Final ID: Su4034
Genetic Screening of Farby Disease from TPMI Biobank in Middle Taiwan: Single Center Experiences
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
The prevalence of Fabry disease (FD) of general population and what most common initial presentation of FD are unknown. In addition to clinical diagnosis, the TPMI (Taiwan Precision Medicine Initiative Program) Biobank offers an unparalleled opportunity to determine the prevalence of FD-causing pathogenic variants in an unselected hospital visiting adult population.
Methods
All TPMI participants were genotyped using the Axiom Genome-Wide TWB 2.0 Array Plate (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The hot spots of Fabry disease-causing pathogenic variants were identified as genetic defined Fabry disease according to ACMG criteria pathogenic or likely pathogenic. All the identified variant were been validated by Sanger sequencing. We compared with genetic defined Fabry disease patients with age and gender matching hospital patients by ratio 1:4 respectively. The clinical renal, cardiac, and neurological manifestation were analyzed.
Results
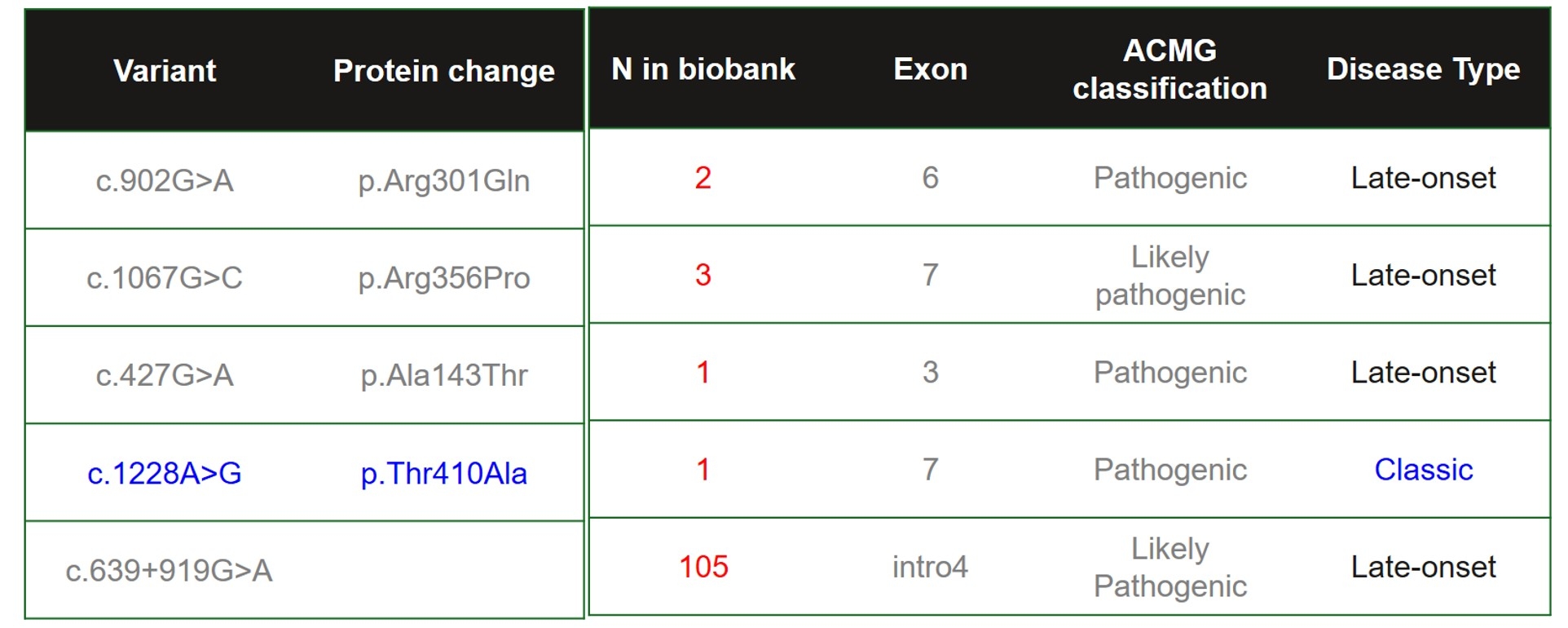
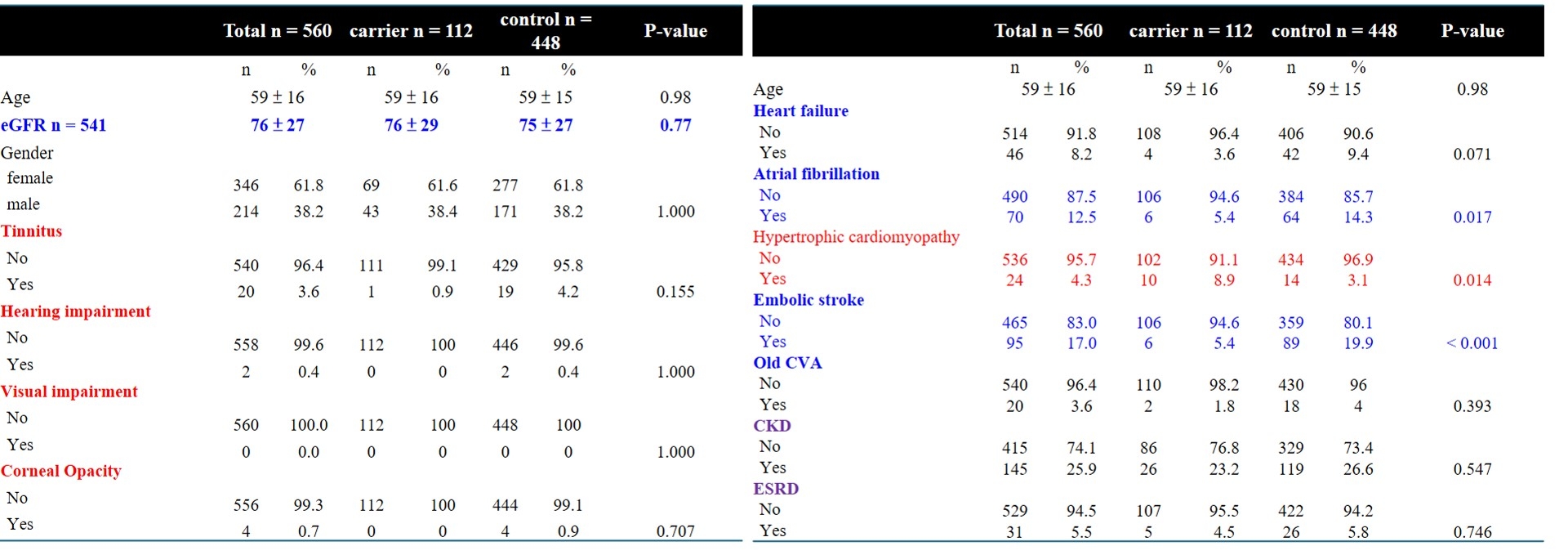
There were 112 genetic defined Fabry disease patients, male vs female: 43 vs 69, found from 43,000 Subjects aged more than 20 in TPMI Biobank from June, 24, 2019 to May 12, 2021. Prevalence was 0.26%. Five different genotype were identified and one was classic genotype GLA: c.1228A>G (N=1), and other 4 were late-onset genotype: GLA: c.902G>A (N=2), GLA:c.1067G>C (N=3), GLA: c.427G>A (N=1), and majority GLA: c.639+919G>A (N=105) (Figure 1). Comparing with matched population (112 vs 448) showed no difference in clinical presentation, including tinnitus, hearing impairment, visual impairment, corneal opacity, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stroke, chronic kidney disease, or end stage renal disease, but higher hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) as presentation was noted in genetic defined Fabry disease patient group (P=0.014) (Figure 2).
Conclusion
The prevalence of genetic defined FD in hospital based biobank was high, 0.26%. The most significant different clinical manifestation is HCM, which might due to most common genetic type is cardiac variant type (GLA: c.639+919G>A, 93%).
The prevalence of Fabry disease (FD) of general population and what most common initial presentation of FD are unknown. In addition to clinical diagnosis, the TPMI (Taiwan Precision Medicine Initiative Program) Biobank offers an unparalleled opportunity to determine the prevalence of FD-causing pathogenic variants in an unselected hospital visiting adult population.
