Final ID: 4146430
Microglia Mediated Neuroinflammation: Understanding Mechanisms of Augmented Sympathetic Nerve Activity in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Excess sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) is thought to be a major mechanism for elevated cardiovascular risk in these patients. However, the mechanisms that drive excess SNA in patients with CKD are not well understood. A growing body of evidence suggests that CKD is associated with inflammation and immune dysfunction. However, the role of neuroinflammation in CKD has not been studied.
Hypothesis
We hypothesize that microglial activation and neuroinflammation underlies excess sympathetic activity in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Aim
Understand the extent to which microglia mediate neuroinflammation and contribute to excess SNA in CKD.
Methods
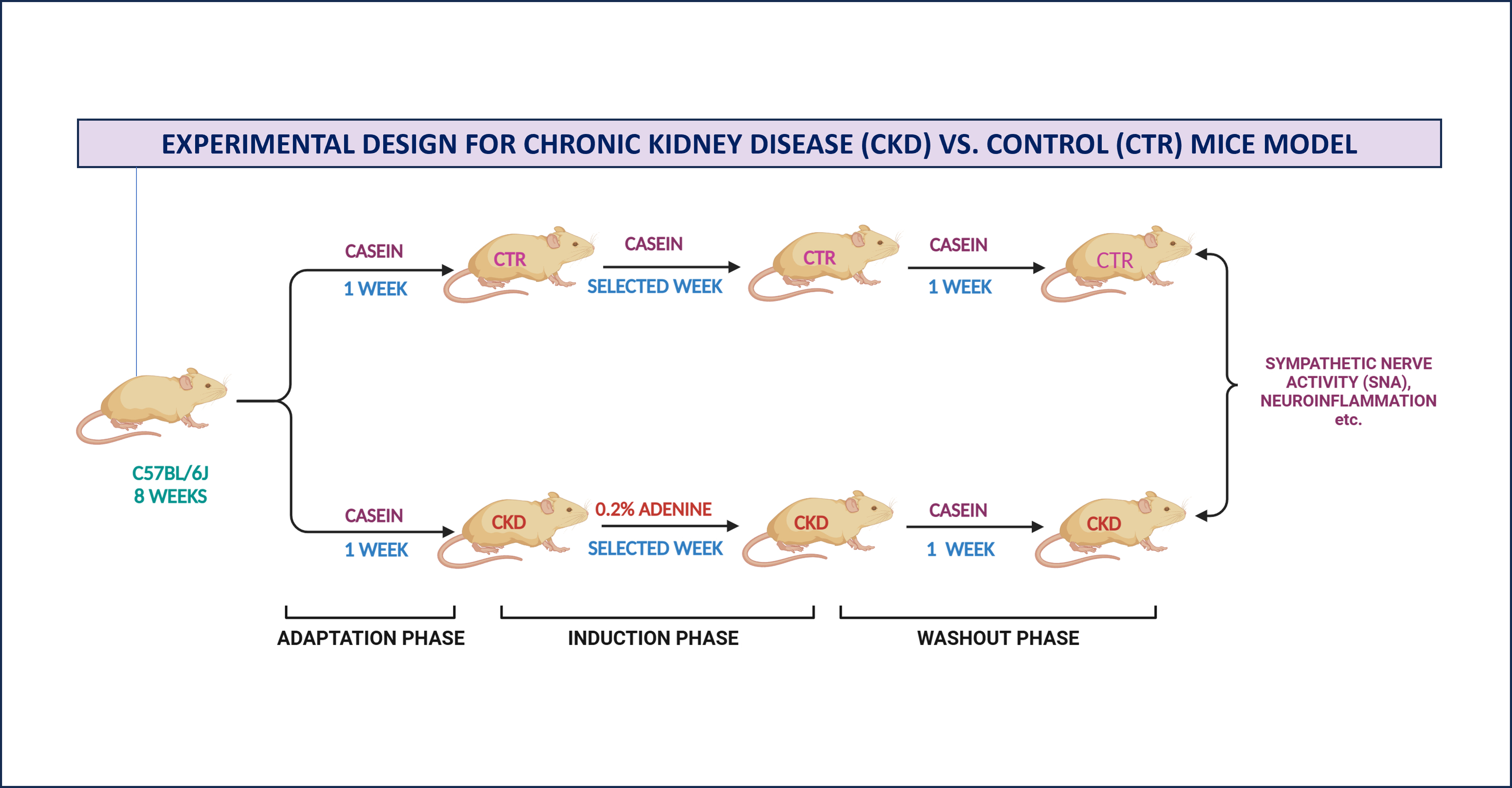
C57/BL6 mice (18-22 gm, 8 weeks old) were randomized to 0.2% adenine in casein (CKD) or continued on casein-only diet (Control) for 2, 4 or 6 weeks. SNA was assessed by heart rate variability, as determined by spectral analysis of the electrocardiogram (Low Frequency / High-Frequency HF/LF ratio) and catecholamine levels (ELISA). Neuroinflammation will be evaluated by profiling the cytokines/chemokines in serum and CSF using Luminex cytokine array. Microglia phenotyping was performed by flow cytometry. Renal function was quantified by serum creatinine and cystatin C levels.
