Final ID: MP2720
Upf1 Lactylation Enhances the Regenerative Potency of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: To identify the role of lactate and protein lactylation in promoting cardiomyocyte proliferation and to evaluate the therapeutic potential of lactylation-mediated regulation for myocardial regeneration following infarction.
Methods: Lactate concentrations in arterial blood from neonates and adults were measured using the WST-8 lactate assay. Differences in protein lactylation levels between neonatal and adult mouse myocardial tissues were analyzed using Pan-Kla immunodetection and 4D-FastDIA-based quantitative lactyl-proteomics. Key differentially modified proteins and specific lactylation sites were identified (Upf1-K924Kla). hiPSCs were transduced with lentiviral constructs encoding a lactylation-deficient mutant (K924R), followed by differentiation into cardiomyocytes (Upf1-K924R+ hiPSC-CMs). An acute myocardial infarction (MI) model was induced in NOD/SCID mice. Animals received intramyocardial injections of 3x105 Upf1-K924R+ hiPSC-CMs or Upf1+ hiPSC-CMs into infarct and peri-infarct regions. PBS-injected MI mice (MI group) and sham-operated animals (Sham group) served as additional controls (n=10 each group). Four weeks post-MI, heart function was evaluated via echocardiography. Engraftment was assessed through human cardiac troponin T staining. Histological analysis including infarction size was analyzed using immunofluorescence. Cell proliferation was assessed via immunostaining in transplanted cardiac tissue and in cultivated hiPSC-CMs using the following markers: Ki67, PH3, and Aurora B.
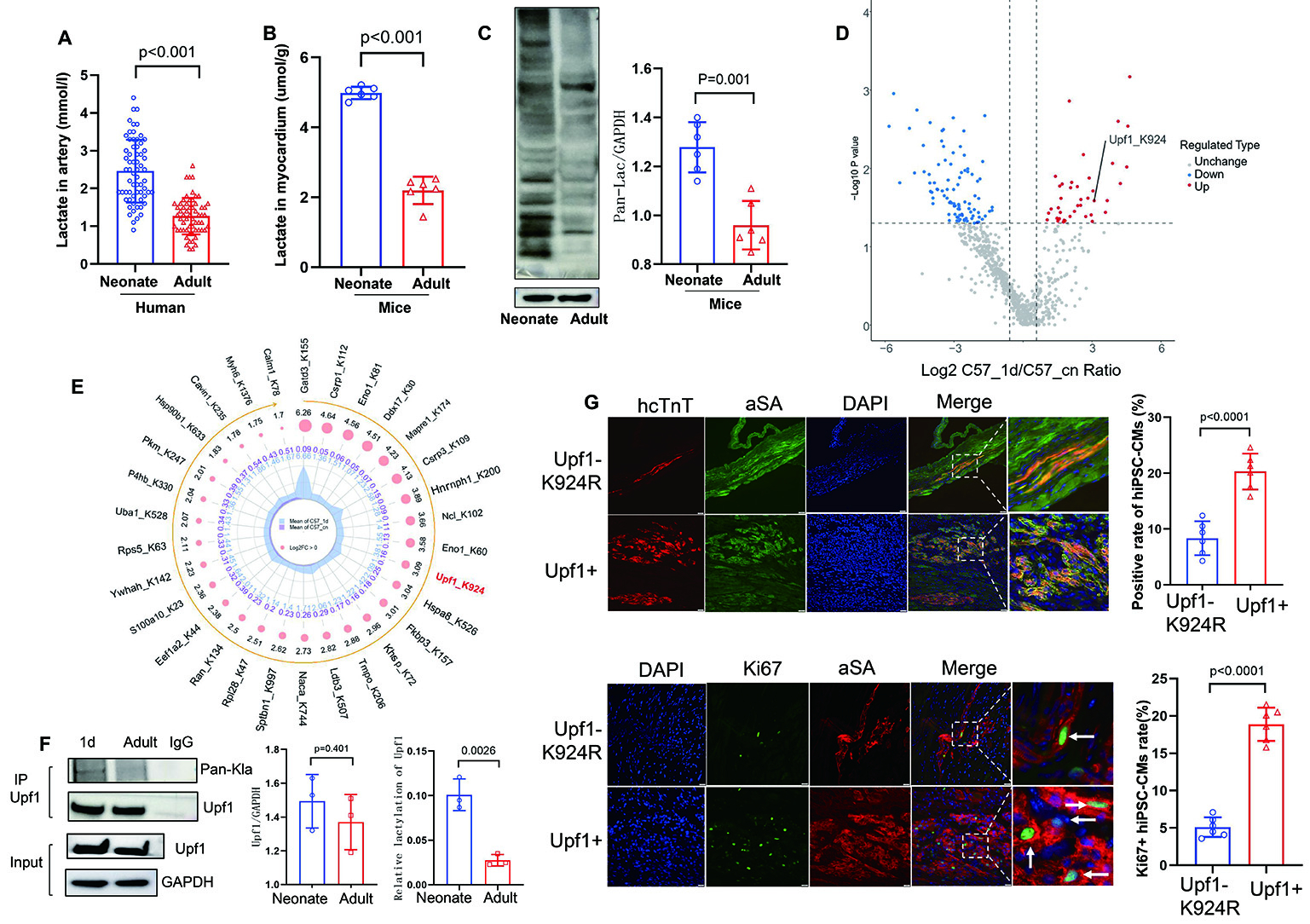
Results: 1. Neonatal myocardium exhibited significantly higher lactate levels and protein lactylation than adult myocardium (Panel A-B). 2. Proteomic analysis revealed that differentially upregulated lactylated proteins in neonatal hearts were enriched in nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments and involved in cell cycle regulation and signaling. Upf1-K924Kla was identified as a key lactylated target (Panel C-F). Overexpression of Upf1 promoted hiPSC-CM proliferation, while the K924R mutant attenuated this effect (Panel G). 3. In the MI model, Upf1+ hiPSC-CM transplantation significantly improved left ventricular function, reduced infarct size, enhanced donor cell retention, and increased proliferative activity (Panel G) compared to NC and MI groups .
Conclusion: Transplantation of Upf1-overexpressing hiPSC-CMs enhances myocardial repair and functional recovery post-MI, highlighting a promising strategy for cardiac regeneration therapy.
