Final ID: Su2042
Association between atherogenic index of plasma and long-term prognosis in patients with Cardiovascular–kidney–metabolic syndrome stages 4: a retrospective cohort study involving 7,672 individuals.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
The atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) is closely associated with various metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and chronic kidney disease, and it has also been shown to correlate with cardiovascular risk in patients with Cardiovascular-kindey-metabolic syndrome (CKM) stages 0-3; however, the role of AIP in the prognosis of patients with CKM stage 4 remains to be investigated.
Methods
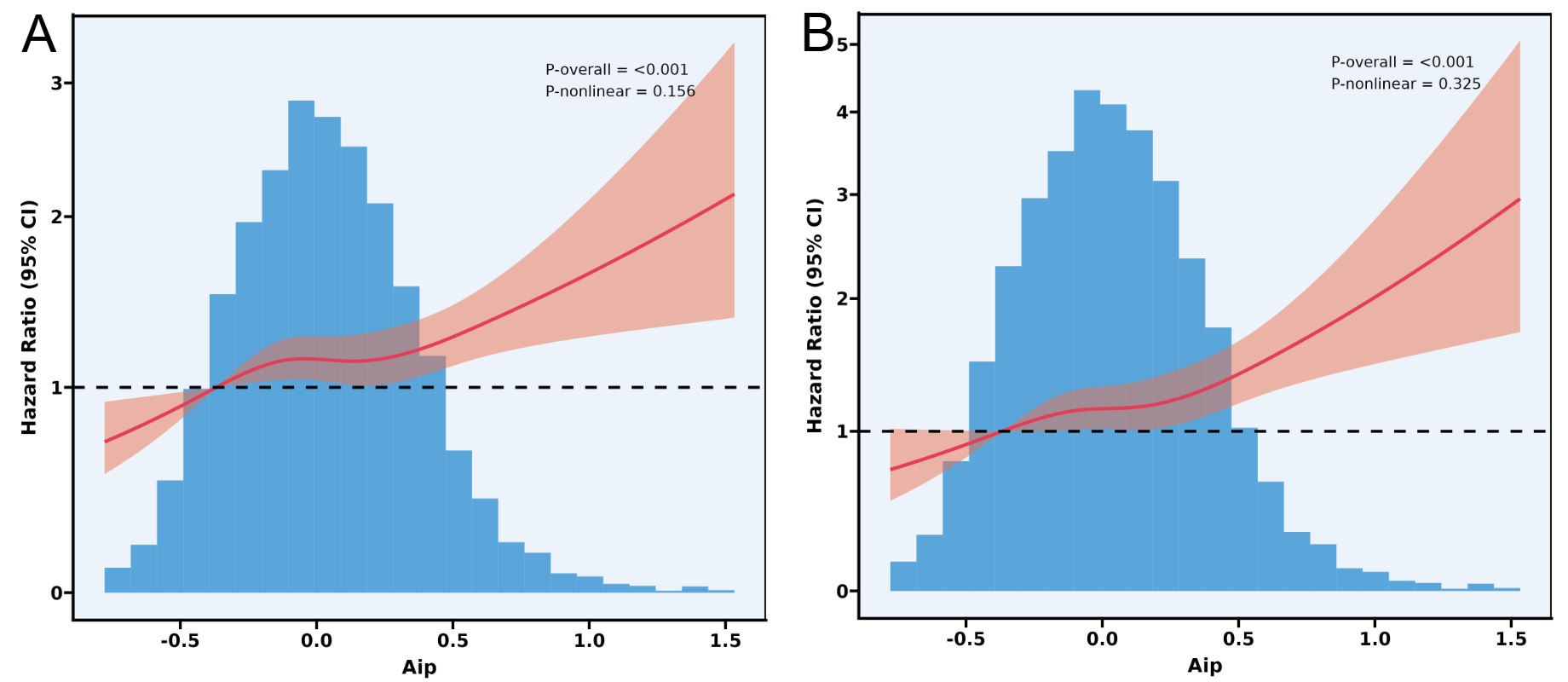
This study used data from the MIMIC database, with outcome events defined as long-term mortality and 365-day mortality. We examined the relationship between the AIP and the occurrence of outcome events in patients with CKM stage 4 using Kaplan-Meier curves, restricted cubic splines (RCS), and Cox proportional hazards models, while ensuring the robustness of our conclusions through subgroup analyses and interaction terms.