Results
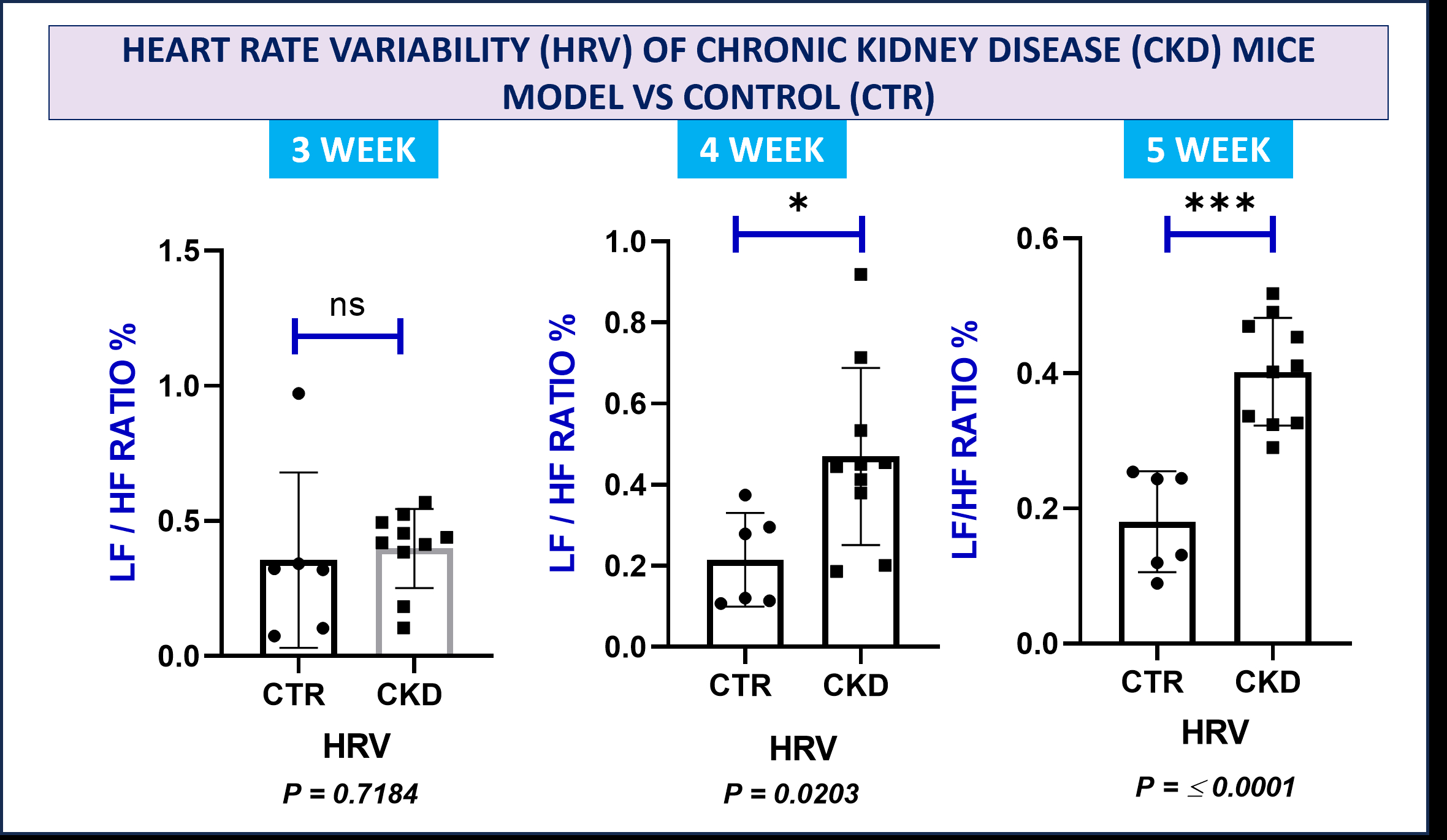
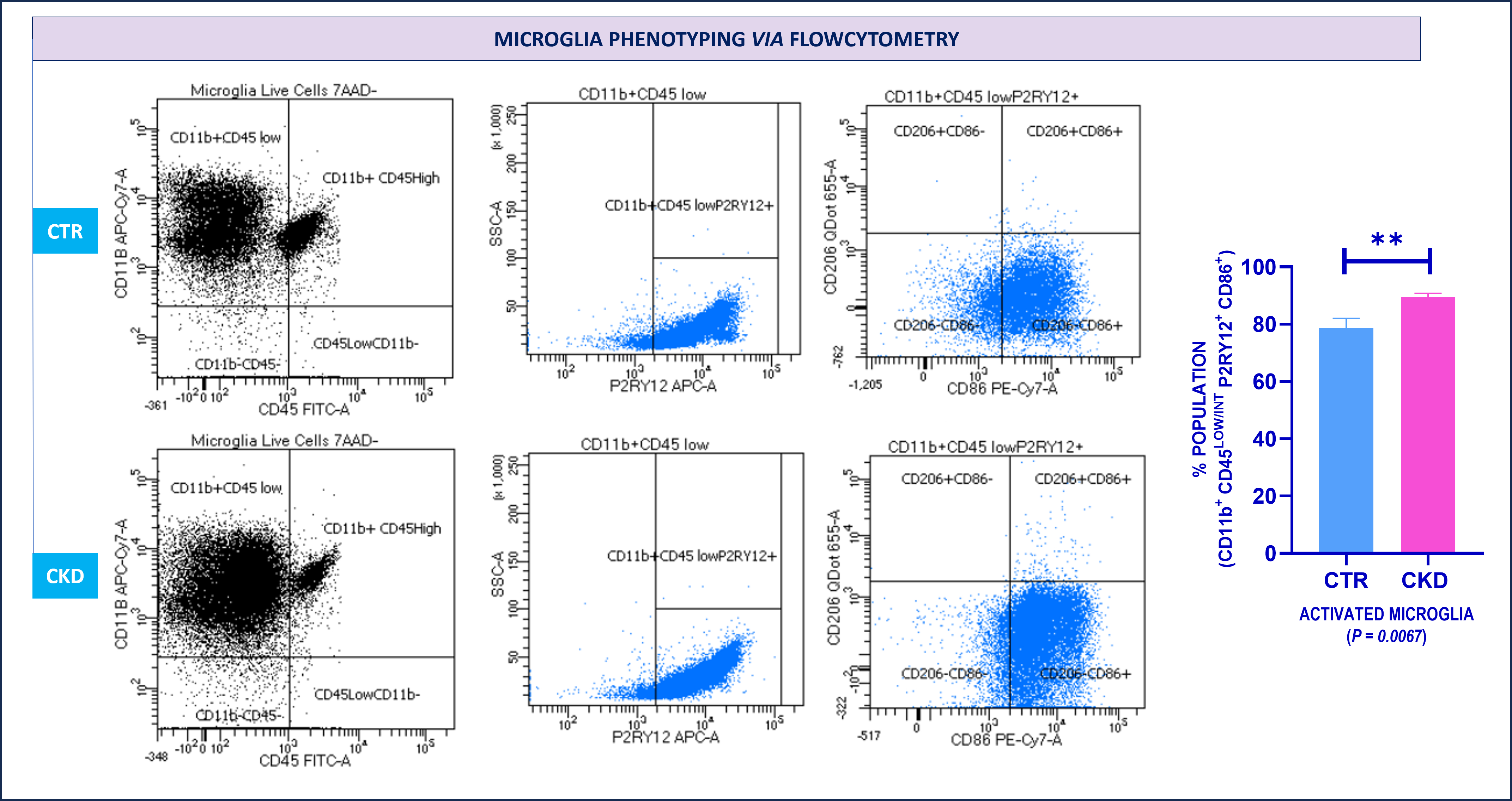
The adenine model resulted in significant CKD by 2 weeks. SNA was increased by week 4 as evidenced by an increased LF/HF ratio [0.46 ± 0.1 in CKD vs. 0.21 ± 0.05 Controls] P = 0.02. There were no differences in SNA at 2 weeks. However, changes in microglia were evident as early as 2 weeks, with CKD mice showing significantly increased numbers of activated microglia (CD11b+ CD45low/int P2RY12+ CD86+) (P = 0.007). The areas of the brain that control sympathetic output showed excess microglia.
Conclusion(s)
Our data suggests that CKD is associated with neuroinflammation in sympathetic areas of the brain. Microglia activation precedes increases in SNA. Experiments to examine the effect of microglia depletion on SNA are ongoing. Together, these experiments will provide comprehensive insight into how microglial function and neuroinflammation synergize to increase SNA in CKD.
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Excess sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) is thought to be a major mechanism for elevated cardiovascular risk