Final ID: MP2748
Cholesterol-Driven Monocyte mTORC1 Activation and Autophagy Suppression in Hypercholesterolemic Patients: A Translational Link to Atherosclerosis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
While statin therapy effectively lowers plasma LDL cholesterol (LDL-C), residual cardiovascular risk remains. Emerging evidence suggests that LDL-C may exert deleterious effects beyond its role in plaque development. Even moderately elevated or borderline LDL-C levels can act as nutrient signals that chronically activate maladaptive pathways in immune cells. In particular, LDL-C can stimulate mTORC1 signaling in monocytes and macrophages — key immune cells involved in atherosclerosis — leading to autophagy suppression, unresolved inflammation, and plaque progression.
Methods:
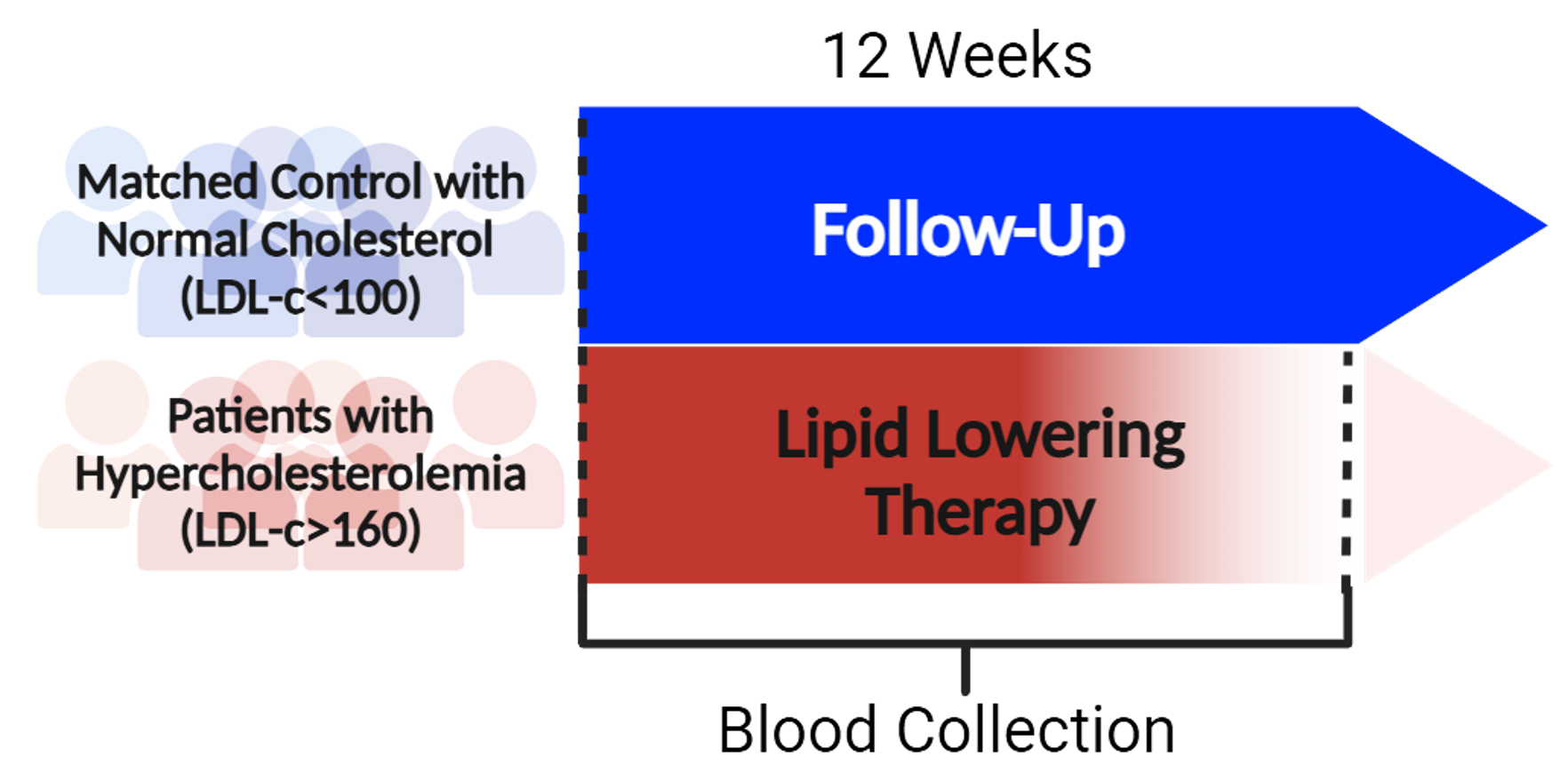
In a translational study, we compared monocyte mTORC1 signaling and autophagic markers in hypercholesterolemic patients (LDL-C >160 mg/dL, n=10) and healthy controls (LDL-C <100 mg/dL, n=10). Monocyte mTORC1 activity was assessed via its downstream target, phosphorylated S6 (pS6), and mTOR–LAMP2 colocalization (lysosomal mTOR recruitment). Autophagy was measured by LC3 intensity using immunofluorescence microscopy. Follow-up samples were collected after 12 weeks of statin therapy, administered as part of routine clinical care. Mechanistic insights were supported by in vitro LDL-C stimulation in human monocyte-derived macrophages (HMDMs) and in vivo studies in ApoE-/- mice.
