Final ID: Su3052
Distinct Clinical Differences Between Right Aortic Arch with Aberrant Left Subclavian Artery and Double Aortic Arch
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Vascular ring (VR) is a rare congenital aortic arch anomality causing external compression on trachea and/or esophagus with variable onset and severity. Two common types are right aortic arch with aberrant left subclavian artery (RAoA/ALSCA) and double aortic arch (DAoA). Although RAoA/ALSCA and DAoA are frequently discussed together, the differences between the two VR have been poorly characterized.
RQ: Are RAoA/ALSCA and DAoA distinct clinical entities?
Methods: Retrospective chart review of pediatric patients diagnosed with isolated VR was performed. Demographic data, classification of VR, clinical presentation, imaging studies, and postoperative course were analyzed. Data is shown as either count (n) and percentage or median and interquartile range (IQR).
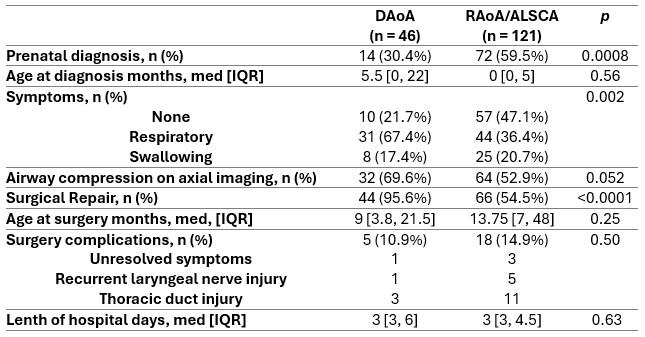
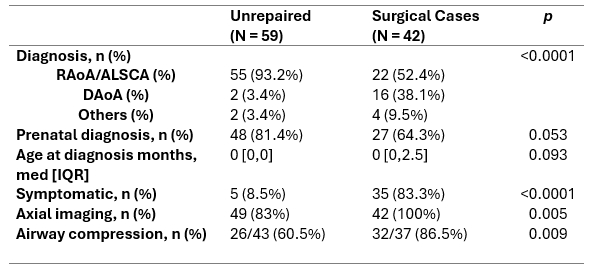
Results: One hundred seventy-six patients were diagnosed with isolated VR from 1998 to 2024 at our cardiac center, including 121 RAoA/ALSCA, 46 DAoA, and 9 others (Table 1). Most patients were diagnosed before 1 year (75.6%), 93 of which were prenatally diagnosed (69.9%). Sixty percent of patients were symptomatic, and 66.4% of patients underwent surgical repair. When RAoA/ALSCA and DAoA were separately studied, prenatal diagnosis was more common in RAoA/ALSCA (Table 2). Respiratory symptoms were more frequent in DAoA than in RAoA/ALSCA. Higher incidence of surgery was noted in DAoA than in RAoA/ALSCA (96.5% vs. 54.5%, p < 0.0001). There was no difference in age at surgery, post-operative hospital days, or incidence of surgical complications between DAoA and RAoA. When unrepaired and repaired VR were analyzed in more recent years (from 2018 to 2024), RAoA/ALSCA was more common among the unrepaired group (Table 3). The unrepaired group was more likely to be asymptomatic and less likely to have airway compression on axial imaging. Majority of DAoA was repaired (88.9%) whereas 71.4% of RAoA/ALSCA was not repaired. Only 5 patients were symptomatic despite 26 patients showing airway compression in an unrepaired group, whereas symptom was well correlated with airway compression in a repaired group.
Conclusions: Although RAoA/ALSCA and DAoA are frequently discussed together as the same clinical entity, there were several notable differences between the two. Majority of DAoA patients were symptomatic and underwent surgical repair more frequently than RAoA/ALSCA. Timing of surgery, incidence of post-operative complications, and length of post operative hospital stay were comparable between the two.
RQ: Are RAoA/ALSCA and DAoA distinct clinical entities?
Methods: Retrospective chart review of pediatric patients diagnosed with isolated VR was performed. Demographic data, classification of VR, clinical presentation, imaging studies, and postoperative course were analyzed. Data is shown as either count (n) and percentage or median and interquartile range (IQR).
Results: One hundred seventy-six patients were diagnosed with isolated VR from 1998 to 2024 at our cardiac center, including 121 RAoA/ALSCA, 46 DAoA, and 9 others (Table 1). Most patients were diagnosed before 1 year (75.6%), 93 of which were prenatally diagnosed (69.9%). Sixty percent of patients were symptomatic, and 66.4% of patients underwent surgical repair. When RAoA/ALSCA and DAoA were separately studied, prenatal diagnosis was more common in RAoA/ALSCA (Table 2). Respiratory symptoms were more frequent in DAoA than in RAoA/ALSCA. Higher incidence of surgery was noted in DAoA than in RAoA/ALSCA (96.5% vs. 54.5%, p < 0.0001). There was no difference in age at surgery, post-operative hospital days, or incidence of surgical complications between DAoA and RAoA. When unrepaired and repaired VR were analyzed in more recent years (from 2018 to 2024), RAoA/ALSCA was more common among the unrepaired group (Table 3). The unrepaired group was more likely to be asymptomatic and less likely to have airway compression on axial imaging. Majority of DAoA was repaired (88.9%) whereas 71.4% of RAoA/ALSCA was not repaired. Only 5 patients were symptomatic despite 26 patients showing airway compression in an unrepaired group, whereas symptom was well correlated with airway compression in a repaired group.
Conclusions: Although RAoA/ALSCA and DAoA are frequently discussed together as the same clinical entity, there were several notable differences between the two. Majority of DAoA patients were symptomatic and underwent surgical repair more frequently than RAoA/ALSCA. Timing of surgery, incidence of post-operative complications, and length of post operative hospital stay were comparable between the two.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Silent Storm: Incidental Discovery of IVC and Right Atrium Thrombus in a Patient with Uterine Stromal Sarcoma
Wasef Natale, Fatima Tehreem, Stys Adam
A Hard Start: Early, Intensive Healthcare Utilization for Children with Critical Congenital Heart DiseaseEllis Danielle, Hall Matthew, Blume Elizabeth, Wolfe Joanne, Snaman Jennifer, Berry Jay