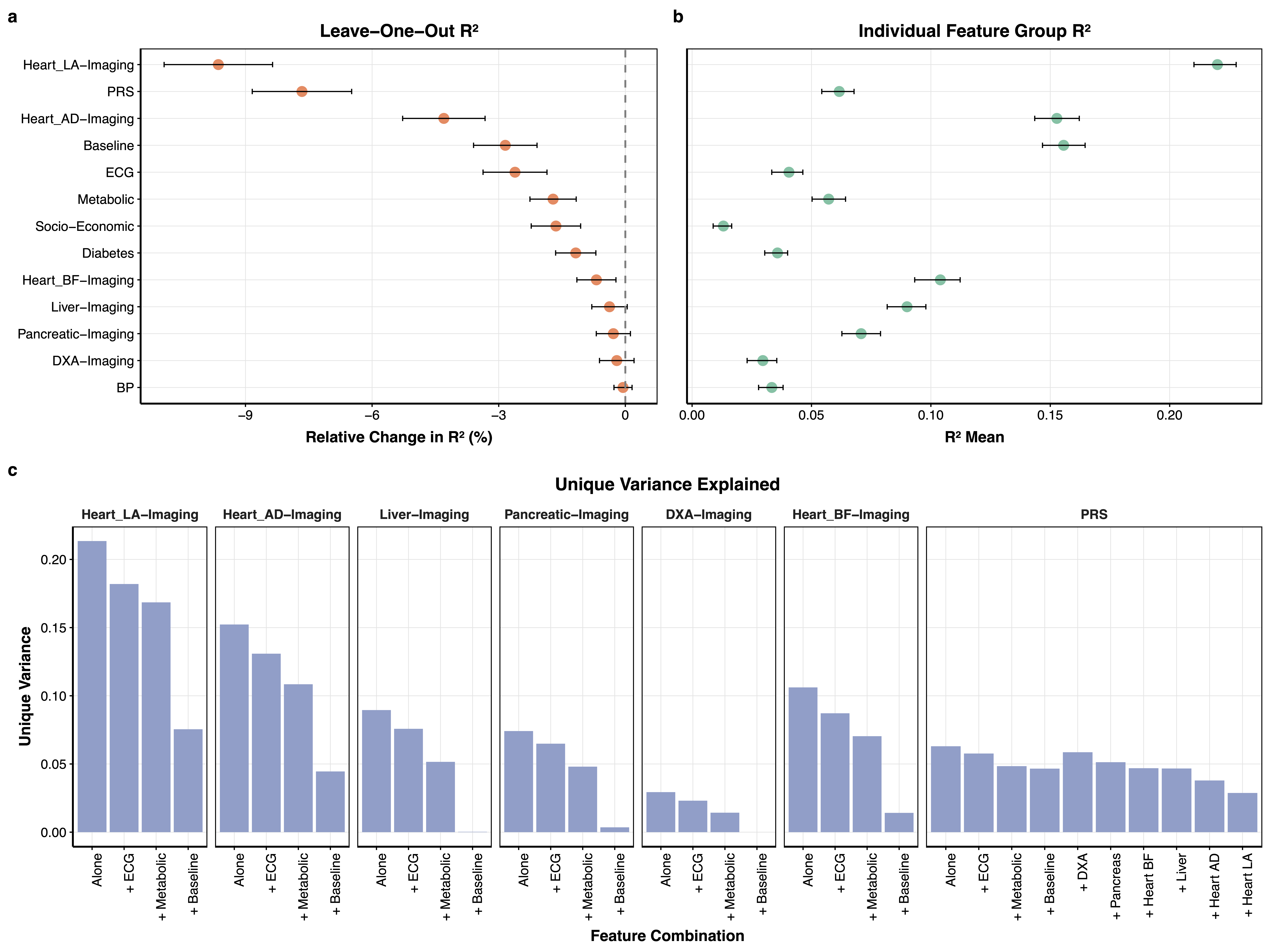
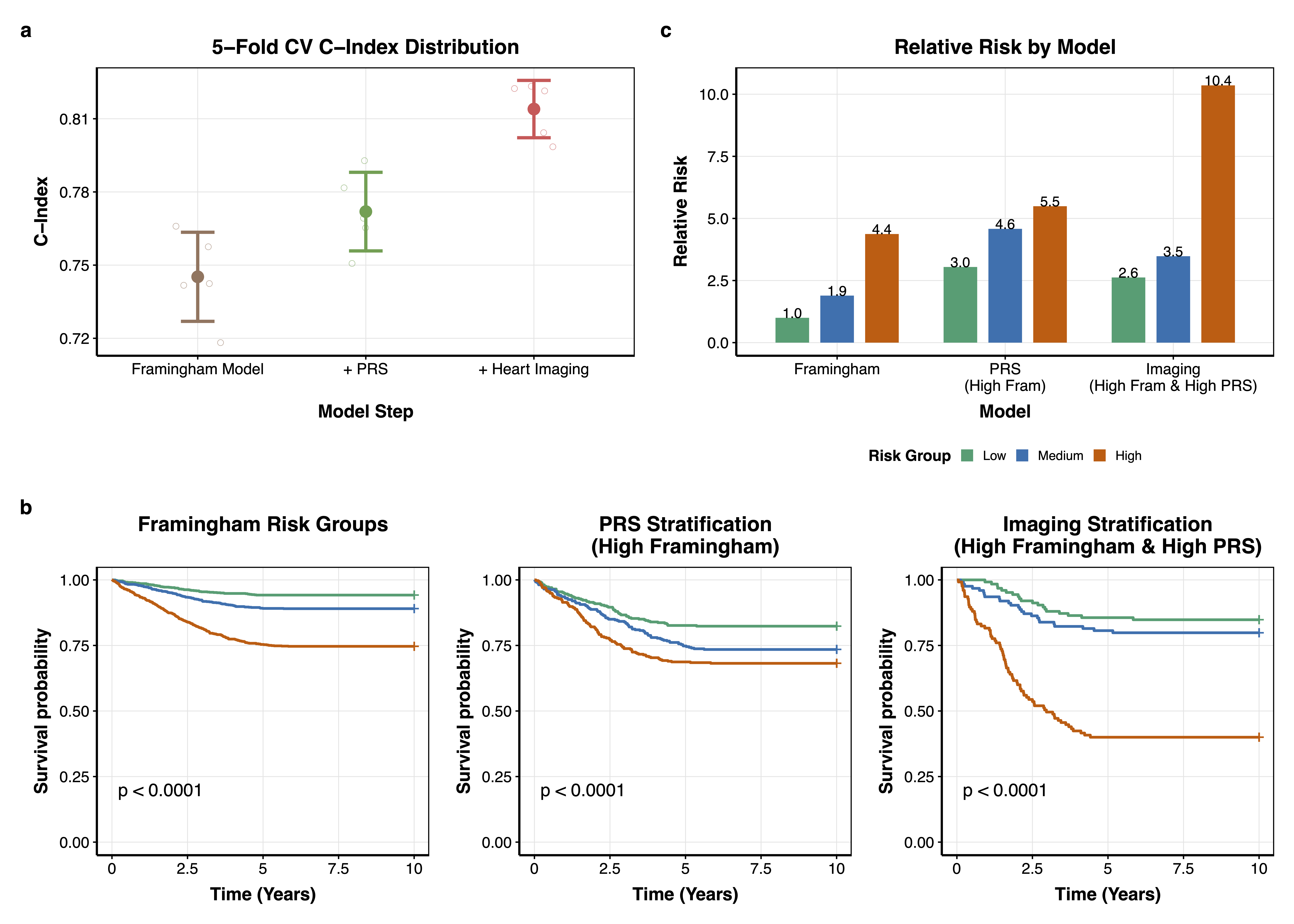
Results: Imaging embeddings outperformed hand-crafted image-derived phenotypes (AUC: 0.794 vs. 0.666). In joint models, only cardiac long-axis and aortic distensibility MRI contributed substantial independent value; liver, pancreas, and DXA features added minimal predictive power after adjusting for baseline traits. PRS alone explained pseudo R2 = 0.08, while the full multimodal model reached 0.45, with imaging contributing nearly three times the incremental variance explained by genetics. Genetic and imaging signals were largely orthogonal, though some genetic risk was partially captured by imaging. A hierarchical stratification framework combining clinical, genetic, and imaging data identified a subgroup with a 10-fold increased CAD risk relative to the low-risk baseline and a 5-fold increase compared to individuals with high clinical and genetic risk. Spatial cross-validation confirmed generalizability across imaging centers (AUC: 0.785-0.822 and C-index 0.751-0.763).