in these patients. However, the mechanisms that drive excess SNA in patients with CKD are not well understood. A growing body of evidence suggests that CKD is associated with inflammation and immune dysfunction. However, the role of neuroinflammation in CKD has not been studied.
Hypothesis
We hypothesize that microglial activation and neuroinflammation underlies excess sympathetic activity in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Aim
Understand the extent to which microglia mediate neuroinflammation and contribute to excess SNA in CKD.
Methods
C57/BL6 mice (18-22 gm, 8 weeks old) were randomized to 0.2% adenine in casein (CKD) or continued on casein-only diet (Control) for 2, 4 or 6 weeks. SNA was assessed by heart rate variability, as determined by spectral analysis of the electrocardiogram (Low Frequency / High-Frequency HF/LF ratio) and catecholamine levels (ELISA). Neuroinflammation will be evaluated by profiling the cytokines/chemokines in serum and CSF using Luminex cytokine array. Microglia phenotyping was performed by flow cytometry. Renal function was quantified by serum creatinine and cystatin C levels.
Results
The adenine model resulted in significant CKD by 2 weeks. SNA was increased by week 4 as evidenced by an increased LF/HF ratio [0.46 ± 0.1 in CKD vs. 0.21 ± 0.05 Controls] P = 0.02. There were no differences in SNA at 2 weeks. However, changes in microglia were evident as early as 2 weeks, with CKD mice showing significantly increased numbers of activated microglia (CD11b+ CD45low/int P2RY12+ CD86+) (P = 0.007). The areas of the brain that control sympathetic output showed excess microglia.
Conclusion(s)
Our data suggests that CKD is associated with neuroinflammation in sympathetic areas of the brain. Microglia activation precedes increases in SNA. Experiments to examine the effect of microglia depletion on SNA are ongoing. Together, these experiments will provide comprehensive insight into how microglial function and neuroinflammation synergize to increase SNA in CKD.
More abstracts on this topic:
Anticoagulation For Patients On Hemodialysis And Atrial Fibrillation
Ebrahimi Ramin, Alvarez Carlos, Dennis Paul
Acute Effects of Isometric Handgrip Exercise on Cardiac Baroreflex Sensitivity in Chronic Kidney DiseaseSabino-carvalho Jeann, Park Jeanie