Final ID: Su1127
Causal Relationship of Obesity with Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetic Nephropathy: A Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): BACKGROUND
Despite there being a significant association between obesity and chronic kidney disease (CKD) there is a paucity of evidence on the causal role of obesity in the development of CKD. Hence, this meta-analysis aims to elucidate a causal relationship between body mass index (BMI) and the risks of CKD and diabetic nephropathy (DN) using Mendelian randomization studies.
METHOD
We searched PubMed/Medline and Google Scholar for the Mendelian Randomization studies evaluating the association of BMI with the occurrence of CKD/renal failure and DN until May 2024. The inverse-variance weighted method was employed for the meta-analysis. The random effects models and I2 statistics were used for pooled odds ratio (OR) and heterogeneity assessment. Leave-one-out sensitivity analyses were also performed to assess the robustness of the findings
RESULT
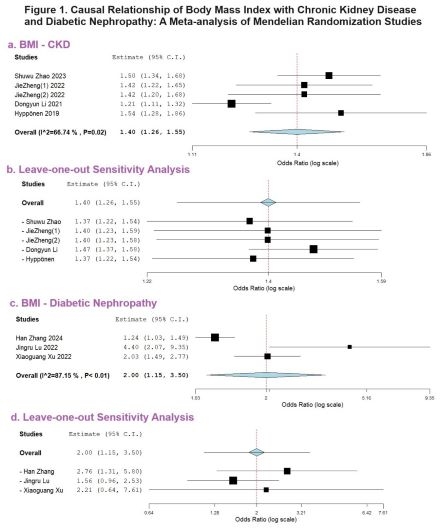
Our search rendered a total of 81 studies which were screened thoroughly. From those, 8 studies, all with a unique instrumental variable database were selected. Out of these 6 studies consisted of cases from European Ancestry and remaining 2 from east asian ancestry. According to our meta-analysis, increased genetically predicted BMI was significantly associated with increased risk of CKD (OR 1.40, 95 % CI: 1.26-1.55, I2= 66.74 %, P < 0.02) and DN (OR 2.00, 95 % CI: 1.15-3.50, I2= 87.15 %, P<0.01). In addition, leave-one-out sensitivity analysis showed that the effect size did not change substantially by removal of any particular study in MR studies.
CONCLUSION
The meta-analysis provides robust evidence supporting a causal relationship between higher BMI and increased risks of CKD and DN. These findings underscore the importance of managing BMI as a modifiable risk factor to mitigate the risk of developing CKD and DN. Further studies should explore the underlying mechanisms and evaluate the impact of BMI management on the progression of CKD and DN.
Despite there being a significant association between obesity and chronic kidney disease (CKD) there is a paucity of evidence on the causal role of obesity in the development of CKD. Hence, this meta-analysis aims to elucidate a causal relationship between body mass index (BMI) and the risks of CKD and diabetic nephropathy (DN) using Mendelian randomization studies.
METHOD
We searched PubMed/Medline and Google Scholar for the Mendelian Randomization studies evaluating the association of BMI with the occurrence of CKD/renal failure and DN until May 2024. The inverse-variance weighted method was employed for the meta-analysis. The random effects models and I2 statistics were used for pooled odds ratio (OR) and heterogeneity assessment. Leave-one-out sensitivity analyses were also performed to assess the robustness of the findings
RESULT
Our search rendered a total of 81 studies which were screened thoroughly. From those, 8 studies, all with a unique instrumental variable database were selected. Out of these 6 studies consisted of cases from European Ancestry and remaining 2 from east asian ancestry. According to our meta-analysis, increased genetically predicted BMI was significantly associated with increased risk of CKD (OR 1.40, 95 % CI: 1.26-1.55, I2= 66.74 %, P < 0.02) and DN (OR 2.00, 95 % CI: 1.15-3.50, I2= 87.15 %, P<0.01). In addition, leave-one-out sensitivity analysis showed that the effect size did not change substantially by removal of any particular study in MR studies.
CONCLUSION
The meta-analysis provides robust evidence supporting a causal relationship between higher BMI and increased risks of CKD and DN. These findings underscore the importance of managing BMI as a modifiable risk factor to mitigate the risk of developing CKD and DN. Further studies should explore the underlying mechanisms and evaluate the impact of BMI management on the progression of CKD and DN.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acute and Chronic Phosphorylation of CaMKII on Coronary Microvascular/Endothelial Function
Iddrisu Hanisah, Xing Hang, Shi Guangbin, Liu Yuhong, Feng Jun
An Epigenetic Drug, GSK126 Mitigates Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition Attenuating Atherosclerosis in DiabetesAziz Misbah, Jandeleitdahm Karin, Khan Abdul Waheed