Conclusions: Genetic risk offers a fixed baseline of inherited susceptibility, but deep learning on non-invasive imaging adds dynamic markers of disease progression. Multimodal modeling offers a practical framework for precision CAD screening at population scale.
Objectives: First, to evaluate whether a multimodal AI model integrating imaging, genetic, and lipid-based risk improves prediction of 10-year incident CAD beyond clinical models. Second, to assess whether genetic risk adds predictive value after accounting for imaging. Third, to determine whether non-cardiac imaging modalities contribute independent information.
Methods: We analyzed data from over 60,000 UK Biobank participants with ~4,000 CAD events after imaging. Vision models were fine-tuned on cardiac, liver, and pancreas MRI and DXA scans. Imaging embeddings were reduced using principal component analysis and integrated with a multi-ancestry PRS (trained on >2M individuals), metabolic and ECG traits, and baseline variables in a unified Cox proportional hazards model. Model performance was assessed using pseudo R2 (leave-one-out) and commonality analysis.
Results: Imaging embeddings outperformed hand-crafted image-derived phenotypes (AUC: 0.794 vs. 0.666). In joint models, only cardiac long-axis and aortic distensibility MRI contributed substantial independent value; liver, pancreas, and DXA features added minimal predictive power after adjusting for baseline traits. PRS alone explained pseudo R2 = 0.08, while the full multimodal model reached 0.45, with imaging contributing nearly three times the incremental variance explained by genetics. Genetic and imaging signals were largely orthogonal, though some genetic risk was partially captured by imaging. A hierarchical stratification framework combining clinical, genetic, and imaging data identified a subgroup with a 10-fold increased CAD risk relative to the low-risk baseline and a 5-fold increase compared to individuals with high clinical and genetic risk. Spatial cross-validation confirmed generalizability across imaging centers (AUC: 0.785-0.822 and C-index 0.751-0.763).
Conclusions: Genetic risk offers a fixed baseline of inherited susceptibility, but deep learning on non-invasive imaging adds dynamic markers of disease progression. Multimodal modeling offers a practical framework for precision CAD screening at population scale.
More abstracts on this topic:
Body Mass Index, Diastolic Blood Pressure, and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Polygenic Background Differentially Modify Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Risk
Abramowitz Sarah, Levin Michael, Hoffman-andrews Lily, Zhang David, Judy Renae, Cappola Thomas, Day Sharlene, Reza Nosheen, Owens Anjali, Damrauer Scott
A Contemporary Machine Learning-Based Risk Stratification for Mortality and Hospitalization in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Using Multimodal Real-World DataFudim Marat, Weerts Jerremy, Patel Manesh, Balu Suresh, Hintze Bradley, Torres Francisco, Micsinai Balan Mariann, Rigolli Marzia, Kessler Paul, Touzot Maxime, Lund Lars, Van Empel Vanessa, Pradhan Aruna, Butler Javed, Zehnder Tobias, Sauty Benoit, Esposito Christian, Balazard Félix, Mayer Imke, Hallal Mohammad, Loiseau Nicolas