Final ID: Sa2038
Assessing the Economic and Healthcare Burden of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Microsimulation Approach to Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Utilization
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder that requires effective management strategies to optimize long-term health outcomes. While metformin is the standard first-line therapy, many patients require second-line treatments to achieve adequate glycemic control. Newer drug classes, such as Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (RA), offer better and more physiologic control of blood sugar along with added cardiovascular benefits. Still, their cost-effectiveness remains uncertain compared to traditional therapies.
Objective: This study uses Markov modeling and microsimulation approach to evaluate the long-term health outcomes, costs, and cost-effectiveness of SGLT-2 inhibitors, GLP1 RAs, and traditional second-line therapies.
Methods: A Markov model using TreeAge Pro software was constructed to simulate T2DM progression over a 40-year horizon, incorporating transitions between key health states: no history of cardiovascular disease (CVD), history of CVD, and death. Cost effectiveness analysis (CEA) was performed with a willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of $100,000 per quality-adjusted life year (QALY). Microsimulation and sensitivity analyses assessed the robustness of findings.
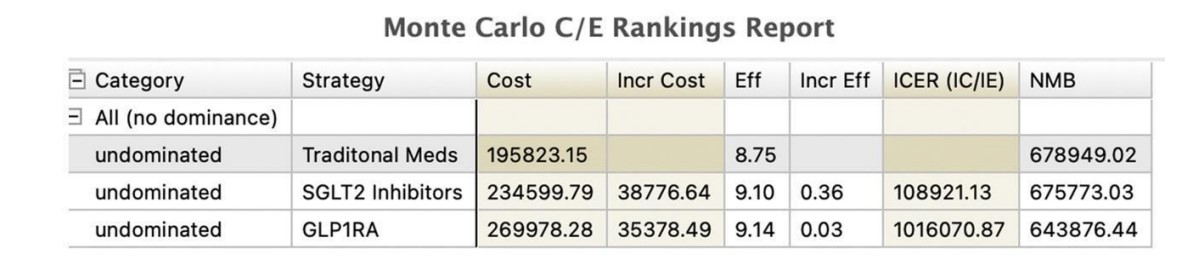
Results: The analysis provides insights into the comparative cost-effectiveness of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 RAs versus traditional second-line therapies. Our findings indicate that while newer therapies offer substantial cardiovascular benefits, their cost effectiveness depends on drug pricing and other parameters. Using the current estimated costs and a WTP of $100,000, neither of the new medicines are cost-effective compared to traditional medicines.
Conclusion: The present study highlights the importance of economic evaluation in selecting second-line therapies for T2DM. The results of our analyses could help formulate future healthcare decision-making and policy development to optimize patient outcomes while managing healthcare costs effectively.
Objective: This study uses Markov modeling and microsimulation approach to evaluate the long-term health outcomes, costs, and cost-effectiveness of SGLT-2 inhibitors, GLP1 RAs, and traditional second-line therapies.
Methods: A Markov model using TreeAge Pro software was constructed to simulate T2DM progression over a 40-year horizon, incorporating transitions between key health states: no history of cardiovascular disease (CVD), history of CVD, and death. Cost effectiveness analysis (CEA) was performed with a willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of $100,000 per quality-adjusted life year (QALY). Microsimulation and sensitivity analyses assessed the robustness of findings.
Results: The analysis provides insights into the comparative cost-effectiveness of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 RAs versus traditional second-line therapies. Our findings indicate that while newer therapies offer substantial cardiovascular benefits, their cost effectiveness depends on drug pricing and other parameters. Using the current estimated costs and a WTP of $100,000, neither of the new medicines are cost-effective compared to traditional medicines.
Conclusion: The present study highlights the importance of economic evaluation in selecting second-line therapies for T2DM. The results of our analyses could help formulate future healthcare decision-making and policy development to optimize patient outcomes while managing healthcare costs effectively.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Right Coronary Artery Chronic Total Occlusion in a Transplanted Heart: To Stent or Not to Stent?
A Longitudinal 20-year Analysis Indicates Acceleration of Cardiometabolic Comorbidities on Dementia Risk
Krayem Hussein, Cooke Richard, Abouzaki Nayef, Kutkut Issa
A Longitudinal 20-year Analysis Indicates Acceleration of Cardiometabolic Comorbidities on Dementia Risk
Lihua Huang, Danish Muhammad, Auyeung Tw, Jenny Lee, Kwok Timothy, Abrigo Jill, Wei Yingying, Lo Cecilia, Fung Erik