Final ID: MP969
RSPO1-Mediated Macrophage Polarization Drives Ventricular Remodeling and Heart Failure after Myocardial Infarctio
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background/ Hypothesis: Macrophages exhibit remarkable heterogeneity and plasticity under diverse pathological conditions]. Precise regulation of macrophage function and phenotypic polarization is closely linked to cardiac remodeling and heart failure (HF) progression following myocardial infarction (MI). However, the molecular mechanisms driving macrophage polarization post-MI remain elusive.
Aims: This study aimed to investigate the role of RSPO1 in post-MI macrophage polarization, elucidate its molecular mechanisms in ventricular remodeling and HF, and explore potential therapeutic interventions by targeting RSPO1.
Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was performed at various time points post-MI to identify differentially expressed genes. RSPO1 expression was validated in the serum of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients. RSPO1 knockout and humanized Rspo1 p.R219W mutation mouse models were utilized to assess its impact on post-MI outcomes. RNA-seq and scRNA-seq were employed to analyze transcriptional differences in cardiac tissue, while SCENIC analysis identified regulatory pathways. Additionally, a RSPO1-neutralizing antibody was developed to evaluate therapeutic potential.
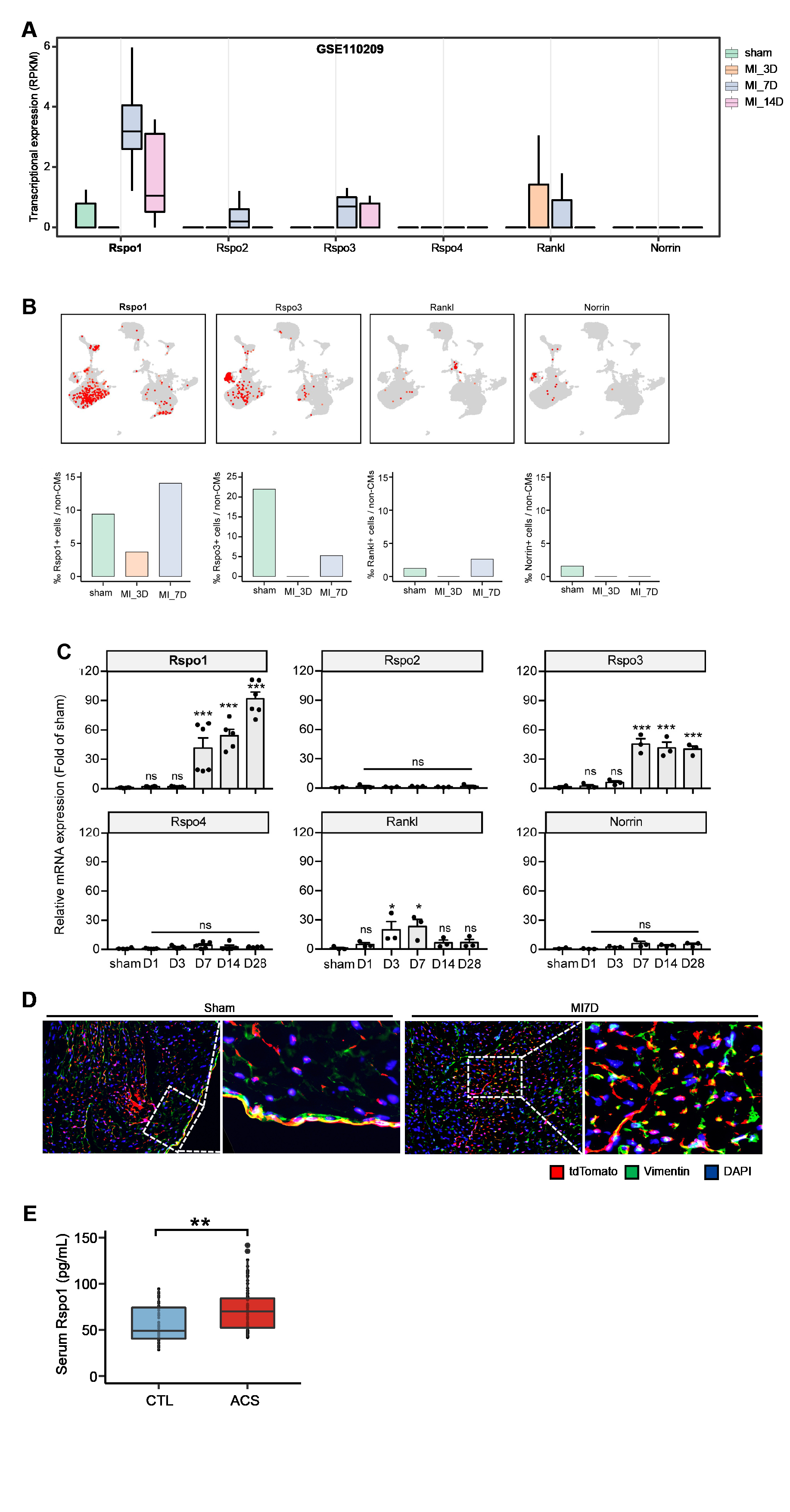
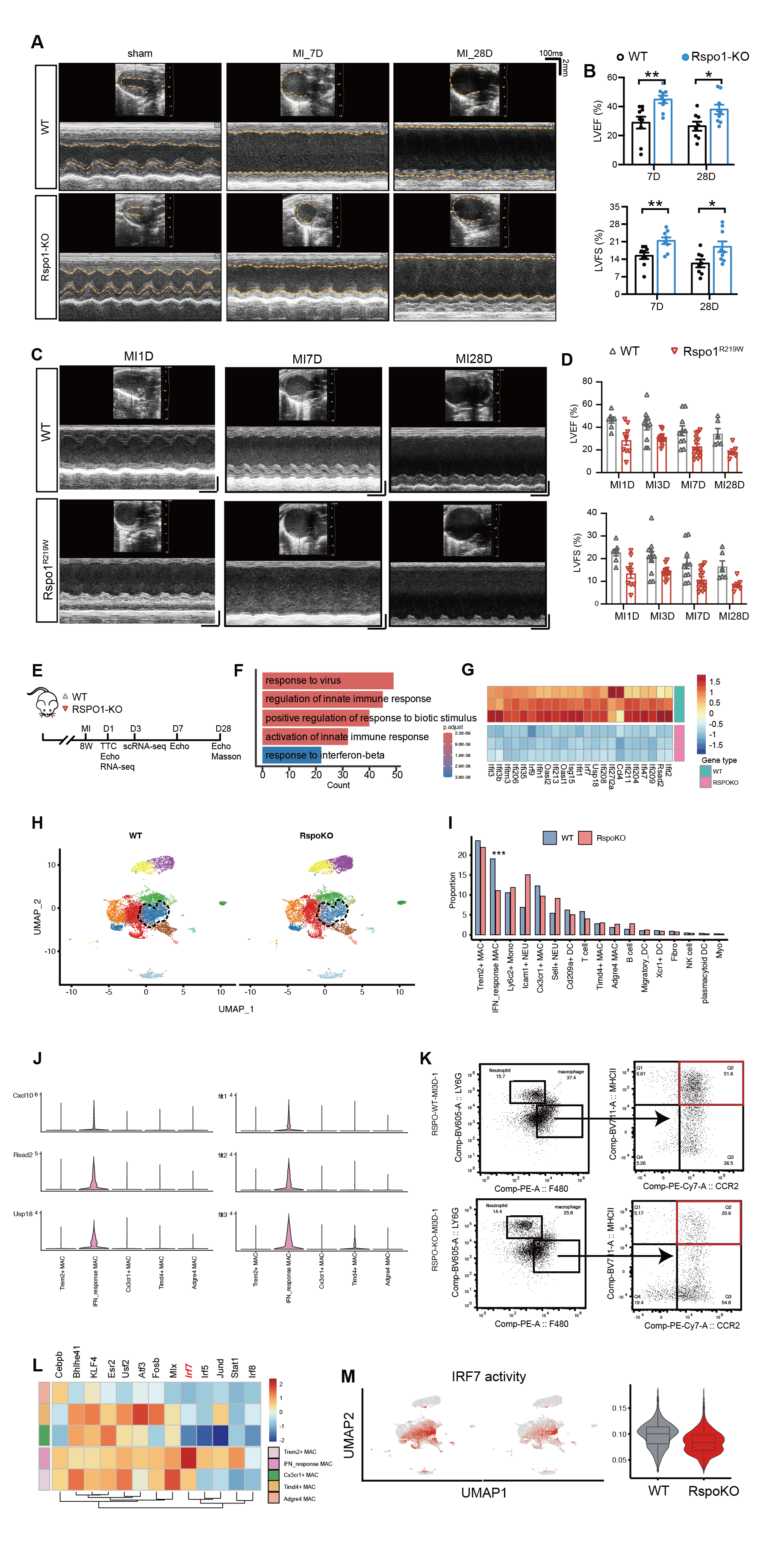
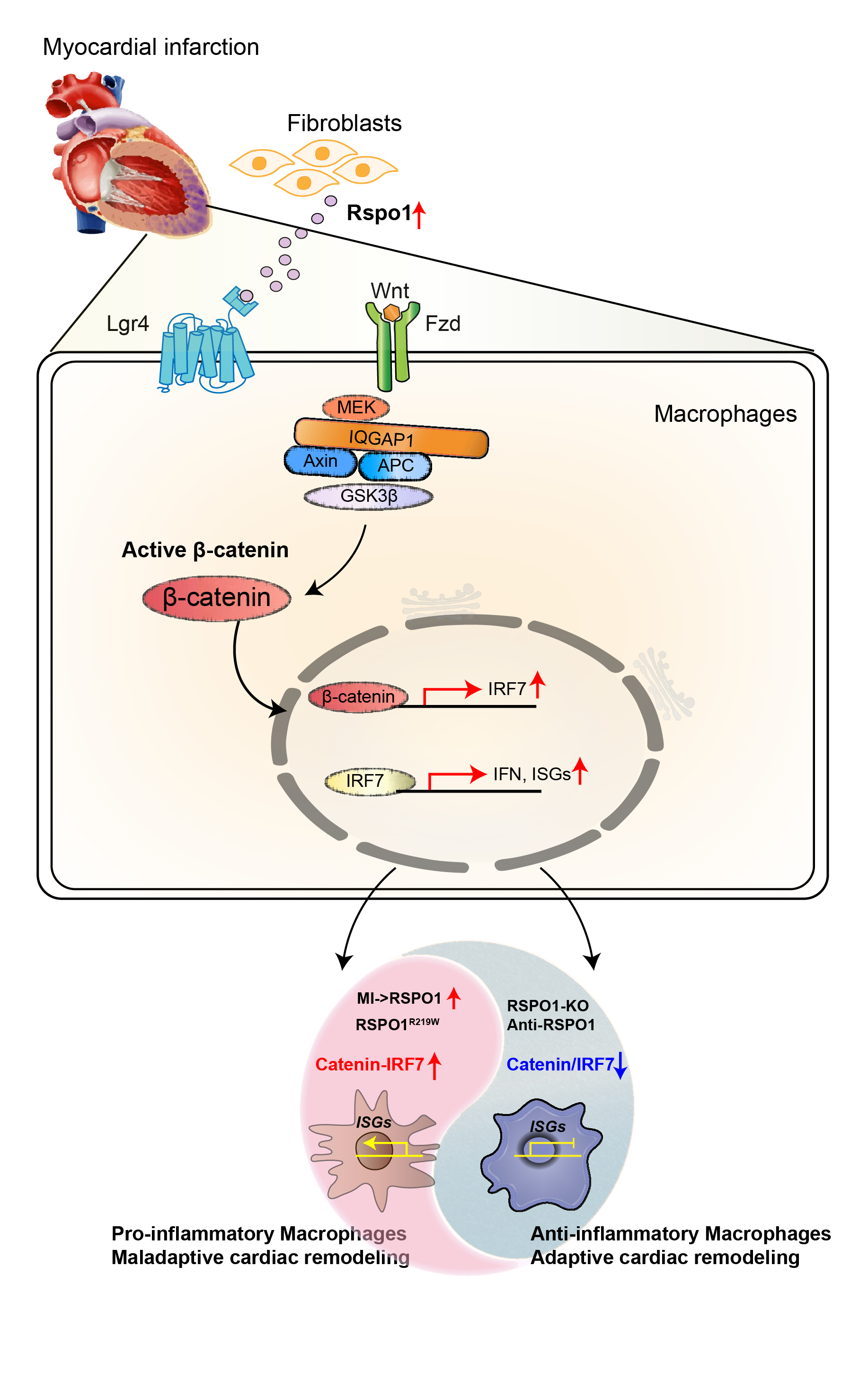
Results: ScRNA-seq identified RSPO1 as one of the most significantly upregulated genes post-MI, with remarkedly elevated levels in ACS patients than the controls. RSPO1 knockout significantly attenuated ventricular remodeling and HF progression in mice, whereas the Rspo1 p.R219W mutation, associated with obesity in human GWAS data, exacerbated cardiac remodeling and dysfunction in humanized mice. RSPO1 knockout reduced the number of IFN-positive macrophages and expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs), a process mediated by the IRF7 signaling pathway as revealed by SCENIC analysis. Mechanistically, RSPO1 activated the LGR4-β-catenin pathway, upregulating IRF7 to enhance interferon activity and pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization. Therapeutically, the RSPO1-neutralizing antibody significantly alleviated HF and suppressed pro-inflammatory macrophage responses post-MI.
Conclusion(s): This study demonstrates that RSPO1 regulates post-MI ventricular remodeling and HF by modulating macrophage polarization via the LGR4-β-catenin-IRF7 axis. Targeting RSPO1 with neutralizing antibodies offers a promising therapeutic strategy for preventing and treating post-MI ventricular remodeling, providing a robust theoretical foundation for future clinical translation.
