Final ID: MP1621
Worsening diet quality and low behavioral health scores among US adults with Preclinical Heart Failure: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2018
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: With heart failure (HF) prevalence rising, targeting its preclinical stages is key to prevention and reduction of morbidity and mortality. The American Heart Association’s Life’s Essential 8 (LE8) framework focuses on modifiable behavioral risk factors (diet, physical activity, smoking, sleep), yet their prevalence in preclinical HF is not well understood. We aimed to assess these behavioral factors in U.S. adults with preclinical HF using LE8 and compare them to those without preclinical HF.
Methods: We analyzed data from 10,748 adults aged ≥20 years without clinical HF using NHANES 2007–2018. Preclinical HF was defined by having at least one of the following: hypertension, diabetes, obesity, ASCVD, or structural heart issues (e.g., MI history). Behavioral factors were scored via the LE8 system (0–100) and grouped as low (<50), moderate (50–79), or high (≥80). Sampling weights accounted for NHANES’s design. We estimated the prevalence and 95% CIs of each behavior group for preclinical HF across cycles and compared mean behavioral scores between those with and without preclinical HF. Linear models assessed score trends over time.
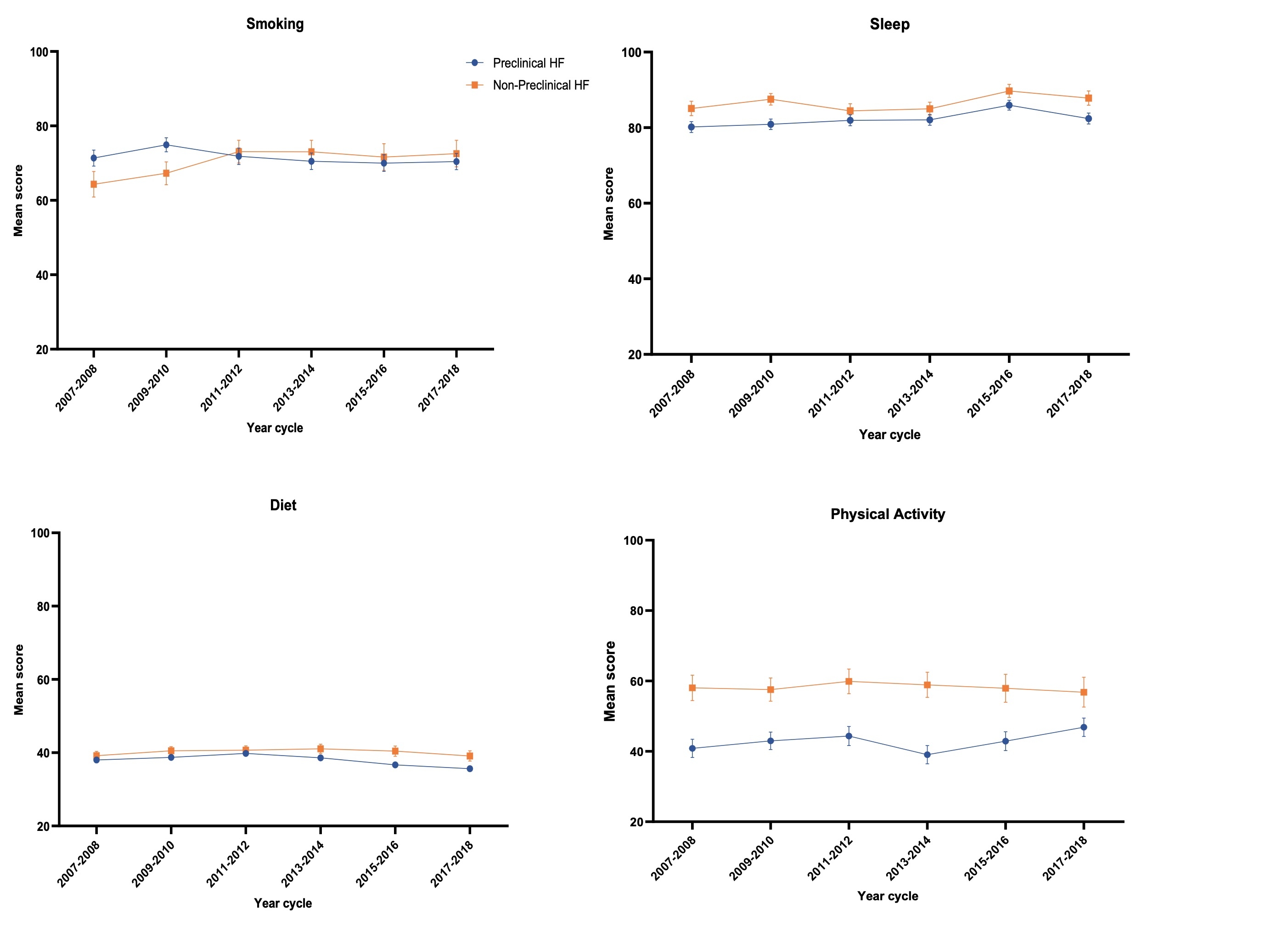
Results: Compared to those without preclinical HF, individuals with preclinical HF showed significantly lower mean scores for diet (37.8; 95%CI: 37.5–38.1 vs. 40.1; 95%CI: 39.6–40.6, P < .0001), physical activity (42.9; 95%CI: 41.8–43.9 vs. 58.2; 95%CI: 56.7–59.6, P < .0001), and sleep (82.3; 95%CI: 81.7–82.8 vs. 86.5; 95%CI: 85.8–87.2, P < .0001), except for smoking (71.4; 95%CI: 70.5–72.3 vs. 70.2; 95%CI: 68.8–71.5, P = 0.10). Overtime, the decade of observation, diet quality declined among individuals with preclinical HF (β = –0.58, P<0.0001), whereas no change was observed among those without preclinical HF (β = –0.002, P= 0.986). Smoking scores also worsened in preclinical HF (β= –0.597,P=0.02 for trend), contrasting with an improvement in non-preclinical HF individuals (β =1.573,P<0.0001 for trend) (P<0.001 for interaction).
Conclusion: Among US adults with preclinical HF, LE8 derived behavioral scores are particularly poor for diet and physical activity and the score for diet is worsening overtime. These results highlight opportunities for targeted interventions in this high-risk population.
