Final ID: MP644
Trends in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Events in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Insurance Claims-Based Review
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a prevalent global disease (T2D). Patients have an increased risk of suffering from atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). The rise of novel medications such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and glucagon-like-peptide-1 agonists (GLP1a) allow cardiovascular protection, and use could result in decline in ASCVD events.
Research Questions
Have trends in ASCVD events in T2D patients decreased? Is this trend the same among all age groups? Are any therapies contributing to this trend?
Goals
The present study aids to achieve the following: (1) quantify trends in ASCVD events such as cerebral vascular accident (CVA -both hemorrhagic and ischemic), coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG), heart failure (HF) hospitalizations, myocardial infarction
(MI), and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with T2D from 2010 to 2023, (2) interrogate possible correlations in deviations of these trends such as in younger patient (<45 years old) or in relation to increase in novel medical therapy usage such as SGLT2i and
GLP1a.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study incorporated data from a large, regional, commercial health insurance company (n=608,933). Members with T2D were tracked for the aforementioned ASCVD events and quantified using Poisson regression. Rate ratios (RR) from Poisson regression estimate the relative change in event rates over the entire study period.
Results
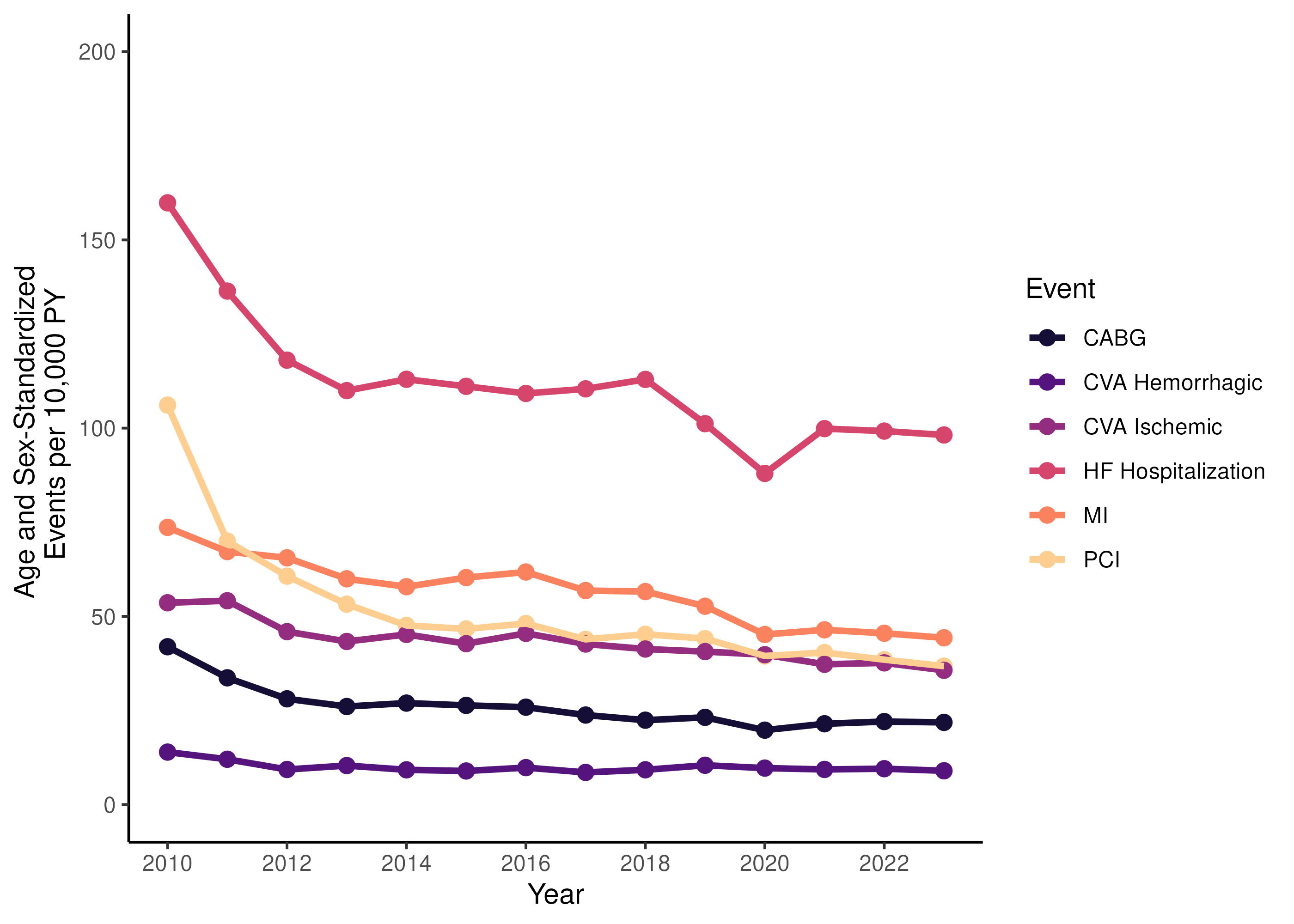
Overall, it was found that there is a decrease in major ASCVD events in all studied clinical endpoints (see Figure 1). Notably, acute MI had a RR=0.60 (95% CI: 0.55, 0.65) indicating 40% decline in acute MI during the study period, CVA-ischemic had a RR=0.68 (0.61, 0.75), and HF hospitalizations with RR=0.75 (0.56, 1.01). Interestingly, the younger population (less than 45 years old) had no significant change in trend of ASCVD events although there was a notable increase in HF hospitalizations with RR=2.40 (1.39, 4.15) in females and RR=2.10
(0.88, 5.01) in males. In addition, there was noted initiation and rise of novel medications with <1% of patients on in 2010 and 17% and 24% in 2023 for SGLT2i and GLP1a, respectively.
Conclusion
From 2010-2023, this study showed decrease in major ASCVD events, most notably acute MI, CVA-ischemic stroke, and HF hospitalizations. These trends are in parallel with the sharp increase in SGLT2i and GLP1a medication use. However, there was a lack of significant trend in patients younger than 45.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a prevalent global disease (T2D). Patients have an increased risk of suffering from atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). The rise of novel medications such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and glucagon-like-peptide-1 agonists (GLP1a) allow cardiovascular protection, and use could result in decline in ASCVD events.
