Final ID: MP574
Global, Regional, and National Burden of Early-onset Atrial Fibrillation/Atrial Flutter: an Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
While atrial fibrillation/flutter is widely recognized as a growing public health concern, the specific burden of early-onset cases remains unclear.
Goals/Aims
The study aims to evaluate the global, regional, and national burden and trends of early-onset atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter (EOAF/AFL) in individuals under 45 years of age from 1990 to 2021.
Methods
Data on the incidence and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) related to EOAF/AFL were sourced from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 study. The study also calculated estimated annual percentage changes (EAPCs) in age-standardized incidence rates (ASIR) and DALY rates (ASDR) across different age groups, sexes, countries, and regions to assess trends over time. Furthermore, the analysis explored the association between EOAF/AFL burden and socio-demographic development levels (measured by the Socio-demographic Index [SDI]).
Results
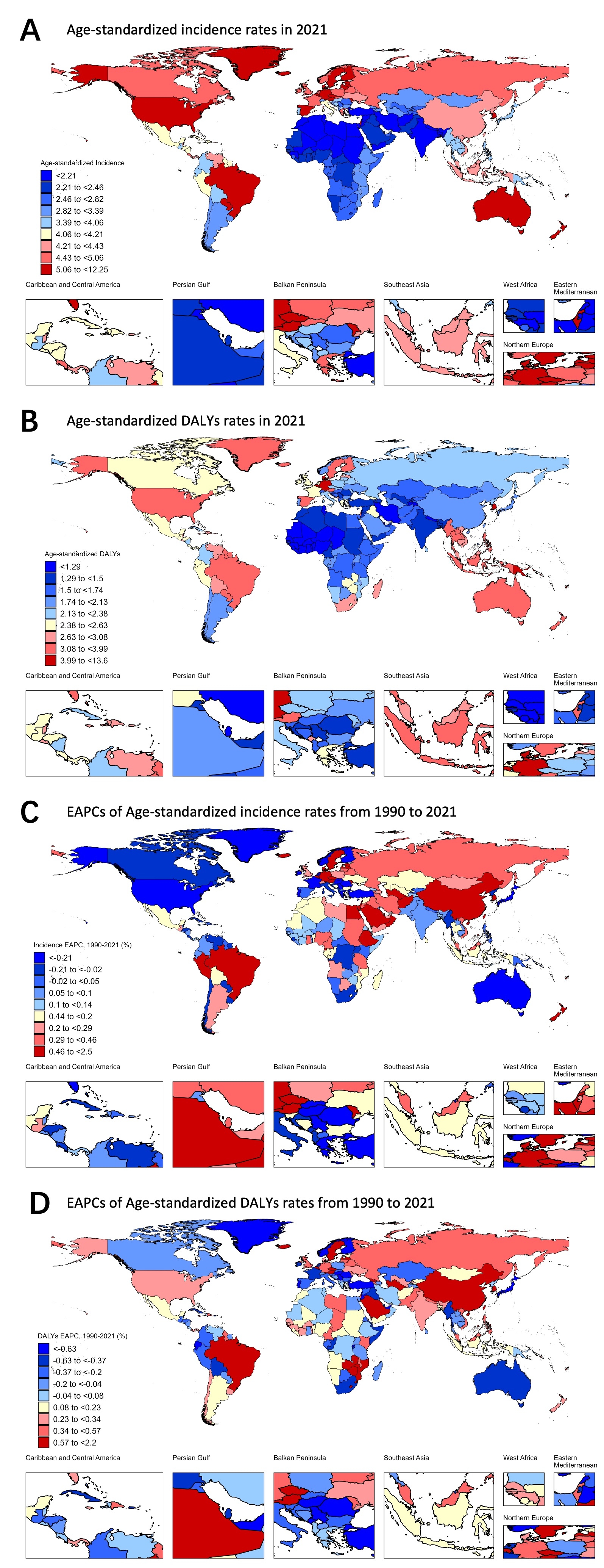
Globally, there were 203,648 EOAF/AFL incident cases in 2021, an increase of 66.58% compared to 122,256 in 1990. The number of EOAF/AFL-associated DALYs increased by 71.16%, from 68,557.93 in 1990 to 117,346.17 in 2021. Despite significant increases in case counts, the EAPCs of the ASIR (0.06% [−0.01, 0.13]) and ASDR (0.07% [0.01, 0.14]) remained relatively stable. Females had fewer cases overall but showed higher ASIR and ASDR compared to males. The incidence and DALYs burden of EOAF/AFL was highest in middle SDI regions, followed by high SDI regions, with the lowest burden in low SDI regions. At the national level, China recorded the largest number of incident cases and DALYs, whereas Belgium showed the highest EAPCs for both ASIR and ASDR.
Conclusion
The increasing global burden of EOAF/AFL highlights the urgent need for customized public health strategies and insurance policies. Additionally, it underscores the importance of conducting diverse researches and fostering international collaboration to effectively tackle this growing challenge.
While atrial fibrillation/flutter is widely recognized as a growing public health concern, the specific burden of early-onset cases remains unclear.
Goals/Aims
The study aims to evaluate the global, regional, and national burden and trends of early-onset atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter (EOAF/AFL) in individuals under 45 years of age from 1990 to 2021.
Methods
Data on the incidence and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) related to EOAF/AFL were sourced from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 study. The study also calculated estimated annual percentage changes (EAPCs) in age-standardized incidence rates (ASIR) and DALY rates (ASDR) across different age groups, sexes, countries, and regions to assess trends over time. Furthermore, the analysis explored the association between EOAF/AFL burden and socio-demographic development levels (measured by the Socio-demographic Index [SDI]).
Results
Globally, there were 203,648 EOAF/AFL incident cases in 2021, an increase of 66.58% compared to 122,256 in 1990. The number of EOAF/AFL-associated DALYs increased by 71.16%, from 68,557.93 in 1990 to 117,346.17 in 2021. Despite significant increases in case counts, the EAPCs of the ASIR (0.06% [−0.01, 0.13]) and ASDR (0.07% [0.01, 0.14]) remained relatively stable. Females had fewer cases overall but showed higher ASIR and ASDR compared to males. The incidence and DALYs burden of EOAF/AFL was highest in middle SDI regions, followed by high SDI regions, with the lowest burden in low SDI regions. At the national level, China recorded the largest number of incident cases and DALYs, whereas Belgium showed the highest EAPCs for both ASIR and ASDR.
Conclusion
The increasing global burden of EOAF/AFL highlights the urgent need for customized public health strategies and insurance policies. Additionally, it underscores the importance of conducting diverse researches and fostering international collaboration to effectively tackle this growing challenge.
More abstracts on this topic:
A novel deep learning framework identified associated genes and Interpretable deep learning translation of GWAS findings for drug repurposing in Atrial Fibrillation
Tonegawa-kuji Reina, Xu Jielin, Guntupalli Suman, Barnard John, Chung Mina, Cheng Feixiong
Association Between Proximity to Hazardous Waste Sites and Cardiometabolic Diseases: Coronary Heart Disease, Stroke, Hypertension, and DiabetesAbadi Azar, Gabriel Kelley, Wickliffe Jeffrey, Levitan Emily, Hussaini Qasim