Final ID: MP770
Prevalence and discrimination of ongoing fibrillation in isolated pulmonary vein in non-paroxysmal atrial fibrillation ablation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Backgrounds
Pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) usually results in abolishment of PV potentials (PVP) rather than concomitant termination of non-paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (non-PAF). It is unclear whether ongoing fibrillation in isolated PVs (OFIP) might co-exist with AF in non-PAF ablation. This study sought to explore the prevalence of OFIP in non-PAF ablation and to develop a concise discriminating algorithm to distinguish between OFIP and isolation failure, thereby minimizing excessive ablation and associated risks.
Methods
Non-PAF patients undergoing first-time ablation were divided into retrospective induction cohort (IC) and prospective validation cohort (VC). In case of ongoing PV fibrillation after PV ablation, PVI completion was assessed based on unique PVP phenomena and after systemic gaps mapping and ablation.
Results
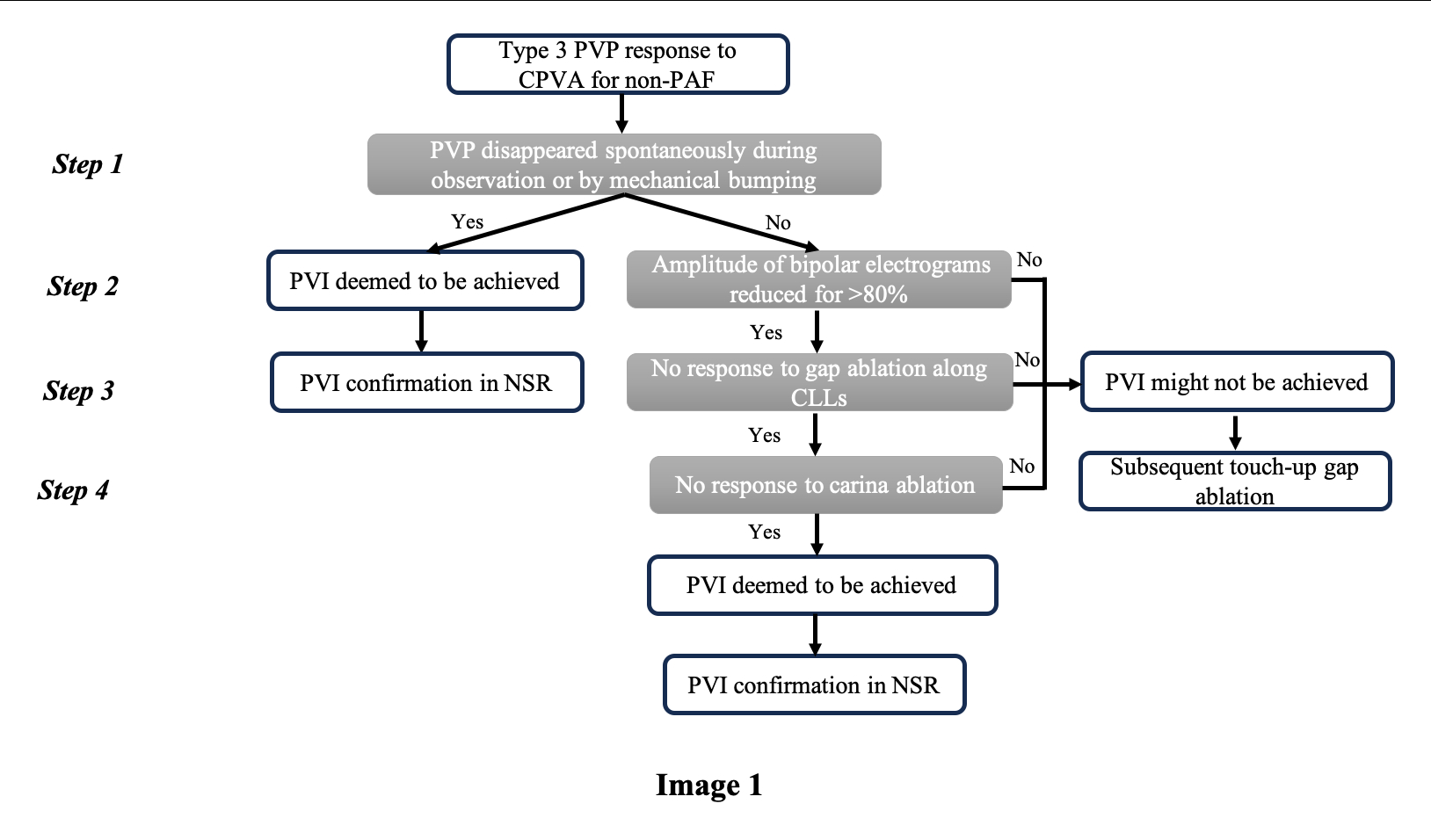
Twenty (3.55%) of 563 had OFIP, including 9/300 from the IC and 11/263 from the VC. No significant predictors of OFIP were identified in terms of baseline characteristics or procedural factors. Based on 3 right-sided, 5 left-sided, 1 bilateral OFIP cases in the IC, either spontaneous or bumping-induced PVP disappearance, or a combination of bipolar voltage reduction > 80%, local activation time later than PV recordings and no response to carina ablation were adopted as the major criteria for developing a discriminating algorithm. In 20 patients with ongoing PV fibrillation in the VC, the algorithm identified true OFIP in 11, false OFIP in 3 and true incomplete PVI in 6. The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value was 100%, 66.7%, 78.6% and 100%, respectively.
Conclusions
OFIP was not negligible in non-PAF ablation procedures for achieving efficient and safe PVI. A novel four-step algorithm was developed to discriminate OFIP with good predictive value.
Pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) usually results in abolishment of PV potentials (PVP) rather than concomitant termination of non-paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (non-PAF). It is unclear whether ongoing fibrillation in isolated PVs (OFIP) might co-exist with AF in non-PAF ablation. This study sought to explore the prevalence of OFIP in non-PAF ablation and to develop a concise discriminating algorithm to distinguish between OFIP and isolation failure, thereby minimizing excessive ablation and associated risks.
Methods
Non-PAF patients undergoing first-time ablation were divided into retrospective induction cohort (IC) and prospective validation cohort (VC). In case of ongoing PV fibrillation after PV ablation, PVI completion was assessed based on unique PVP phenomena and after systemic gaps mapping and ablation.
Results
Twenty (3.55%) of 563 had OFIP, including 9/300 from the IC and 11/263 from the VC. No significant predictors of OFIP were identified in terms of baseline characteristics or procedural factors. Based on 3 right-sided, 5 left-sided, 1 bilateral OFIP cases in the IC, either spontaneous or bumping-induced PVP disappearance, or a combination of bipolar voltage reduction > 80%, local activation time later than PV recordings and no response to carina ablation were adopted as the major criteria for developing a discriminating algorithm. In 20 patients with ongoing PV fibrillation in the VC, the algorithm identified true OFIP in 11, false OFIP in 3 and true incomplete PVI in 6. The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value was 100%, 66.7%, 78.6% and 100%, respectively.
Conclusions
OFIP was not negligible in non-PAF ablation procedures for achieving efficient and safe PVI. A novel four-step algorithm was developed to discriminate OFIP with good predictive value.
More abstracts on this topic:
Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials with Reconstructed Time-to-Event Data
4-5 Years Outcomes of Left Atrial Appendage Closure vs. Oral Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis:
Mi Jiaqi, Katapadi Aashish, Darden Douglas, Uppalapati Sree Varuntej, Kabra Aanya, Katapadi Aashika
4-5 Years Outcomes of Left Atrial Appendage Closure vs. Oral Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis:
Khan Muhammad Aslam, Haider Taimoor, Bhattarai Shraddha, Afzal Hafsa, Khan Bilal, Muhammad Anza, Shafique Nouman, Bhatia Hitesh, Aafreen Asna, Adil Abid Nawaz Khan, Akbar Usman, Khan Alamzaib, Haider Muhammad Adnan