Final ID: MDP1459
Chronotropic Incompetence in Amyloid Cardiac Disease: A Marker of Severity?
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiac amyloidosis is a rapidly progressing and severe condition leading to heart failure and reduced quality of life. Amyloid deposits impair both chronotropic and pumping functions of the heart. The Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test (CPET) is a vital tool in assessing the severity and progression of this disease.
Aims: This study aims to investigate the differences in chronotropic function associated with the stages of heart failure in patients with cardiac amyloidosis and outcomes.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted involving 194 patients diagnosed with cardiac amyloidosis who underwent at least one CPET from February 2010 to February 2024. Medical records were reviewed for data on the type of amyloidosis, comorbidities, and CPET results. The cohort was divided into two groups according to the Weber Classification: Weber Class A/B and Weber Class C/D. Patients who had CPET studies post-heart transplant were excluded. Statistical analyses, including Fisher’s exact test and chi-square test, were used. Cox regression model analysis, proportional hazards model for time to event. Adjustment for beta-blocker use was made to assess chronotropic incompetence. A p-value <0.05 was considered significant.
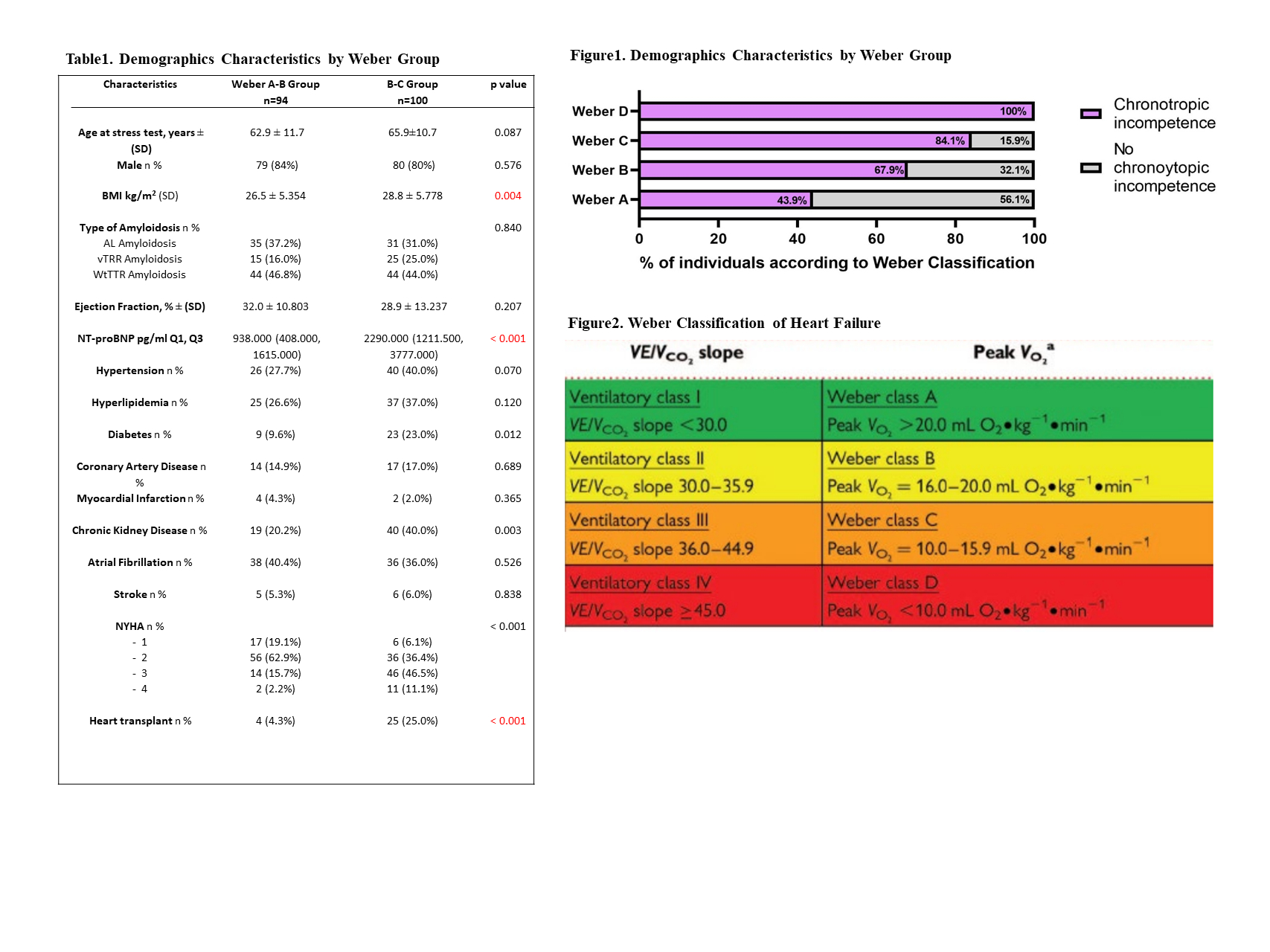
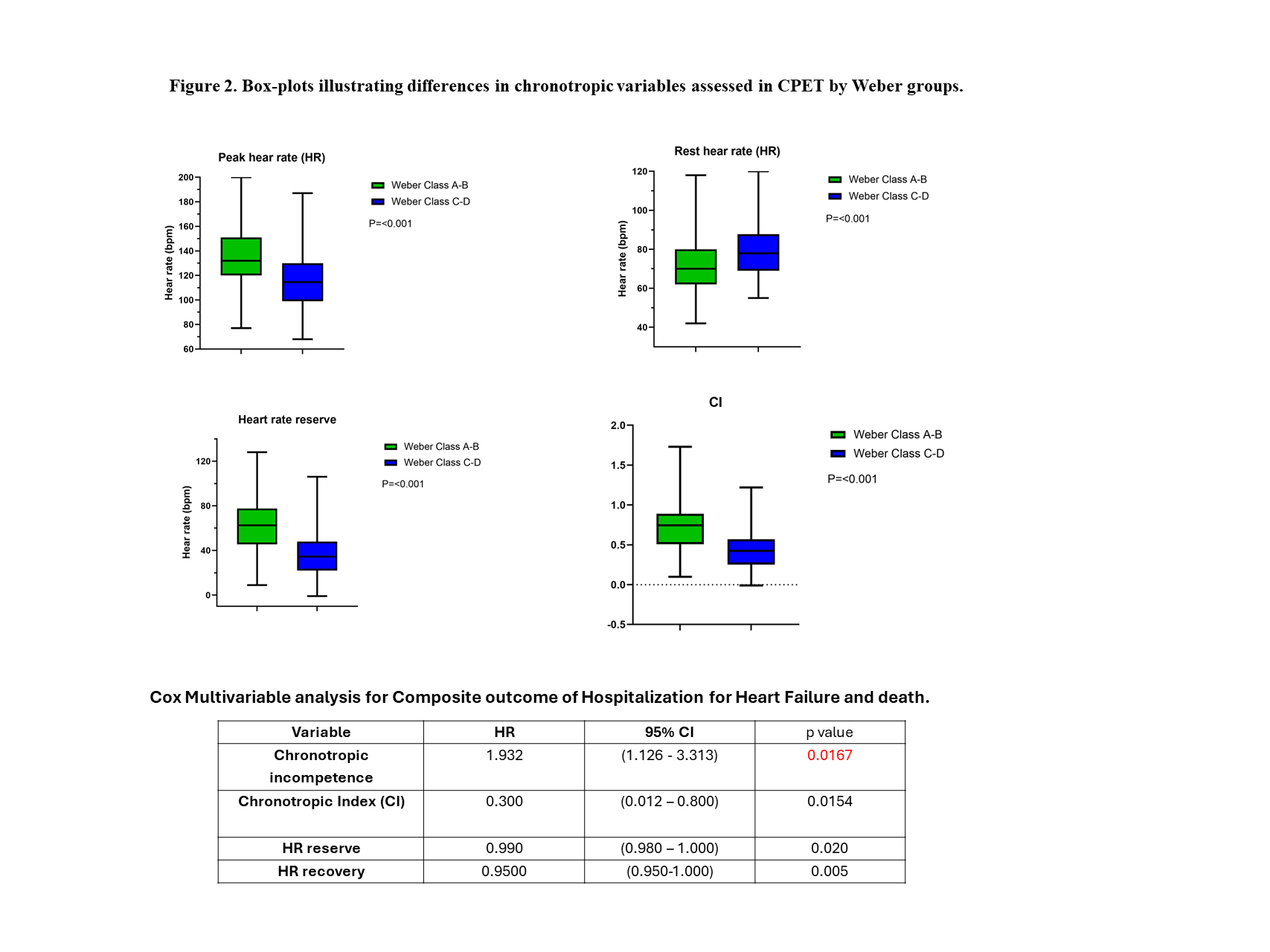
Results: Among the 194 patients, 94 were classified as Weber A/B and 100 as Weber C/D. The average age at the time of the stress test was similar between the groups: 62.9 ± 11.7 years for Weber A/B and 62.3 ± 10.7 years for Weber C/D (p=0.087) Table 1. Chronotropic function, evaluated through CPET, showed significant differences. Heart rate reserve was significantly lower in the Weber C-D group compared to the A-B group (p<0.001). The chronotropic index was also significantly lower in the Weber C-D group Figure 2. Chronotropic incompetence was observed in 43.9% of the Weber A and increased progressively, being significantly more prevalent in the Weber D group (100%) (p<0.001). Additionally, Chronotropic incompetence was strongly associated with the composite outcome of (hospitalization for heart failure and death) HR 1.932 (1.126 -3.313) p =0.0167 (Table 2).
