Final ID: MDP1643
Explainable AI Better Predicts 3-Year MACE Risk Compared to Clinical and ASCVD Models in the UK Biobank Cohort
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Hypothesis: Artificial intelligence (AI)-derived retinal microvascular architecture from fundus images predicts time to MACE events.
Objectives: To establish associations of retinal vessel features with 3-year MACE risk, and compare AI-derived retinal vessel-based MACE risk with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) risk calculator.
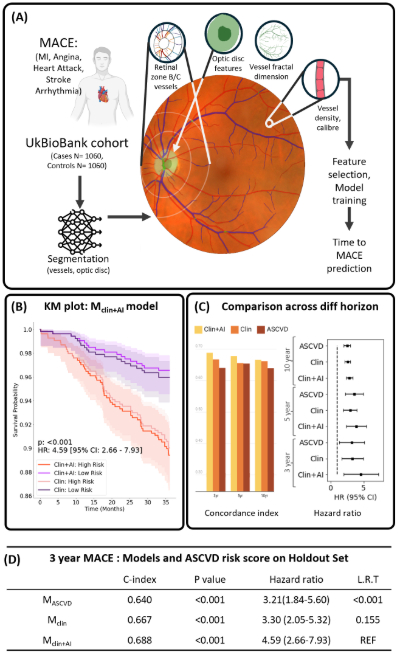
Methods: Baseline retinal fundus scans were identified for 2120 patients with no prior CVD events, from UK Biobank Cohort. Retinal features such as angle, tortuosity, curvature, and caliber, were extracted (Fig. A). A Cox proportional hazards model was trained using demographics and clinical risk factors (Mclin). AI-derived top 6 features extracted from retinal vessel analysis (Mclin+AI) were integrated and compared with ASCVD risk calculator. The models were trained on 1060 individuals (50%) and validated on a holdout set of 1060 individuals (50%). Performance was assessed using the concordance index (C-Index), hazard ratio (HR), and Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves, and models were compared using the Likelihood Ratio Test (L.R.T.)
Results: In the holdout set, Mclin+AI risk score achieved a C-index of 0.688, HR of 4.59 (2.66 -7.93, p<0.001) for 3-year MACE event prediction compared to Mclin (C-index=0.667, 3.30 (95% CI: 2.05-5.32), p<0.001). Mclin+AI was significantly better (L.R.T p<0.001) than ASCVD risk calculator (C-index=0.640, 3.21 (95% CI: 1.84-5.60), p<0.001), suggesting that retinal features hold promise for capturing novel information not included in current risk assessment tools, enabling improved immediate risk evaluation. Mclin+AI demonstrates a notable advantage over other models for MACE risk prediction over 3, 5, and 10-year periods, with highest predictive power in the shorter term.
Conclusion: AI-derived retinal features are strongly associated with 3-year MACE. Further multisite prospective validation is warranted.
Objectives: To establish associations of retinal vessel features with 3-year MACE risk, and compare AI-derived retinal vessel-based MACE risk with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) risk calculator.
Methods: Baseline retinal fundus scans were identified for 2120 patients with no prior CVD events, from UK Biobank Cohort. Retinal features such as angle, tortuosity, curvature, and caliber, were extracted (Fig. A). A Cox proportional hazards model was trained using demographics and clinical risk factors (Mclin). AI-derived top 6 features extracted from retinal vessel analysis (Mclin+AI) were integrated and compared with ASCVD risk calculator. The models were trained on 1060 individuals (50%) and validated on a holdout set of 1060 individuals (50%). Performance was assessed using the concordance index (C-Index), hazard ratio (HR), and Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves, and models were compared using the Likelihood Ratio Test (L.R.T.)
Results: In the holdout set, Mclin+AI risk score achieved a C-index of 0.688, HR of 4.59 (2.66 -7.93, p<0.001) for 3-year MACE event prediction compared to Mclin (C-index=0.667, 3.30 (95% CI: 2.05-5.32), p<0.001). Mclin+AI was significantly better (L.R.T p<0.001) than ASCVD risk calculator (C-index=0.640, 3.21 (95% CI: 1.84-5.60), p<0.001), suggesting that retinal features hold promise for capturing novel information not included in current risk assessment tools, enabling improved immediate risk evaluation. Mclin+AI demonstrates a notable advantage over other models for MACE risk prediction over 3, 5, and 10-year periods, with highest predictive power in the shorter term.
Conclusion: AI-derived retinal features are strongly associated with 3-year MACE. Further multisite prospective validation is warranted.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Deep Learning Digital Biomarker for Mitral Valve Prolapse using Echocardiogram Videos
Al-alusi Mostafa, Khurshid Shaan, Sanborn Danita, Picard Michael, Ho Jennifer, Maddah Mahnaz, Ellinor Patrick, Lau Emily, Small Aeron, Reeder Christopher, Shnitzer Dery Tal, Andrews Carl, Kany Shinwan, Ramo Joel, Haimovich Julian
A Case of Transient Cortical Blindness occurring during Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angiography for Acute Coronary Syndrome.Adelakun Adeniyi, Farouji Iyad, Haddad Ahmad, Szwed Stanley