Final ID: MDP1272
Guideline-directed medical therapy improves cell viability in an iPSC-derived cardiomyocyte hypoxia injury model
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Beta blockers, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone antagonists, and mineralocorticoid antagonists are mainstays of current guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. They have been shown to reduce morbidity and mortality in heart failure patients, reverse remodeling, and improve left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in landmark human clinical trials. GDMT has been hypothesized to interact and have protective effects in bioenergetics in cardiac injury by reducing cardiac workload and energy demand. We have previously used a human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived cardiomyocytes (iCM) injury model to provide an in vitro validation of bioenergetics through measurement of cell viability and proliferation, intracellular measurement of ATP, contractility, and respiratory function. The application of GDMT in this in vitro model has not been previously assessed.
Methods:
Highly pure iCMs were differentiated from a healthy, human monoclonal iPSC line using CHIR99021 followed by C59 to modulate Wnt pathway activity. Upon spontaneous contractility, iCMs were replated for purification. Prior to hypoxia exposure, iCMs were treated with either 5uM metoprolol, 5uM losartan, 5uM spironolactone, or a control for 24 hours. To mimic in vivo ischemia, iCM are placed in a glucose deprived media (GDM) in a hypoxia inductor chamber with <1% oxygen-containing mixed gas in a 37°C incubator for 18 hours. A second iCM group is similarly treated in GDM for 18 hours in a normoxic setting. Cell viability and proliferation was then studied using MTT assay.
Results:
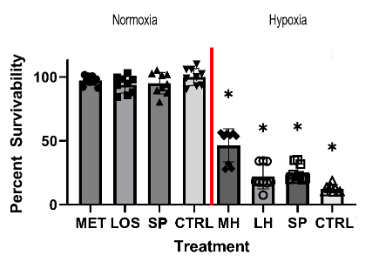
The metoprolol, losartan, and spironolactone treatment groups significantly improved cell viability after hypoxic injury when compared to the control treatment groups. Metoprolol treatment had the highest cell viability after hypoxic injury (46%), followed by spironolactone (23%) and losartan (22%), compared to control (13%). In the normoxic group, metoprolol, losartan, and spironolactone treatment showed no significant difference in viability compared to the control group.
Conclusion:
iPSC-derived iCMs treated with GDMT improved cell viability after hypoxic injury. The iPSC hypoxia-injury model appears to be a promising in vitro platform for studying the effects of GDMT on cellular bioenergetics.
Beta blockers, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone antagonists, and mineralocorticoid antagonists are mainstays of current guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. They have been shown to reduce morbidity and mortality in heart failure patients, reverse remodeling, and improve left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in landmark human clinical trials. GDMT has been hypothesized to interact and have protective effects in bioenergetics in cardiac injury by reducing cardiac workload and energy demand. We have previously used a human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived cardiomyocytes (iCM) injury model to provide an in vitro validation of bioenergetics through measurement of cell viability and proliferation, intracellular measurement of ATP, contractility, and respiratory function. The application of GDMT in this in vitro model has not been previously assessed.
Methods:
Highly pure iCMs were differentiated from a healthy, human monoclonal iPSC line using CHIR99021 followed by C59 to modulate Wnt pathway activity. Upon spontaneous contractility, iCMs were replated for purification. Prior to hypoxia exposure, iCMs were treated with either 5uM metoprolol, 5uM losartan, 5uM spironolactone, or a control for 24 hours. To mimic in vivo ischemia, iCM are placed in a glucose deprived media (GDM) in a hypoxia inductor chamber with <1% oxygen-containing mixed gas in a 37°C incubator for 18 hours. A second iCM group is similarly treated in GDM for 18 hours in a normoxic setting. Cell viability and proliferation was then studied using MTT assay.
Results:
The metoprolol, losartan, and spironolactone treatment groups significantly improved cell viability after hypoxic injury when compared to the control treatment groups. Metoprolol treatment had the highest cell viability after hypoxic injury (46%), followed by spironolactone (23%) and losartan (22%), compared to control (13%). In the normoxic group, metoprolol, losartan, and spironolactone treatment showed no significant difference in viability compared to the control group.
Conclusion:
iPSC-derived iCMs treated with GDMT improved cell viability after hypoxic injury. The iPSC hypoxia-injury model appears to be a promising in vitro platform for studying the effects of GDMT on cellular bioenergetics.
More abstracts on this topic:
Chimpanzee Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)-derived Cardiomyocytes as Surrogates for Human iPSCs in Cardiomyocyte Research and Cross-Species Chimeric Embryo Development
Roodgar Morteza, Parham Maryam, Suchi Fabian, Bajpai Vivek, Nakauchi Hiromitsu, Wu Joseph, Snyder Michael
A Case of Concomitant Wild-Type Transthyretin and Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis Involving Separate OrgansChiu Leonard, Afrough Aimaz, Nadeem Urooba, Jebakumar Deborah, Grodin Justin