Research Questions
Have trends in ASCVD events in T2D patients decreased? Is this trend the same among all age groups? Are any therapies contributing to this trend?
Goals
The present study aids to achieve the following: (1) quantify trends in ASCVD events such as cerebral vascular accident (CVA -both hemorrhagic and ischemic), coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG), heart failure (HF) hospitalizations, myocardial infarction
(MI), and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with T2D from 2010 to 2023, (2) interrogate possible correlations in deviations of these trends such as in younger patient (<45 years old) or in relation to increase in novel medical therapy usage such as SGLT2i and
GLP1a.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study incorporated data from a large, regional, commercial health insurance company (n=608,933). Members with T2D were tracked for the aforementioned ASCVD events and quantified using Poisson regression. Rate ratios (RR) from Poisson regression estimate the relative change in event rates over the entire study period.
Results
Overall, it was found that there is a decrease in major ASCVD events in all studied clinical endpoints (see Figure 1). Notably, acute MI had a RR=0.60 (95% CI: 0.55, 0.65) indicating 40% decline in acute MI during the study period, CVA-ischemic had a RR=0.68 (0.61, 0.75), and HF hospitalizations with RR=0.75 (0.56, 1.01). Interestingly, the younger population (less than 45 years old) had no significant change in trend of ASCVD events although there was a notable increase in HF hospitalizations with RR=2.40 (1.39, 4.15) in females and RR=2.10
(0.88, 5.01) in males. In addition, there was noted initiation and rise of novel medications with <1% of patients on in 2010 and 17% and 24% in 2023 for SGLT2i and GLP1a, respectively.
Conclusion
From 2010-2023, this study showed decrease in major ASCVD events, most notably acute MI, CVA-ischemic stroke, and HF hospitalizations. These trends are in parallel with the sharp increase in SGLT2i and GLP1a medication use. However, there was a lack of significant trend in patients younger than 45.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adiposomal microRNAs Mediate Vascular Dysfunction in Obesity-Associated Type 2 Diabetes
Mirza Imaduddin, Morsy Mohammed, Levitan Irena, Raj Usha, Mahmoud Abeer
10-Year Trends in Last Known Well to Arrival Time in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: 2014-2023Ferrone Nicholas, Sanmartin Maria, O'hara Joseph, Jimenez Jean, Ferrone Sophia, Wang Jason, Katz Jeffrey, Sanelli Pina