Final ID: Sa1008
Amyloidogenic Medin Induces Prothrombotic Activation in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The endothelium plays a major role in preventing thrombosis. Aging leads to a hypercoagulable state with increased procoagulant factors without accompanying rise in anticoagulant factors, shifting the balance to a prothrombotic profile. This increases the risk for conditions such as stroke or myocardial infarction. The mediator/s of this change remains unknown. Medin is a 50 amino acid cleavage product of MFGE8, accumulates in the vasculature with aging and is the most common human amyloid. Vascular medin burden is increased in vascular dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and aortic aneurysms. Medin was shown to induce endothelial and smooth muscle dysfunction and endothelial pro-inflammatory activation. Its role in aging-associated prothrombotic activation is unknown.
Aim: To determine the effect of medin on human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVECs) expression and function of thrombomodulin (a transmembrane glycoprotein that is a major anticoagulant through its interaction with thrombin leading to activation of protein C and S which in turn degrades factors Va and VIIIa) and HBMVEC expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and tissue factor (major procoagulant proteins).
Methods: Primary HBMVECs (passages 6-8) were exposed for 20 hours to physiologic doses of recombinant human medin (1 or 5 uM) and gene and protein expression of thrombomodulin, PAI-1 and tissue factor were measured using rtPCR or Western blot, respectively. In separate