Final ID: MP261
Trends in Stroke Mortality and Burden Due to High Blood Pressure: A Comparison of the U.S. and High Sociodemographic Index Countries
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
Stroke remains a leading cause of death and disability globally. High blood pressure (BP), particularly elevated systolic levels, is a major modifiable risk factor for stroke and contributes substantially to its burden. However, stroke mortality and burden due to high BP across regions, including high socio-demographic index (SDI) countries and the U.S., remain underexplored.
Methods
Data on stroke attributable to high BP were sourced from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 study. Age-standardized death rates (ASDR) and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) from 1990 to 2021 were analyzed for the U.S. and compared to high SDI countries. Temporal trends were assessed using annual percentage change (APC), average annual percentage change difference (AAPCD), and their 95% confidence intervals (CI), with significance set at p<0.05.
Results
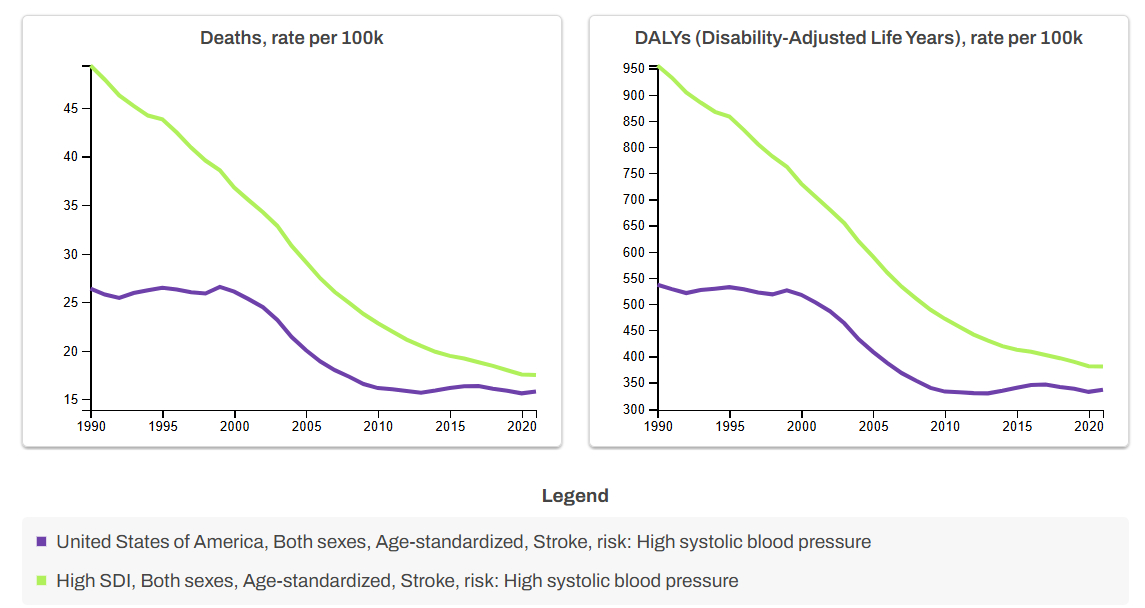
In the U.S., ASDR for declined from 26.4 (95% CI: 19.8–32.1) in 1990 to 15.8 (95% CI: 11.1–20.2) in 2021. It remained stable during 1990–2001 (APC: -0.08; 95% CI: -0.41 to 0.26; p=0.56), declined in 2001–2009 (APC: -5.76; 95% CI: -6.48 to -5.17; p<0.01), and stabilized again from 2009–2021 (APC: -0.11; 95% CI: -0.46 to 0.29; p=0.40). In contrast, high SDI countries experienced a continuous decline in ASDR from 49.4 (95% CI: 37.4–58.9) to 17.5 (95% CI: 12.6–21.8), without stable periods (Figure 1: Left Panel). The overall decline was significantly greater in high SDI countries vs. the U.S. (AAPCD: 1.49; 95% CI: 1.14 to 1.83; p<0.01).
