Final ID: Su1038
Multi-Omic Profiling of Adiposity Distribution Patterns
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Distribution patterns for visceral (VAT), abdominal subcutaneous (ASAT), and gluteofemoral (GFAT) adipose tissue are strongly associated with cardiovascular disease. Circulating metabolites and proteins are dynamic indicators of biological processes and reflect metabolic health. It is not yet clear how these analytes are associated with adiposity distribution patterns.
Aims: To determine the multi-omic profiles of adiposity distribution and their associated metabolomic and proteomic measurements.
Methods: MRI-derived volumes of VAT, ASAT, and GFAT adjusted for BMI were available for 40,032 UK Biobank participants. Circulating metabolites and proteins were measured using the Nightingale Health NMR biomarker platform and Olink platform, respectively. We used linear regression models to assess the association between each analyte and VAT, ASAT, and GFAT. Models were adjusted for sex, age at MRI, MRI batch, and time between enrollment and MRI. Functional protein pathway enrichment was performed using the DAVID annotation tool.
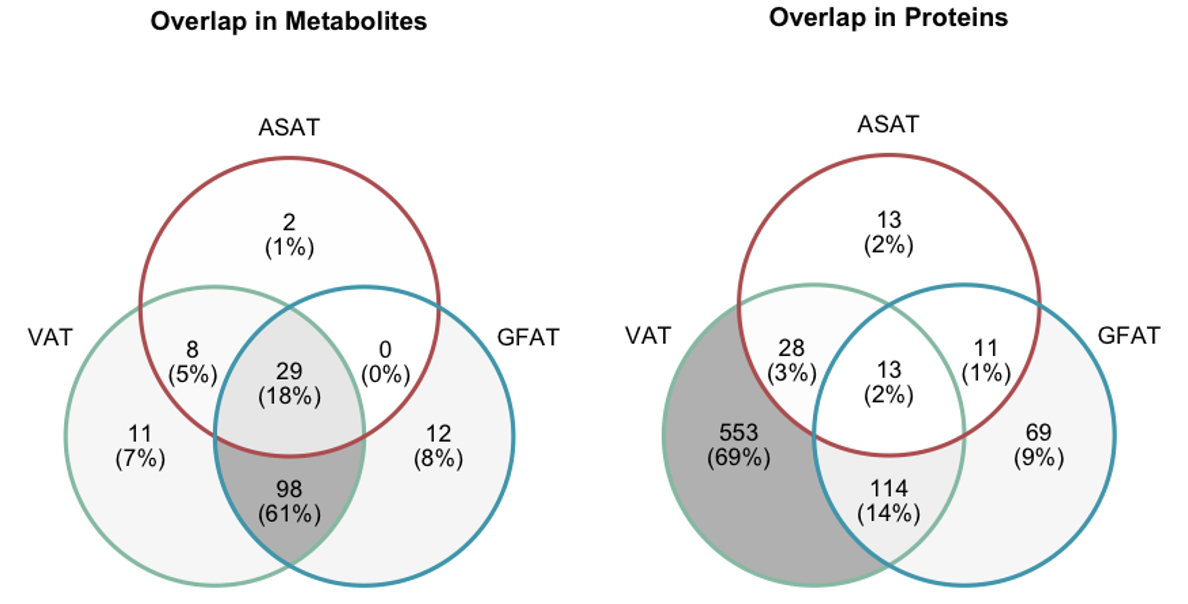
Results: Among 40,032 UK Biobank participants with adiposity volumes, 22,630 (56.5%) and 5023 (12.5%) had 168 metabolomic and 2910 proteomic measurements, respectively. In the metabolomic subset, the mean (SD) age was 55.7 (7.5) years, 10,992 (48.6%) were male, and all self-reported as white. In the proteomic subset, the mean (SD) age was 54.9 (7.8) years, 2417 (48.1%) were male, and all self-reported as white. Multi-variable linear regression revealed 39, 139, and 146 significant metabolite associations (P <1.7e-5) and 65, 207, and 708 significant protein associations (P <1.7e-5) for ASAT, GFAT, and VAT, respectively. We observed opposite directions of effect for 126 (99.2%) metabolites significantly associated with VAT and GFAT, except for pyruvate. Additionally, while proteins involved in cell adhesion were associated with all fat depots, inflammatory response proteins were only associated with VAT.
Conclusion: Among the fat depots, VAT had the most associations with circulating proteins and metabolites, while ASAT had the least. Assessment of associations with coronary artery disease may further delineate connections between fat deposition and cardiometabolic health.
Aims: To determine the multi-omic profiles of adiposity distribution and their associated metabolomic and proteomic measurements.
Methods: MRI-derived volumes of VAT, ASAT, and GFAT adjusted for BMI were available for 40,032 UK Biobank participants. Circulating metabolites and proteins were measured using the Nightingale Health NMR biomarker platform and Olink platform, respectively. We used linear regression models to assess the association between each analyte and VAT, ASAT, and GFAT. Models were adjusted for sex, age at MRI, MRI batch, and time between enrollment and MRI. Functional protein pathway enrichment was performed using the DAVID annotation tool.
Results: Among 40,032 UK Biobank participants with adiposity volumes, 22,630 (56.5%) and 5023 (12.5%) had 168 metabolomic and 2910 proteomic measurements, respectively. In the metabolomic subset, the mean (SD) age was 55.7 (7.5) years, 10,992 (48.6%) were male, and all self-reported as white. In the proteomic subset, the mean (SD) age was 54.9 (7.8) years, 2417 (48.1%) were male, and all self-reported as white. Multi-variable linear regression revealed 39, 139, and 146 significant metabolite associations (P <1.7e-5) and 65, 207, and 708 significant protein associations (P <1.7e-5) for ASAT, GFAT, and VAT, respectively. We observed opposite directions of effect for 126 (99.2%) metabolites significantly associated with VAT and GFAT, except for pyruvate. Additionally, while proteins involved in cell adhesion were associated with all fat depots, inflammatory response proteins were only associated with VAT.
Conclusion: Among the fat depots, VAT had the most associations with circulating proteins and metabolites, while ASAT had the least. Assessment of associations with coronary artery disease may further delineate connections between fat deposition and cardiometabolic health.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Body Composition and Incident Heart Failure and Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in postmenopausal women
Eaton Charles, Madani Mir Mad, Miller Connor, Odegaard Andrew, Lamonte Michael
Adiposomal microRNAs Mediate Vascular Dysfunction in Obesity-Associated Type 2 DiabetesMirza Imaduddin, Morsy Mohammed, Levitan Irena, Raj Usha, Mahmoud Abeer