Results:
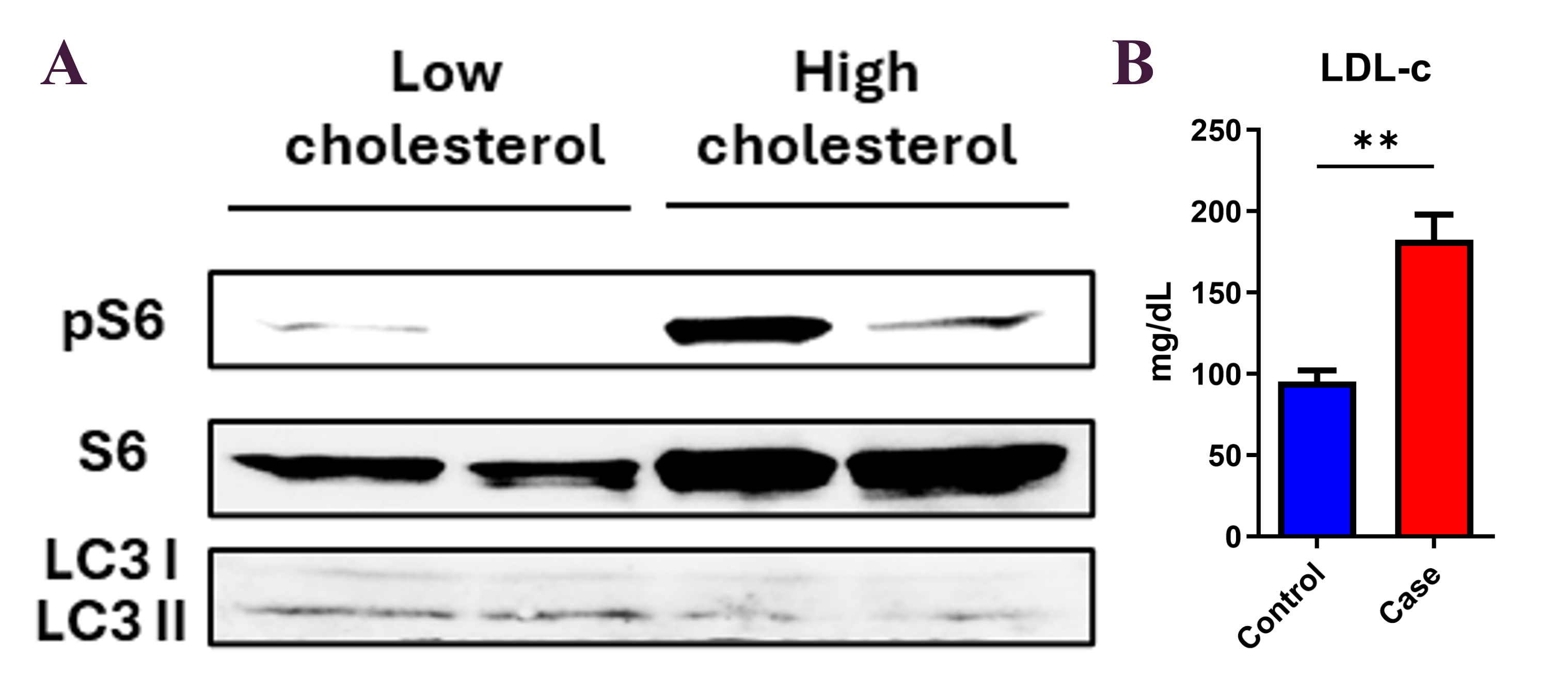
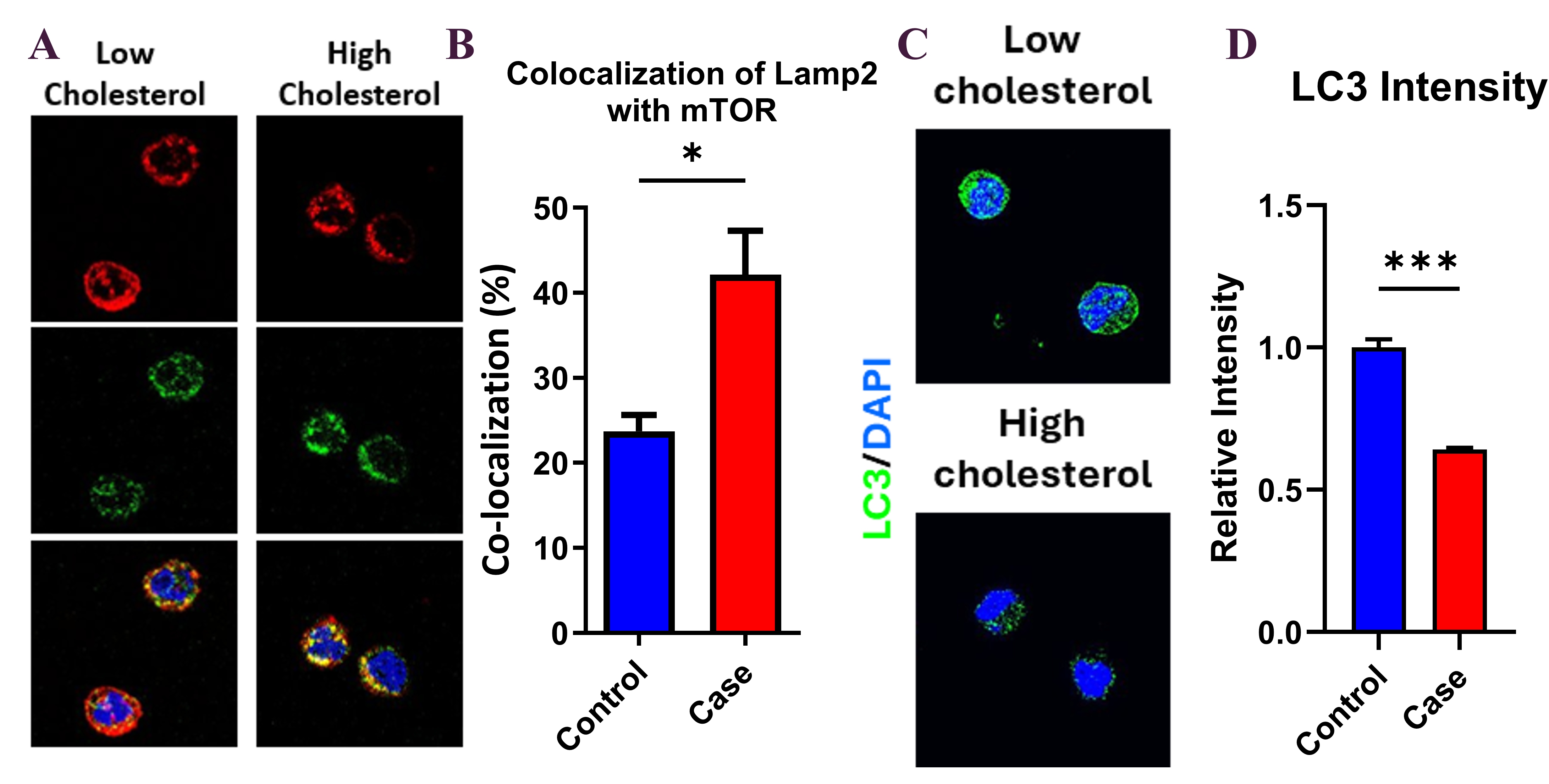
Hypercholesterolemic patients exhibited a ~3.5-fold increase in monocyte pS6/Total S6 levels and ~1.5-fold higher mTOR–LAMP2 colocalization compared to controls, consistent with elevated mTORC1 activity. LC3 intensity was reduced by approximately 50%, indicating suppressed autophagy. In vitro, LDL-C triggered mTORC1 activation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and apoptosis in HMDMs. In mice, dietary cholesterol increased monocyte mTORC1 signaling, which reversed after a switch to chow. Preliminary follow-up data suggests partial normalization of mTOR activity after statin treatment.
