Final ID: MP558
Effects of cardiac rehabilitation on body composition changes in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have been shown to reduce weight. However, the degree to which this involves loss of fat and/or lean muscle mass remains uncertain, as does the potential for exercise to mitigate these effects.
Aims
To evaluate changes in body composition among patients on GLP-1RAs who completed a structured exercise program of cardiac rehabilitation (CR), compared to patients on GLP-1RAs alone.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that completion of CR while on a GLP-1RA would be associated with preservation of muscle mass and greater reductions in body fat than GLP-1RA therapy alone.
Methods
We performed a retrospective review of patients who completed CR at our institution between June 2018 and April 2025, identifying 51 patients on a GLP-1RA that underwent bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) of body composition before and after CR (GLP-1RA+CR group). A comparison group consisted of patients on GLP-1RAs who did not participate in CR and who underwent BIA during routine follow-up (GLP-1RA group). Demographic and clinical data were obtained from the electronic medical record. Descriptive statistics included chi-square analysis for categorical variables and non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis tests and proportion t-tests for quantitative variables (RStudio, v 2024.12.1+563).
Results
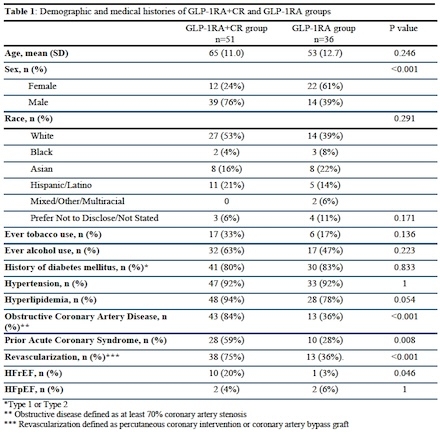
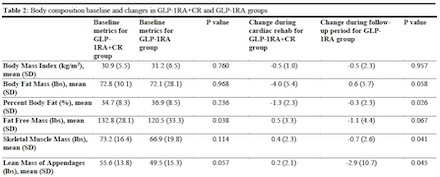
The GLP-1RA+CR and GLP-1RA groups were similar in age (mean 65 vs 61 years; p=0.246) and racial composition, though the GLP-1RA+CR group had more men (76% vs 39%; p<0.001). Median time between BIA analyses was 3 months for the GLP-1RA+CR group and 4 months for the GLP-1RA group. Both groups had similar rates of diabetes (80% vs 83%). Baseline BMI was comparable (mean 30.9 kg/m2 in GLP-1RA+CR group vs 31.2 kg/m2 in GLP-1RA group), with both groups’ BMI dropping 0.5 kg/m2. However, the GLP-1RA+CR group experienced greater percent body fat loss (mean -1.3% vs -0.3%; p=0.026). Notably, skeletal muscle mass increased in the GLP-1RA+CR group (+0.4lbs) but decreased in the GLP-1RA group (-0.7lbs; p=0.041), with greater appendicular muscle mass loss (-2.9lbs vs +0.2lbs; p=0.045). Sex differences were noted such that in women, the GLP-1RA+CR group had even greater body fat loss (-2.1% vs -0.4%; p=0.015) and skeletal muscle gain (1.2lbs vs -0.6lbs; p=0.014).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest exercise may prevent GLP-1RAs from causing skeletal muscle mass loss, while also decreasing markers of adiposity, such as BMI and percent body fat, particularly in women.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have been shown to reduce weight. However, the degree to which this involves loss of fat and/or lean muscle mass remains uncertain, as does the potential for exercise to mitigate these effects.
Aims
To evaluate changes in body composition among patients on GLP-1RAs who completed a structured exercise program of cardiac rehabilitation (CR), compared to patients on GLP-1RAs alone.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that completion of CR while on a GLP-1RA would be associated with preservation of muscle mass and greater reductions in body fat than GLP-1RA therapy alone.
Methods
We performed a retrospective review of patients who completed CR at our institution between June 2018 and April 2025, identifying 51 patients on a GLP-1RA that underwent bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) of body composition before and after CR (GLP-1RA+CR group). A comparison group consisted of patients on GLP-1RAs who did not participate in CR and who underwent BIA during routine follow-up (GLP-1RA group). Demographic and clinical data were obtained from the electronic medical record. Descriptive statistics included chi-square analysis for categorical variables and non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis tests and proportion t-tests for quantitative variables (RStudio, v 2024.12.1+563).
Results
The GLP-1RA+CR and GLP-1RA groups were similar in age (mean 65 vs 61 years; p=0.246) and racial composition, though the GLP-1RA+CR group had more men (76% vs 39%; p<0.001). Median time between BIA analyses was 3 months for the GLP-1RA+CR group and 4 months for the GLP-1RA group. Both groups had similar rates of diabetes (80% vs 83%). Baseline BMI was comparable (mean 30.9 kg/m2 in GLP-1RA+CR group vs 31.2 kg/m2 in GLP-1RA group), with both groups’ BMI dropping 0.5 kg/m2. However, the GLP-1RA+CR group experienced greater percent body fat loss (mean -1.3% vs -0.3%; p=0.026). Notably, skeletal muscle mass increased in the GLP-1RA+CR group (+0.4lbs) but decreased in the GLP-1RA group (-0.7lbs; p=0.041), with greater appendicular muscle mass loss (-2.9lbs vs +0.2lbs; p=0.045). Sex differences were noted such that in women, the GLP-1RA+CR group had even greater body fat loss (-2.1% vs -0.4%; p=0.015) and skeletal muscle gain (1.2lbs vs -0.6lbs; p=0.014).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest exercise may prevent GLP-1RAs from causing skeletal muscle mass loss, while also decreasing markers of adiposity, such as BMI and percent body fat, particularly in women.
More abstracts on this topic:
A functional survey of postnatal heart maturation with in vivo Perturb-seq in spatial and temporal resolution
Wang Haofei, Liu Jiandong, Dong Yanhan, Shi Huitong, Colon Marazzano, Liu Xingyan, Farber Gregory, Qian Yunzhe, Anthony Nicholas, Qian Li
Association Between Meeting Physical Activity Time-Intensity Guidelines and Calf Muscle Oxygen Saturation in Patients with Symptomatic Peripheral Artery DiseaseGardner Andrew, Montgomery Polly, Wang Ming, Xu Xifei