Final ID: 4170777
PanEcho: Complete AI-enabled echocardiography interpretation with multi-task deep learning
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is integral to cardiovascular evaluation but relies on manual reporting. Artificial intelligence (AI) promises to automate cardiac pathology detection, however existing applications of AI to TTE reporting have focused on individual conditions and echocardiographic views. To bridge this gap, we developed PanEcho, a view-agnostic, multi-task AI model that automates TTE interpretation across views and acquisitions for all key echocardiographic metrics and findings.
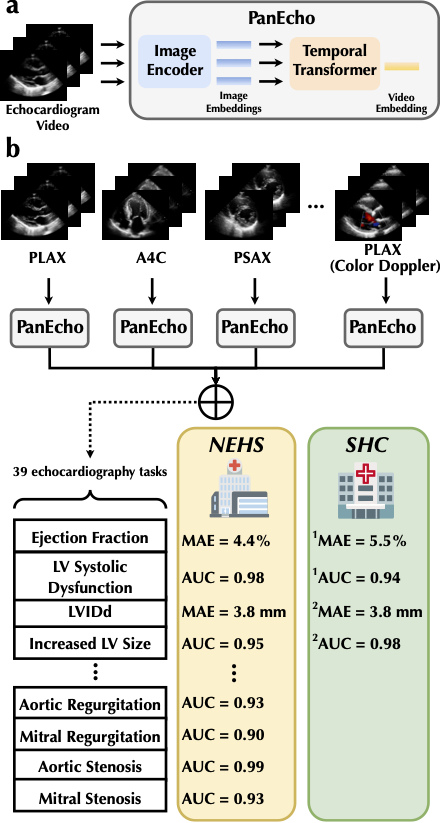
Methods: PanEcho was developed using 1.23 million echocardiographic videos from 33,927 TTE studies (mean age 67 years, 52.2% male) performed at a New England Health System (NEHS) from Jan 2016-Jun 2022. The model can perform 39 TTE reporting tasks, spanning the full spectrum of myocardial and valvular structure and function from any parasternal, apical, and subcostal views, including B-mode and color Doppler videos. It consists of an image encoder to learn spatial features, a Transformer for temporal modeling, and task-specific output heads; PanEcho was evaluated on a temporally distinct YNHHS cohort from Jul-Dec 2022 and two external California cohorts from 2008-2020 (Fig 1). We assessed both its off-the-shelf diagnostic performance and ability to function as a foundation model for fine-tuning in novel domains.
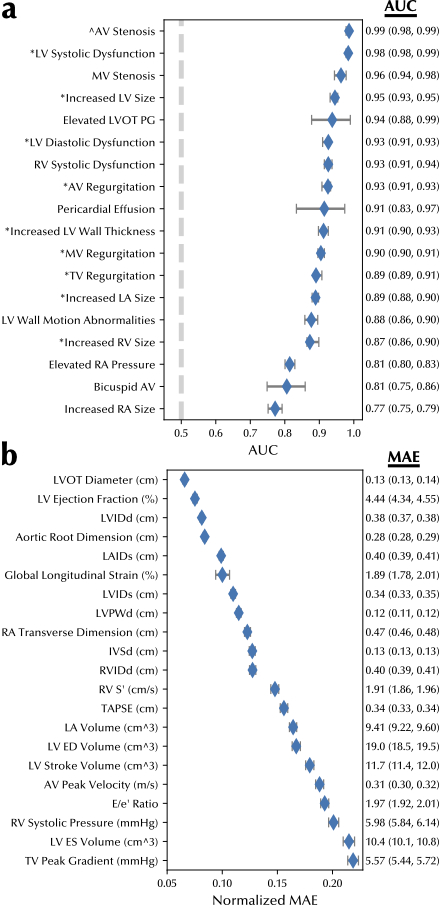
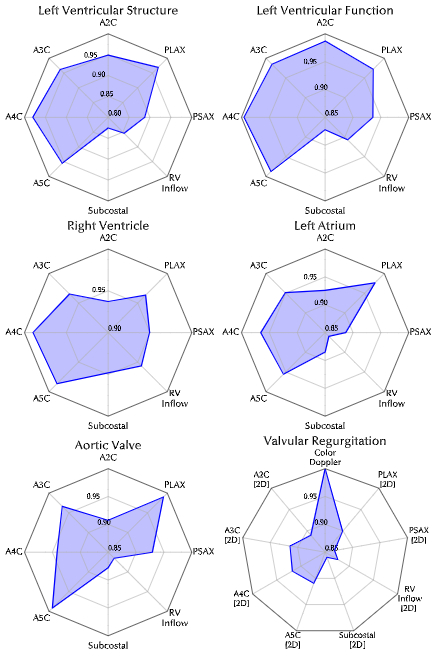
Results: PanEcho achieves a median area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.91 across 18 classification tasks, detecting severe aortic stenosis with 0.99 AUC, moderate-severe left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction with 0.98 AUC (0.94 AUC externally), moderate-severe LV dilation with 0.95 AUC (0.98 AUC externally), among others. (Fig 2A). The model estimates continuous metrics with a median normalized mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.13 across 21 tasks, e.g., defining LV ejection fraction (EF) with 4.4% MAE (5.5% MAE externally) and LV internal diameter with 3.8 mm MAE (Fig 2B). Multi-view evaluation confirms PanEcho’s ability to identify which views are most informative for each task (Fig 3). Further, the learned representations efficiently transfer to LVEF estimation in novel pediatric populations, outperforming existing approaches (3.9% MAE vs. next-best 4.5% MAE).
Conclusion: PanEcho is a view-agnostic, multi-task, externally validated, open-source AI model that enables echocardiographic interpretation across a broad range of TTE views and labels, representing a flexible foundation model for echocardiography.