Conclusions:
These findings show that elevated LDL-C is linked to increased mTORC1 activity and autophagy suppression in monocytes. Using both pS6 and lysosomal mTOR localization provided complementary evidence of pathway activation. Targeting the cholesterol nutrient-sensing mTOR–autophagy axis may offer new strategies to reduce atherosclerotic risk beyond standard lipid-lowering. This approach could support precision cardiovascular medicine by tailoring treatment to individual cellular and metabolic profiles, rather than relying solely on population-level LDL thresholds.
While statin therapy effectively lowers plasma LDL cholesterol (LDL-C), residual cardiovascular risk remains. Emerging evidence suggests that LDL-C may exert deleterious effects beyond its role in plaque development. Even moderately elevated or borderline LDL-C levels can act as nutrient signals that chronically activate maladaptive pathways in immune cells. In particular, LDL-C can stimulate mTORC1 signaling in monocytes and macrophages — key immune cells involved in atherosclerosis — leading to autophagy suppression, unresolved inflammation, and plaque progression.
Methods:
In a translational study, we compared monocyte mTORC1 signaling and autophagic markers in hypercholesterolemic patients (LDL-C >160 mg/dL, n=10) and healthy controls (LDL-C <100 mg/dL, n=10). Monocyte mTORC1 activity was assessed via its downstream target, phosphorylated S6 (pS6), and mTOR–LAMP2 colocalization (lysosomal mTOR recruitment). Autophagy was measured by LC3 intensity using immunofluorescence microscopy. Follow-up samples were collected after 12 weeks of statin therapy, administered as part of routine clinical care. Mechanistic insights were supported by in vitro LDL-C stimulation in human monocyte-derived macrophages (HMDMs) and in vivo studies in ApoE-/- mice.
Results:
Hypercholesterolemic patients exhibited a ~3.5-fold increase in monocyte pS6/Total S6 levels and ~1.5-fold higher mTOR–LAMP2 colocalization compared to controls, consistent with elevated mTORC1 activity. LC3 intensity was reduced by approximately 50%, indicating suppressed autophagy. In vitro, LDL-C triggered mTORC1 activation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and apoptosis in HMDMs. In mice, dietary cholesterol increased monocyte mTORC1 signaling, which reversed after a switch to chow. Preliminary follow-up data suggests partial normalization of mTOR activity after statin treatment.
Conclusions:
These findings show that elevated LDL-C is linked to increased mTORC1 activity and autophagy suppression in monocytes. Using both pS6 and lysosomal mTOR localization provided complementary evidence of pathway activation. Targeting the cholesterol nutrient-sensing mTOR–autophagy axis may offer new strategies to reduce atherosclerotic risk beyond standard lipid-lowering. This approach could support precision cardiovascular medicine by tailoring treatment to individual cellular and metabolic profiles, rather than relying solely on population-level LDL thresholds.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Community-Based Intervention to Improve Cardiovascular Health Understanding in the Dallas-Fort Worth South Asian Community
Deo Parminder, Rohatgi Anand, Sharma Parul, Sathyamoorthy Mohanakrishnan
Beclin-1-Dependent Autophagy Prevents Hyperaldosternism-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction And HypertensionCosta Rafael, Bruder Nascimento Ariane, Tostes Rita, Bruder Thiago