Final ID: Sa1039
Overall, Race and Regional trends in Ischemic heart disease mortality among adults with Chronic Kidney Disease: Insights from CDC WONDER (1999–2020)
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)-related mortality is a significant burden among US adults. This study investigates trends in CKD and IHD-related mortality in adults aged 25 and older focusing on overall, geographic, and racial/ethnic disparities from 1999 to 2020.
Methods
A retrospective analysis was conducted using death certificate data from the CDC WONDER database from 1999 to 2020. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs), annual percent change (APC), and average annual percentage change (AAPC) were calculated per 100,000 persons, stratified by year, sex, race/ethnicity, and geographical region.
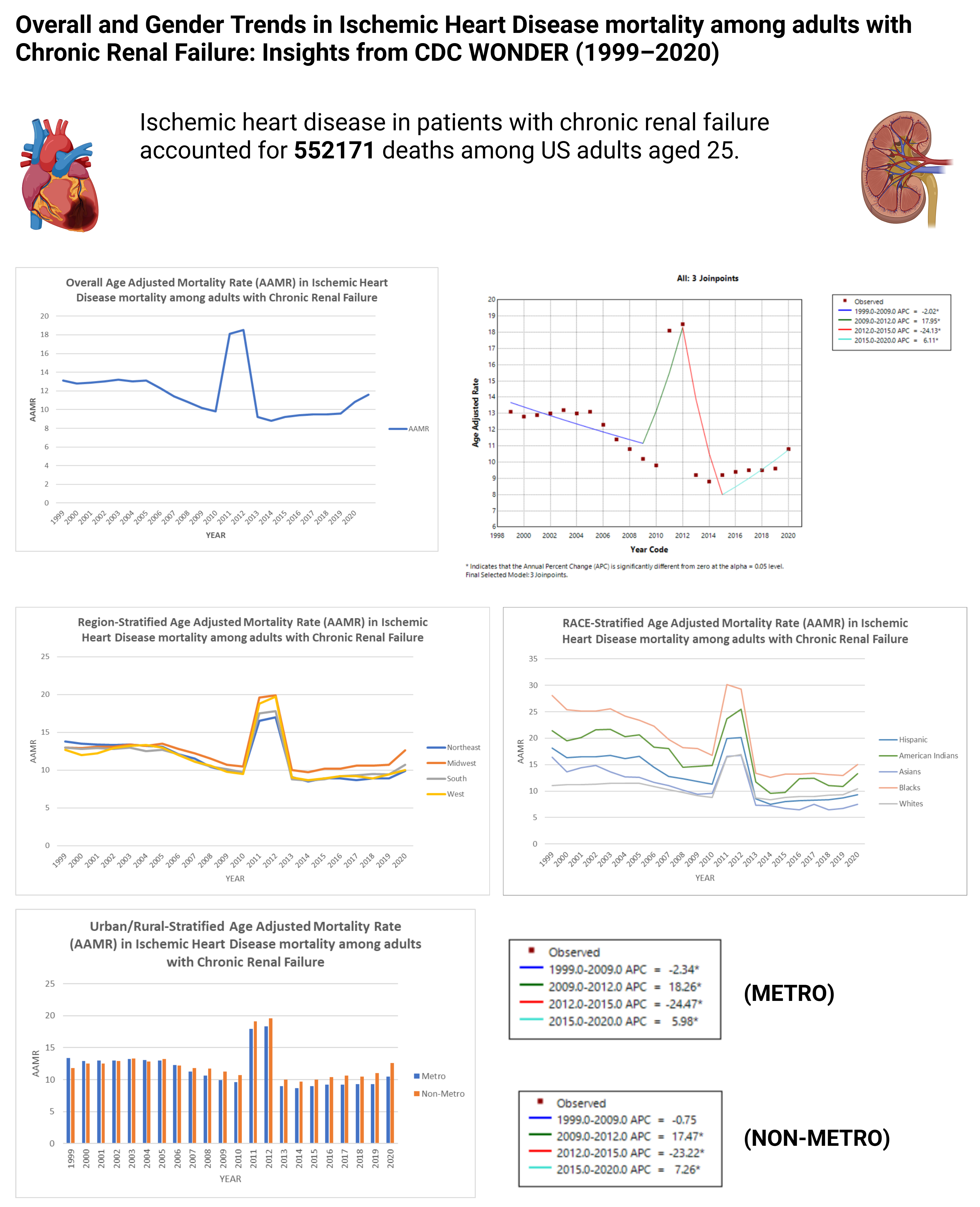
Results
CKD and IHD-related mortality accounted for 552171 deaths among US adults aged 25+. Most deaths occurred at a medical facility (45.30%) and the patient’s home (19.90%). The overall AAMR decreased from 13.1 in 1999 to 10.8 in 2020, with an AAPC of -1.1378 (95 % CI: -4.1816 to 2.0028, p = 0.473276). It is worth noting from 2015 to 2020 the APC has been 6.1116 (95 % CI: 2.1479 to 10.2291, p = 0.005627) suggesting an acute rise. Racial/ethnic disparities showed the highest AAMRs in Blacks (19), followed by American Indians (15.7), Hispanics (12), Whites (10.6), and Asians (9.9). Over the years, racial stratification showed a decrease in mortality among all races. The most significant decrease was in Asians (AAPC: -4.0767, p = 0.000034) and Hispanics (AAPC: -3.8230, p = 0.000122). Geographically, AAMRs ranged from 5.6 in Nevada to 18.3 in West Virginia, with the highest mortality observed in the Midwest (AAMR: 12.4) followed by the West (AAMR: 11.4). Over the years, the mortality has been decreasing in all the regions with the most significant decline being in the Northeastern (AAPC of -2.3167, p = 0.000741) followed by the Western states (AAPC of -1.8062, p = 0.046572). Nonmetropolitan areas exhibited higher AAMRs (12.2) than metropolitan areas (11.4). Overall trends (1999 to 2020) show a decline in mortality for both metro and non-metro however from 2015 to 2020 the mortality has increased in both areas with a sharper increase in the non-metropolitan areas (APC: 7.2592, p = 0.001435) than in the metropolitan areas (APC: 5.9817, p = 0.008059).
Conclusion
We believe better cardiorenal interventions are required to combat this acute rise of the IHD burden in CKD patients with a special focus on the Black and American Indian populations, the Midwest, and non-metropolitan areas.
Background