Methods: Lactate concentrations in arterial blood from neonates and adults were measured using the WST-8 lactate assay. Differences in protein lactylation levels between neonatal and adult mouse myocardial tissues were analyzed using Pan-Kla immunodetection and 4D-FastDIA-based quantitative lactyl-proteomics. Key differentially modified proteins and specific lactylation sites were identified (Upf1-K924Kla). hiPSCs were transduced with lentiviral constructs encoding a lactylation-deficient mutant (K924R), followed by differentiation into cardiomyocytes (Upf1-K924R+ hiPSC-CMs). An acute myocardial infarction (MI) model was induced in NOD/SCID mice. Animals received intramyocardial injections of 3x105 Upf1-K924R+ hiPSC-CMs or Upf1+ hiPSC-CMs into infarct and peri-infarct regions. PBS-injected MI mice (MI group) and sham-operated animals (Sham group) served as additional controls (n=10 each group). Four weeks post-MI, heart function was evaluated via echocardiography. Engraftment was assessed through human cardiac troponin T staining. Histological analysis including infarction size was analyzed using immunofluorescence. Cell proliferation was assessed via immunostaining in transplanted cardiac tissue and in cultivated hiPSC-CMs using the following markers: Ki67, PH3, and Aurora B.
Results: 1. Neonatal myocardium exhibited significantly higher lactate levels and protein lactylation than adult myocardium (Panel A-B). 2. Proteomic analysis revealed that differentially upregulated lactylated proteins in neonatal hearts were enriched in nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments and involved in cell cycle regulation and signaling. Upf1-K924Kla was identified as a key lactylated target (Panel C-F). Overexpression of Upf1 promoted hiPSC-CM proliferation, while the K924R mutant attenuated this effect (Panel G). 3. In the MI model, Upf1+ hiPSC-CM transplantation significantly improved left ventricular function, reduced infarct size, enhanced donor cell retention, and increased proliferative activity (Panel G) compared to NC and MI groups .
Conclusion: Transplantation of Upf1-overexpressing hiPSC-CMs enhances myocardial repair and functional recovery post-MI, highlighting a promising strategy for cardiac regeneration therapy.
More abstracts on this topic:
Endothelial cell regeneration by secretome obtained from P53 silenced bone marrow derived mesenchymal stromal cells (BM-MSCs)
Nandula Seshagiri Rao, Sen Sabyasachi
Efficient Intramyocardial Delivery of EV-Encapsulated AAVs to Target Cardiomyocytes in a Pre-Clinical Swine ModelGallinat Alex, Sahoo Susmita, La Salvia Sabrina, Li Xisheng, Raisinghani Nikhil, Zhang Shihong, Shao Alan, Phan Anh, Mavropoulos Spyros, Ishikawa Kiyotake