Final ID: MP405
Trends in Acute Myocardial Infarction and Chronic Kidney Disease-Related Mortality in the Elderly Population in the United States, A CDC WONDER Database Analysis (1999-2020)
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
The presence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) among patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI) is associated with poor prognosis, and contributes to significant mortality. Furthermore, the trends and disparities in such deaths among the elderly population remain understudied. The aim of this analysis was to evaluate mortality trends related to acute MI and CKD among adults aged 65 and above in the United States.
Methods
An analysis of the CDC WONDER database was conducted, focusing on death certificate data from 1999 to 2020. Specifically, we examined acute MI and CKD-related mortality among adults aged 65 years and older. Age-Adjusted Mortality Rates (AAMRs) were calculated with 95% confidence interval (CIs), adjusting for variables including year, sex, race/ethnicity, and geographic location.
Results
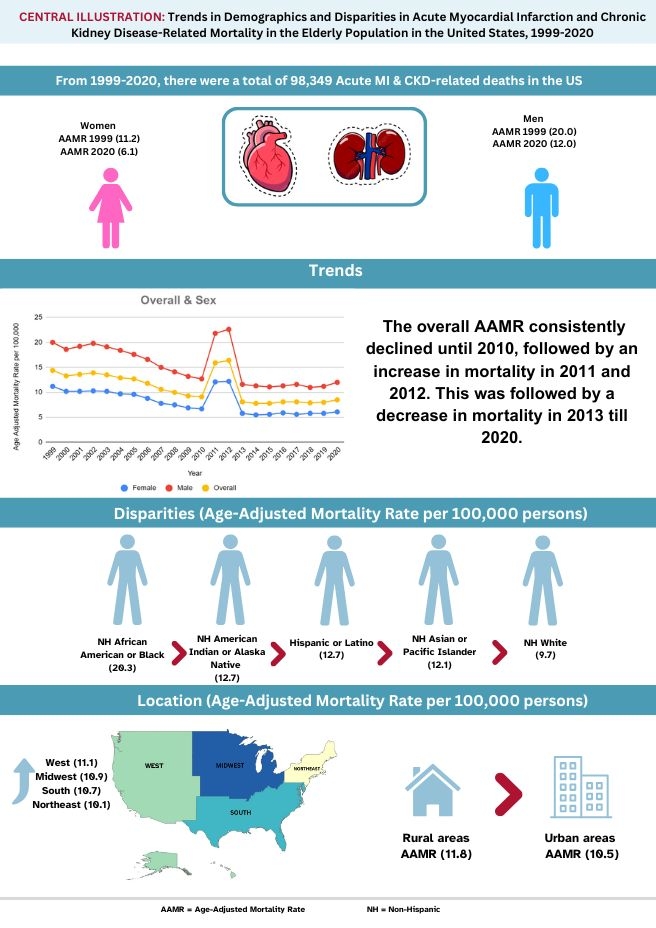
A total of 98,349 acute MI and CKD-related deaths occurred between 1999 to 2020, with the majority occurring in medical facilities (68.3%), followed by the decedent's home (14.1%). There was a significant decrease in AAMR from 14.4 in 1999 to 8.5 in 2020 (APC: -3.0; 95% CI: -4.3 to -1.8). The overall AAMR was twice as high in men (14.9) compared to women (7.9). Non-Hispanic (NH) Black or African American had the highest AAMR (20.3), followed by NH American Indian or Alaska Native (12.7) and Hispanic (12.7). This was followed by NH Asian or Pacific Islander (12.1), and then by NH White (9.7). The West had the highest AAMR (11.1), followed by Midwest (10.9), South (10.7), and Northeast (10.1). North Dakota, Texas, California, South Carolina, Tennessee, Ohio, West Virginia, District of Columbia, Maryland, and Rhode Island were states that fell at or above the upper 90th percentile while Arizona, Colorado, Georgia, Kansas, Nebraska, New Mexico, Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, Nevada, and Utah fell at or below the lower 10th percentile. Urban (10.5) and rural areas (11.8) both had similar AAMRs.
Conclusion
Acute MI and CKD-related deaths remain a significant concern in the elderly population. Persistent disparities in gender, ethnicity, and regions were noted. Further research is needed to understand the underlying factors to help develop preventative strategies.
The presence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) among patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI) is associated with poor prognosis, and contributes to significant mortality. Furthermore, the trends and disparities in such deaths among the elderly population remain understudied. The aim of this analysis was to evaluate mortality trends related to acute MI and CKD among adults aged 65 and above in the United States.
Methods
An analysis of the CDC WONDER database was conducted, focusing on death certificate data from 1999 to 2020. Specifically, we examined acute MI and CKD-related mortality among adults aged 65 years and older. Age-Adjusted Mortality Rates (AAMRs) were calculated with 95% confidence interval (CIs), adjusting for variables including year, sex, race/ethnicity, and geographic location.
Results
A total of 98,349 acute MI and CKD-related deaths occurred between 1999 to 2020, with the majority occurring in medical facilities (68.3%), followed by the decedent's home (14.1%). There was a significant decrease in AAMR from 14.4 in 1999 to 8.5 in 2020 (APC: -3.0; 95% CI: -4.3 to -1.8). The overall AAMR was twice as high in men (14.9) compared to women (7.9). Non-Hispanic (NH) Black or African American had the highest AAMR (20.3), followed by NH American Indian or Alaska Native (12.7) and Hispanic (12.7). This was followed by NH Asian or Pacific Islander (12.1), and then by NH White (9.7). The West had the highest AAMR (11.1), followed by Midwest (10.9), South (10.7), and Northeast (10.1). North Dakota, Texas, California, South Carolina, Tennessee, Ohio, West Virginia, District of Columbia, Maryland, and Rhode Island were states that fell at or above the upper 90th percentile while Arizona, Colorado, Georgia, Kansas, Nebraska, New Mexico, Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, Nevada, and Utah fell at or below the lower 10th percentile. Urban (10.5) and rural areas (11.8) both had similar AAMRs.
Conclusion
Acute MI and CKD-related deaths remain a significant concern in the elderly population. Persistent disparities in gender, ethnicity, and regions were noted. Further research is needed to understand the underlying factors to help develop preventative strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adaptive Cardiac Arrest Training Curriculum for Capacity Building in Northern Ghana: Addressing Contextual Challenges for Sustainability
Ahadzi Dzifa, Boateng Laud, Hernandez Odalys Rivera, Akanbong Prosper, Leung Claudia, Al-hassan Rahma, Baba Yabasin Iddrisu, Yakubu Abdul-subulr, Cournooh Annette, Ikeda Scott, Alomatu Samuel, Sakeah Patience
ACTIVATION AND TARGETABILITY OF TYMP-IL-6-TF AXIS IN THE SKIN MICROENVIRONMENT IN UREMIC CALCIPHYLAXISLotfollahzadeh Saran, Chitalia Vipul