experiments, assessment of thrombomodulin function was determined by exposing HBMVECs for 20 hours to medin, after which human protein C (0.2 uM) and α-thrombin (10 nM) were added for 1 hour and amount of activated protein C in media was measured using ELISA.
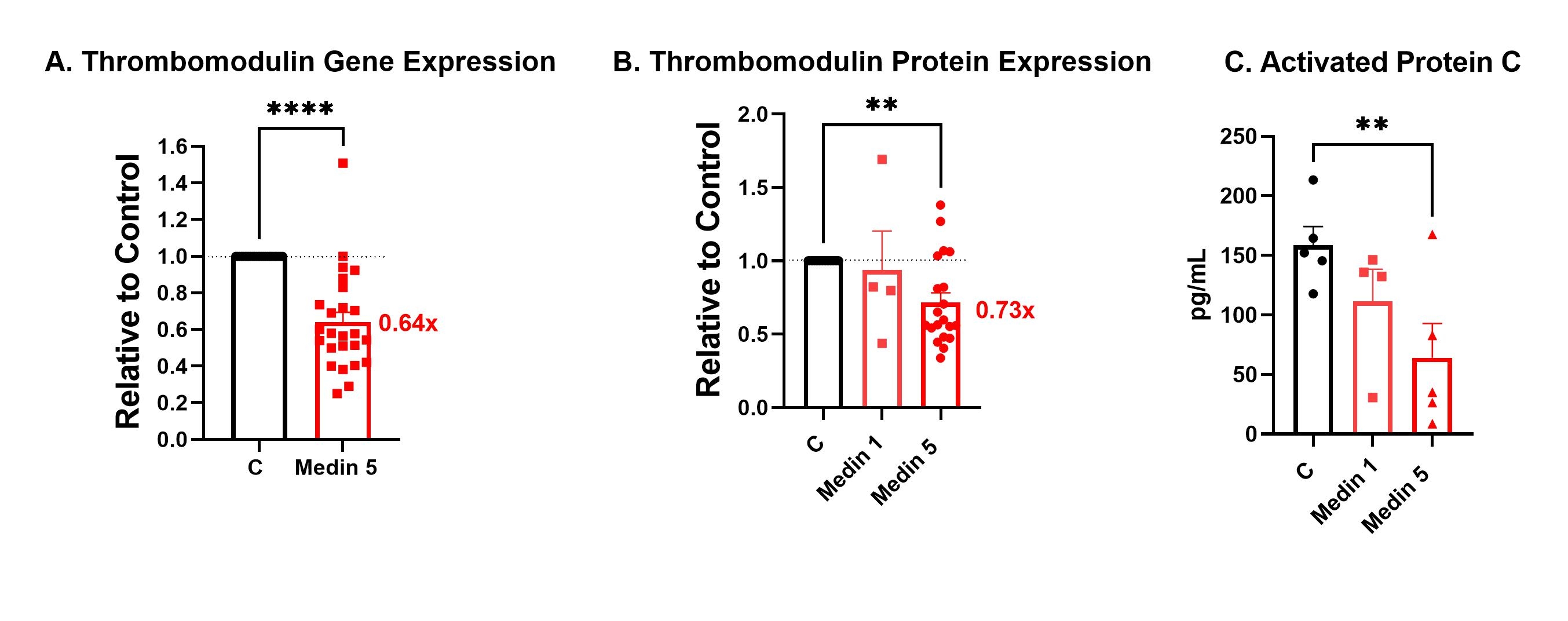
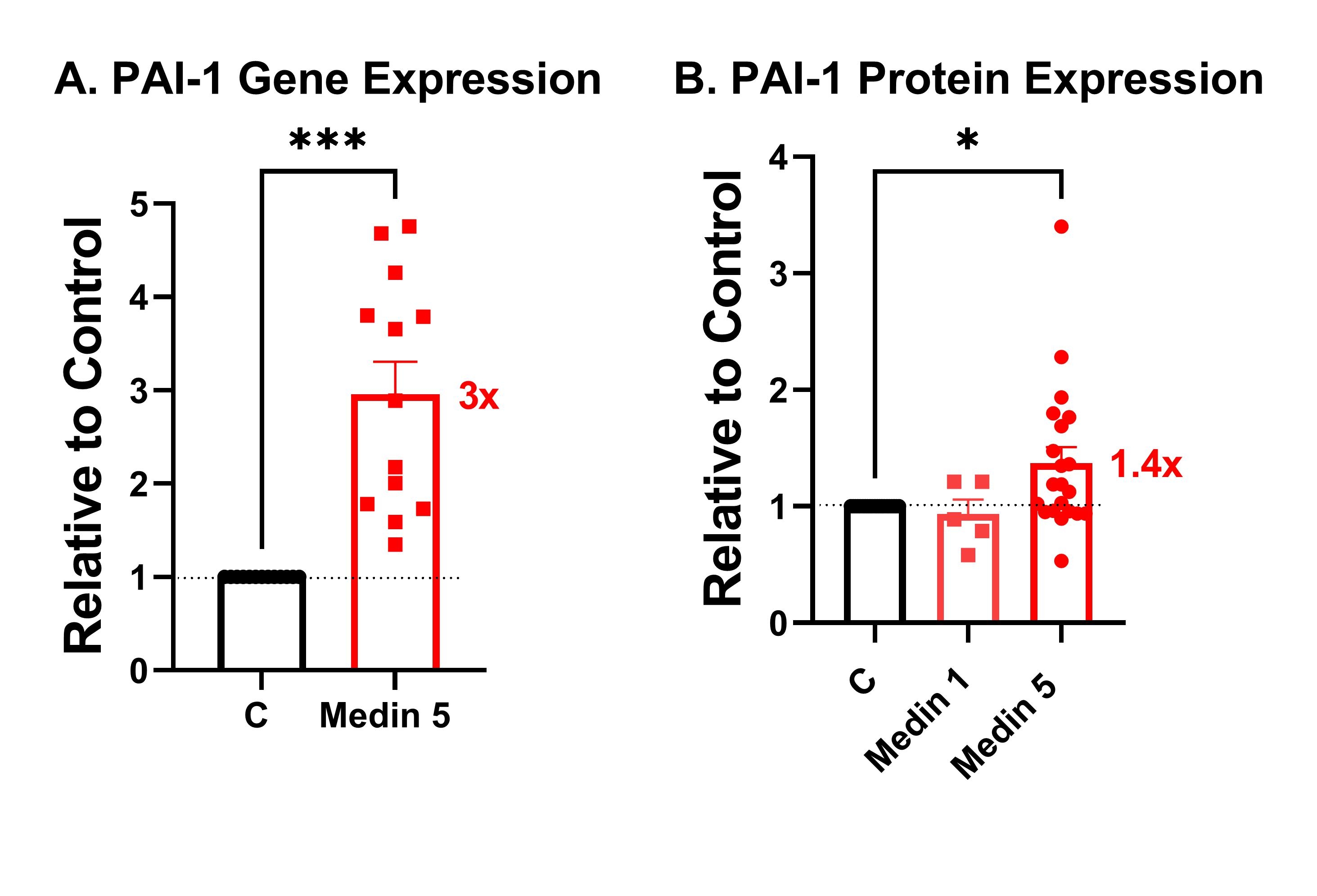
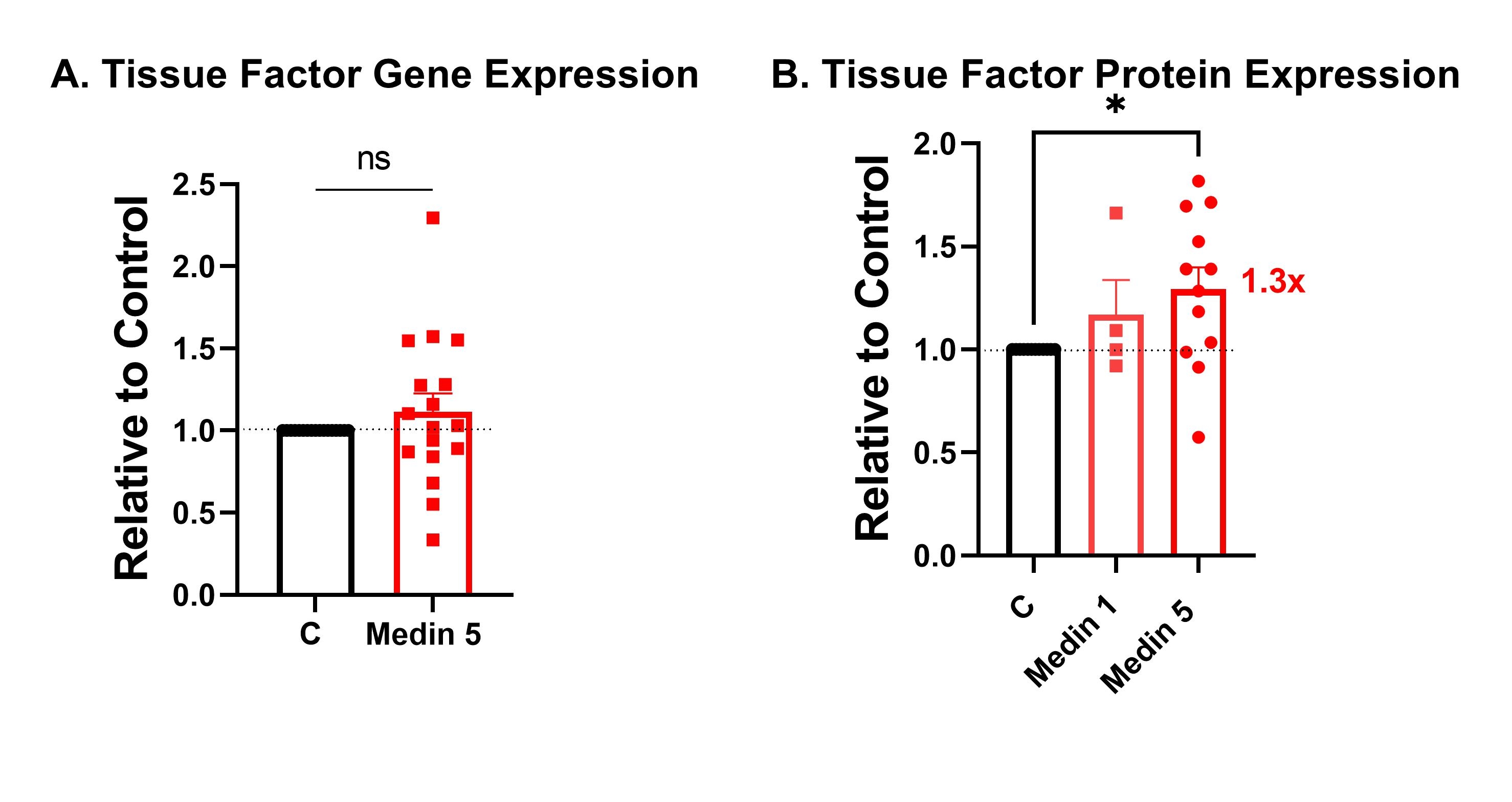
Results: Physiologic dose of medin (5 uM) given to HBMVECs resulted in reduced gene and protein expression of thrombomodulin (Fig. 1), increased gene and protein expression of PAI-1 (Fig. 2), and modest increased protein, but not gene expression of tissue factor (Fig. 3). Medin exposure also reduced HBMVEC ability to convert protein C to activated protein C in the presence of thrombin.
Conclusions: Medin reduced HBMVEC production of anticoagulant protein thrombomodulin and increased protein expression of procoagulant proteins PAI-1 and tissue factor. Medin is a potential novel mediator of aging-associated hypercoagulability and could be a promising target in thrombotic diseases such as stroke.
Aim: To determine the effect of medin on human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVECs) expression and function of thrombomodulin (a transmembrane glycoprotein that is a major anticoagulant through its interaction with thrombin leading to activation of protein C and S which in turn degrades factors Va and VIIIa) and HBMVEC expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and tissue factor (major procoagulant proteins).