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)-related mortality is a significant burden among US adults. This study investigates trends in CKD and IHD-related mortality in adults aged 25 and older focusing on overall, geographic, and racial/ethnic disparities from 1999 to 2020.
Methods
A retrospective analysis was conducted using death certificate data from the CDC WONDER database from 1999 to 2020. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs), annual percent change (APC), and average annual percentage change (AAPC) were calculated per 100,000 persons, stratified by year, sex, race/ethnicity, and geographical region.
Results
CKD and IHD-related mortality accounted for 552171 deaths among US adults aged 25+. Most deaths occurred at a medical facility (45.30%) and the patient’s home (19.90%). The overall AAMR decreased from 13.1 in 1999 to 10.8 in 2020, with an AAPC of -1.1378 (95 % CI: -4.1816 to 2.0028, p = 0.473276). It is worth noting from 2015 to 2020 the APC has been 6.1116 (95 % CI: 2.1479 to 10.2291, p = 0.005627) suggesting an acute rise. Racial/ethnic disparities showed the highest AAMRs in Blacks (19), followed by American Indians (15.7), Hispanics (12), Whites (10.6), and Asians (9.9). Over the years, racial stratification showed a decrease in mortality among all races. The most significant decrease was in Asians (AAPC: -4.0767, p = 0.000034) and Hispanics (AAPC: -3.8230, p = 0.000122). Geographically, AAMRs ranged from 5.6 in Nevada to 18.3 in West Virginia, with the highest mortality observed in the Midwest (AAMR: 12.4) followed by the West (AAMR: 11.4). Over the years, the mortality has been decreasing in all the regions with the most significant decline being in the Northeastern (AAPC of -2.3167, p = 0.000741) followed by the Western states (AAPC of -1.8062, p = 0.046572). Nonmetropolitan areas exhibited higher AAMRs (12.2) than metropolitan areas (11.4). Overall trends (1999 to 2020) show a decline in mortality for both metro and non-metro however from 2015 to 2020 the mortality has increased in both areas with a sharper increase in the non-metropolitan areas (APC: 7.2592, p = 0.001435) than in the metropolitan areas (APC: 5.9817, p = 0.008059).
Conclusion
We believe better cardiorenal interventions are required to combat this acute rise of the IHD burden in CKD patients with a special focus on the Black and American Indian populations, the Midwest, and non-metropolitan areas.
More abstracts on this topic:
Assessing Health Literacy and the Role of Race and Social Determinants in Cardiac Patients.
Odigwe Celestine, Lakkis Nasser, Mayfield Hanna, Mulyala Rajasekhar, Riad Mariam, Malik Hajira, Ruiz Brent, Mulekar Madhuri, Malozzi Christopher, Omar Bassam
ACTIVATION AND TARGETABILITY OF TYMP-IL-6-TF AXIS IN THE SKIN MICROENVIRONMENT IN UREMIC CALCIPHYLAXISLotfollahzadeh Saran, Chitalia Vipul