Results
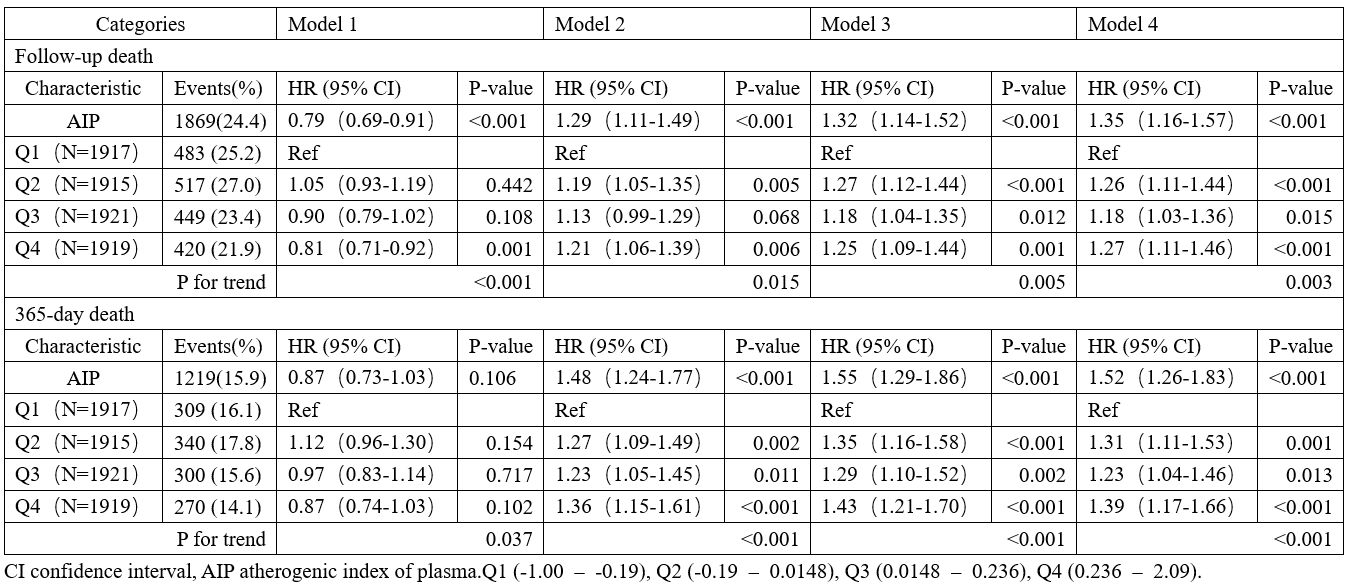
A total of 7,672 patients were included, of whom 4,466 (58.2%) were male. Multivariable Cox analysis revealed that compared to the lowest quartile, the hazard ratio (HR) for follow-up mortality in the highest quartile was 1.27 (95% CI: 1.11-1.46, P<0.001), and the HR for 365-day mortality was 1.39 (95% CI: 1.17-1.66, P<0.001). The risk of death increased linearly with increasing AIP (P for trend < 0.05). The results from the RCS, subgroup analyses, and interaction terms confirmed the robustness of these conclusions.
Conclusions
AIP is an independent risk factor for the long-term prognosis of patients with CKM stage 4, and this index can serve as an effective indicator for risk stratification upon admission and long-term prognosis assessment. Monitoring AIP and implementing early interventions for dyslipidemia may help improve survival rates in patients with CKM stage 4.
Keywords: Atherogenic index of plasma, Cardiovascular-kindey-metabolic syndrome, Long-term prognosis, Retrospective cohort study
The atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) is closely associated with various metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and chronic kidney disease, and it has also been shown to correlate with cardiovascular risk in patients with Cardiovascular-kindey-metabolic syndrome (CKM) stages 0-3; however, the role of AIP in the prognosis of patients with CKM stage 4 remains to be investigated.
Methods
This study used data from the MIMIC database, with outcome events defined as long-term mortality and 365-day mortality. We examined the relationship between the AIP and the occurrence of outcome events in patients with CKM stage 4 using Kaplan-Meier curves, restricted cubic splines (RCS), and Cox proportional hazards models, while ensuring the robustness of our conclusions through subgroup analyses and interaction terms.
Results
A total of 7,672 patients were included, of whom 4,466 (58.2%) were male. Multivariable Cox analysis revealed that compared to the lowest quartile, the hazard ratio (HR) for follow-up mortality in the highest quartile was 1.27 (95% CI: 1.11-1.46, P<0.001), and the HR for 365-day mortality was 1.39 (95% CI: 1.17-1.66, P<0.001). The risk of death increased linearly with increasing AIP (P for trend < 0.05). The results from the RCS, subgroup analyses, and interaction terms confirmed the robustness of these conclusions.
Conclusions
AIP is an independent risk factor for the long-term prognosis of patients with CKM stage 4, and this index can serve as an effective indicator for risk stratification upon admission and long-term prognosis assessment. Monitoring AIP and implementing early interventions for dyslipidemia may help improve survival rates in patients with CKM stage 4.
Keywords: Atherogenic index of plasma, Cardiovascular-kindey-metabolic syndrome, Long-term prognosis, Retrospective cohort study
More abstracts on this topic:
A major uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate impairs macrophage efferocytosis and accelerates atherogenesis: a potential mechanism for cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney disease
Jha Prabhash, Kasai Taku, Vromman Amelie, Holden Rachel, Libby Peter, Tabas Ira, Singh Sasha, Aikawa Elena, Aikawa Masanori, Lupieri Adrien, Sonawane Abhijeet, Le Thanh-dat, Becker-greene Dakota, Chelvanambi Sarvesh, Turner Mandy, Nakamura Yuto, Passos Livia
A Mechanistic Insight Into The Connection Between Metabolism And Differentiation In ACTA2 P. R179 Smooth Muscle CellsEsparza Pinelo Jose, Krenz Hannah, Chen Jessica, Kaw Anita, Milewicz Dianna, Kwartler Callie