Methods: PanEcho was developed using 1.23 million echocardiographic videos from 33,927 TTE studies (mean age 67 years, 52.2% male) performed at a New England Health System (NEHS) from Jan 2016-Jun 2022. The model can perform 39 TTE reporting tasks, spanning the full spectrum of myocardial and valvular structure and function from any parasternal, apical, and subcostal views, including B-mode and color Doppler videos. It consists of an image encoder to learn spatial features, a Transformer for temporal modeling, and task-specific output heads; PanEcho was evaluated on a temporally distinct YNHHS cohort from Jul-Dec 2022 and two external California cohorts from 2008-2020 (Fig 1). We assessed both its off-the-shelf diagnostic performance and ability to function as a foundation model for fine-tuning in novel domains.
Results: PanEcho achieves a median area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.91 across 18 classification tasks, detecting severe aortic stenosis with 0.99 AUC, moderate-severe left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction with 0.98 AUC (0.94 AUC externally), moderate-severe LV dilation with 0.95 AUC (0.98 AUC externally), among others. (Fig 2A). The model estimates continuous metrics with a median normalized mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.13 across 21 tasks, e.g., defining LV ejection fraction (EF) with 4.4% MAE (5.5% MAE externally) and LV internal diameter with 3.8 mm MAE (Fig 2B). Multi-view evaluation confirms PanEcho’s ability to identify which views are most informative for each task (Fig 3). Further, the learned representations efficiently transfer to LVEF estimation in novel pediatric populations, outperforming existing approaches (3.9% MAE vs. next-best 4.5% MAE).
Conclusion: PanEcho is a view-agnostic, multi-task, externally validated, open-source AI model that enables echocardiographic interpretation across a broad range of TTE views and labels, representing a flexible foundation model for echocardiography.
More abstracts on this topic:
Accuracy of cardiologist reporting of severe aortic stenosis and its impact on clinical management: Insights from decision-support artificial intelligence applied to 28,491 men and women undergoing echocardiography.
Bhat Vikas, Strange Geoff, Butcher Steele, Deans Renae, Mahoney Thomas, Barnes Cara, Playford David
Acoustic Biomarkers Harvested from 911 Calls Differ among Patients with Cardiac and Non-Cardiac Chest PainMazhar Harris, Zegre-hemsey Jessica, Lee Kyungbok, Tian Baotong, Heydari Mojtaba, Cushman Jeremy, Duan Zhiyao, Dzikowicz Dillon