Methods: We analyzed data from 10,748 adults aged ≥20 years without clinical HF using NHANES 2007–2018. Preclinical HF was defined by having at least one of the following: hypertension, diabetes, obesity, ASCVD, or structural heart issues (e.g., MI history). Behavioral factors were scored via the LE8 system (0–100) and grouped as low (<50), moderate (50–79), or high (≥80). Sampling weights accounted for NHANES’s design. We estimated the prevalence and 95% CIs of each behavior group for preclinical HF across cycles and compared mean behavioral scores between those with and without preclinical HF. Linear models assessed score trends over time.
Results: Compared to those without preclinical HF, individuals with preclinical HF showed significantly lower mean scores for diet (37.8; 95%CI: 37.5–38.1 vs. 40.1; 95%CI: 39.6–40.6, P < .0001), physical activity (42.9; 95%CI: 41.8–43.9 vs. 58.2; 95%CI: 56.7–59.6, P < .0001), and sleep (82.3; 95%CI: 81.7–82.8 vs. 86.5; 95%CI: 85.8–87.2, P < .0001), except for smoking (71.4; 95%CI: 70.5–72.3 vs. 70.2; 95%CI: 68.8–71.5, P = 0.10). Overtime, the decade of observation, diet quality declined among individuals with preclinical HF (β = –0.58, P<0.0001), whereas no change was observed among those without preclinical HF (β = –0.002, P= 0.986). Smoking scores also worsened in preclinical HF (β= –0.597,P=0.02 for trend), contrasting with an improvement in non-preclinical HF individuals (β =1.573,P<0.0001 for trend) (P<0.001 for interaction).
Conclusion: Among US adults with preclinical HF, LE8 derived behavioral scores are particularly poor for diet and physical activity and the score for diet is worsening overtime. These results highlight opportunities for targeted interventions in this high-risk population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Achieving Guidelines within a 24-Hour Movement Paradigm and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality in United States Adults
Boudreaux Benjamin, Xu Chang, Dooley Erin, Hornikel Bjoern, Munson Alexandra, Shechter Ari, Palta Priya, Gabriel Kelley, Diaz Keith
Disaggregating Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Mortality among Asian Subgroups in the United StatesSaleem Hira, Shahid Izza, Dong Weichuan, Nasir Khurram, Al-kindi Sadeer