Methods
All TPMI participants were genotyped using the Axiom Genome-Wide TWB 2.0 Array Plate (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The hot spots of Fabry disease-causing pathogenic variants were identified as genetic defined Fabry disease according to ACMG criteria pathogenic or likely pathogenic. All the identified variant were been validated by Sanger sequencing. We compared with genetic defined Fabry disease patients with age and gender matching hospital patients by ratio 1:4 respectively. The clinical renal, cardiac, and neurological manifestation were analyzed.
Results
There were 112 genetic defined Fabry disease patients, male vs female: 43 vs 69, found from 43,000 Subjects aged more than 20 in TPMI Biobank from June, 24, 2019 to May 12, 2021. Prevalence was 0.26%. Five different genotype were identified and one was classic genotype GLA: c.1228A>G (N=1), and other 4 were late-onset genotype: GLA: c.902G>A (N=2), GLA:c.1067G>C (N=3), GLA: c.427G>A (N=1), and majority GLA: c.639+919G>A (N=105) (Figure 1). Comparing with matched population (112 vs 448) showed no difference in clinical presentation, including tinnitus, hearing impairment, visual impairment, corneal opacity, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stroke, chronic kidney disease, or end stage renal disease, but higher hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) as presentation was noted in genetic defined Fabry disease patient group (P=0.014) (Figure 2).
Conclusion
The prevalence of genetic defined FD in hospital based biobank was high, 0.26%. The most significant different clinical manifestation is HCM, which might due to most common genetic type is cardiac variant type (GLA: c.639+919G>A, 93%).
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Association of Darier’s Disease and Dilated Cardiomyopathy: A Case Report Exploring the Cardiac Implications of ATP2A2 Mutation
Jacob Nidhi
Atrial Fibrillation in Genotyped Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Epidemiology and Associated Risk Factors - Insights from the SHaRe ConsortiumHeymans Astrid, Reza Nosheen, Helms Adam, Shore Supriya, Prasad Sanjay, Tayal Upasana, Wheeler Matthew, Fornaro Alessandra, Olivotto Iacopo, Mestroni Luisa, Wilsbacher Lisa, Balakrishnan Iswaree, Khan Sadiya, Sinagra Gianfranco, Merlo Marco, Rossano Joseph, Lin Kimberly, Ho Carolyn, Heymans Stephane, Parikh Victoria, Verdonschot Job, Lakdawala Neal, Claggett Brian, Stroeks Sophie, Stewart Garrick, Seidman Christine, Beelen Nina, Owens Anjali, Day Sharlene