Aims: This study aimed to investigate the role of RSPO1 in post-MI macrophage polarization, elucidate its molecular mechanisms in ventricular remodeling and HF, and explore potential therapeutic interventions by targeting RSPO1.
Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was performed at various time points post-MI to identify differentially expressed genes. RSPO1 expression was validated in the serum of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients. RSPO1 knockout and humanized Rspo1 p.R219W mutation mouse models were utilized to assess its impact on post-MI outcomes. RNA-seq and scRNA-seq were employed to analyze transcriptional differences in cardiac tissue, while SCENIC analysis identified regulatory pathways. Additionally, a RSPO1-neutralizing antibody was developed to evaluate therapeutic potential.
Results: ScRNA-seq identified RSPO1 as one of the most significantly upregulated genes post-MI, with remarkedly elevated levels in ACS patients than the controls. RSPO1 knockout significantly attenuated ventricular remodeling and HF progression in mice, whereas the Rspo1 p.R219W mutation, associated with obesity in human GWAS data, exacerbated cardiac remodeling and dysfunction in humanized mice. RSPO1 knockout reduced the number of IFN-positive macrophages and expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs), a process mediated by the IRF7 signaling pathway as revealed by SCENIC analysis. Mechanistically, RSPO1 activated the LGR4-β-catenin pathway, upregulating IRF7 to enhance interferon activity and pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization. Therapeutically, the RSPO1-neutralizing antibody significantly alleviated HF and suppressed pro-inflammatory macrophage responses post-MI.
Conclusion(s): This study demonstrates that RSPO1 regulates post-MI ventricular remodeling and HF by modulating macrophage polarization via the LGR4-β-catenin-IRF7 axis. Targeting RSPO1 with neutralizing antibodies offers a promising therapeutic strategy for preventing and treating post-MI ventricular remodeling, providing a robust theoretical foundation for future clinical translation.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Combination: Postpartum SCAD With Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Hassan Rafla, Humayun Sara, Callejas Liam, Woosman Miranda, Nguyen-luu Tristan, Singh Anil
A Novel Cardiomyocyte Targeting Peptide Enhances Calcium HandlingLopuszynski Jack, Wang Jingyu, Dyer Roy, Sahagun Daniella, Zahid Maliha