Methods: Primary HBMVECs (passages 6-8) were exposed for 20 hours to physiologic doses of recombinant human medin (1 or 5 uM) and gene and protein expression of thrombomodulin, PAI-1 and tissue factor were measured using rtPCR or Western blot, respectively. In separate experiments, assessment of thrombomodulin function was determined by exposing HBMVECs for 20 hours to medin, after which human protein C (0.2 uM) and α-thrombin (10 nM) were added for 1 hour and amount of activated protein C in media was measured using ELISA.
Results: Physiologic dose of medin (5 uM) given to HBMVECs resulted in reduced gene and protein expression of thrombomodulin (Fig. 1), increased gene and protein expression of PAI-1 (Fig. 2), and modest increased protein, but not gene expression of tissue factor (Fig. 3). Medin exposure also reduced HBMVEC ability to convert protein C to activated protein C in the presence of thrombin.
Conclusions: Medin reduced HBMVEC production of anticoagulant protein thrombomodulin and increased protein expression of procoagulant proteins PAI-1 and tissue factor. Medin is a potential novel mediator of aging-associated hypercoagulability and could be a promising target in thrombotic diseases such as stroke.
More abstracts on this topic:
Administration of the Recombinant Activated Protein C Rescues the Cardiac Vulnerability to Ischemic Insults in Aging through Modulating Inflammatory Response during Ischemia and Reperfusion
Slotabec Lily, Rouhi Nadiyeh, Seale Blaise, Wang Hao, Filho Fernanda, Adenawoola Michael, Li Ji
Advanced Age Increases Susceptibility to Ischemic Myopathy after Murine Hindlimb IschemiaKulkarni Deepali, Massie Pierce, Justus Matthew, Mazloumibakhshayesh Milad, Coffman Brittany, Pace Carolyn, Clark Ross