Conclusion: CPET assessment of chronotropic function correlates with VO2 parameter evaluated in Weber classification. Patients with higher Weber stages of heart failure in amyloidosis exhibited a higher prevalence of chronotropic incompetence, indicating it could serve as a marker of cardiac function.
Aims: This study aims to investigate the differences in chronotropic function associated with the stages of heart failure in patients with cardiac amyloidosis and outcomes.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted involving 194 patients diagnosed with cardiac amyloidosis who underwent at least one CPET from February 2010 to February 2024. Medical records were reviewed for data on the type of amyloidosis, comorbidities, and CPET results. The cohort was divided into two groups according to the Weber Classification: Weber Class A/B and Weber Class C/D. Patients who had CPET studies post-heart transplant were excluded. Statistical analyses, including Fisher’s exact test and chi-square test, were used. Cox regression model analysis, proportional hazards model for time to event. Adjustment for beta-blocker use was made to assess chronotropic incompetence. A p-value <0.05 was considered significant.
Results: Among the 194 patients, 94 were classified as Weber A/B and 100 as Weber C/D. The average age at the time of the stress test was similar between the groups: 62.9 ± 11.7 years for Weber A/B and 62.3 ± 10.7 years for Weber C/D (p=0.087) Table 1. Chronotropic function, evaluated through CPET, showed significant differences. Heart rate reserve was significantly lower in the Weber C-D group compared to the A-B group (p<0.001). The chronotropic index was also significantly lower in the Weber C-D group Figure 2. Chronotropic incompetence was observed in 43.9% of the Weber A and increased progressively, being significantly more prevalent in the Weber D group (100%) (p<0.001). Additionally, Chronotropic incompetence was strongly associated with the composite outcome of (hospitalization for heart failure and death) HR 1.932 (1.126 -3.313) p =0.0167 (Table 2).
Conclusion: CPET assessment of chronotropic function correlates with VO2 parameter evaluated in Weber classification. Patients with higher Weber stages of heart failure in amyloidosis exhibited a higher prevalence of chronotropic incompetence, indicating it could serve as a marker of cardiac function.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acoramidis Reduces All-Cause Mortality (ACM) and Cardiovascular-Related Hospitalization (CVH): Initial Outcomes From the ATTRibute-CM Open-Label Extension (OLE) Study
Judge Daniel, Masri Ahmad, Obici Laura, Poulsen Steen, Sarswat Nitasha, Shah Keyur, Soman Prem, Cao Xiaofan, Wang Kevin, Pecoraro Maria, Tamby Jean-francois, Gillmore Julian, Katz Leonid, Fox Jonathan, Maurer Mathew, Alexander Kevin, Ambardekar Amrut, Cappelli Francesco, Fontana Marianna, Garcia-pavia Pablo, Grogan Martha, Hanna Mazen
A Case of Concomitant Wild-Type Transthyretin and Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis Involving Separate OrgansChiu Leonard, Afrough Aimaz, Nadeem Urooba, Jebakumar Deborah, Grodin Justin