U.S. DALY rates declined from 536.6 (95% CI: 402.1–650.5) in 1990 to 335.9 (95% CI: 241.3–424.5) in 2021. There was a modest drop from 1990–2001 (APC: -0.36; 95% CI: -0.59 to -0.12; p<0.01), a steeper decline in 2001–2009 (APC: -5.28; 95% CI: -5.76 to -4.87; p<0.01), and a stable trend from 2009–2021 (APC: 0.18; 95% CI: -0.06 to 0.43; p=0.10). DALY rates in high SDI countries consistently declined from 955.5 (95% CI: 723.9–1142.6) to 380.3 (95% CI: 280.2–469.9) (Figure 1: Right Panel), with a significantly larger overall reduction compared to the U.S. (AAPCD: 1.31; 95% CI: 1.00 to 1.62; p<0.01).
Conclusions
While both the U.S. and high SDI countries saw declines in stroke mortality and DALY rates due to high BP, the reductions were significantly greater in high SDI countries, with a recent plateau in the U.S. These findings underscore the need for stricter BP monitoring and control strategies in the U.S., particularly for patients with stroke risk factors and a high preponderance to it.
Background
Stroke remains a leading cause of death and disability globally. High blood pressure (BP), particularly elevated systolic levels, is a major modifiable risk factor for stroke and contributes substantially to its burden. However, stroke mortality and burden due to high BP across regions, including high socio-demographic index (SDI) countries and the U.S., remain underexplored.
Methods
Data on stroke attributable to high BP were sourced from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 study. Age-standardized death rates (ASDR) and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) from 1990 to 2021 were analyzed for the U.S. and compared to high SDI countries. Temporal trends were assessed using annual percentage change (APC), average annual percentage change difference (AAPCD), and their 95% confidence intervals (CI), with significance set at p<0.05.
Results
In the U.S., ASDR for declined from 26.4 (95% CI: 19.8–32.1) in 1990 to 15.8 (95% CI: 11.1–20.2) in 2021. It remained stable during 1990–2001 (APC: -0.08; 95% CI: -0.41 to 0.26; p=0.56), declined in 2001–2009 (APC: -5.76; 95% CI: -6.48 to -5.17; p<0.01), and stabilized again from 2009–2021 (APC: -0.11; 95% CI: -0.46 to 0.29; p=0.40). In contrast, high SDI countries experienced a continuous decline in ASDR from 49.4 (95% CI: 37.4–58.9) to 17.5 (95% CI: 12.6–21.8), without stable periods (Figure 1: Left Panel). The overall decline was significantly greater in high SDI countries vs. the U.S. (AAPCD: 1.49; 95% CI: 1.14 to 1.83; p<0.01).
U.S. DALY rates declined from 536.6 (95% CI: 402.1–650.5) in 1990 to 335.9 (95% CI: 241.3–424.5) in 2021. There was a modest drop from 1990–2001 (APC: -0.36; 95% CI: -0.59 to -0.12; p<0.01), a steeper decline in 2001–2009 (APC: -5.28; 95% CI: -5.76 to -4.87; p<0.01), and a stable trend from 2009–2021 (APC: 0.18; 95% CI: -0.06 to 0.43; p=0.10). DALY rates in high SDI countries consistently declined from 955.5 (95% CI: 723.9–1142.6) to 380.3 (95% CI: 280.2–469.9) (Figure 1: Right Panel), with a significantly larger overall reduction compared to the U.S. (AAPCD: 1.31; 95% CI: 1.00 to 1.62; p<0.01).
Conclusions
While both the U.S. and high SDI countries saw declines in stroke mortality and DALY rates due to high BP, the reductions were significantly greater in high SDI countries, with a recent plateau in the U.S. These findings underscore the need for stricter BP monitoring and control strategies in the U.S., particularly for patients with stroke risk factors and a high preponderance to it.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Longitudinal 20-year Analysis Indicates Acceleration of Cardiometabolic Comorbidities on Dementia Risk
Lihua Huang, Danish Muhammad, Auyeung Tw, Jenny Lee, Kwok Timothy, Abrigo Jill, Wei Yingying, Lo Cecilia, Fung Erik
A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies Comparing Short and Longterm Outcomes of Trans-Catheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Patient with and without Cancer:Khan Muhammad Aslam, Haider Adnan, Haider Taimoor, Bhattarai Shraddha, Khan Bilal, Lamichhane Bikal, Shafique Nouman, Rahman Hammad, Aafreen Asna, Muhammad Anza, Bhatia Hitesh, Khan Abid Nawaz Khan, Akbar Usman, Khan Alamzaib