Final ID: Mo4175
Sex Differences in Clinical Profile and Outcomes of Infective Endocarditis: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Infective endocarditis (IE) presents significant morbidity and mortality, with potential sex differences in clinical profile and outcomes. This meta-analysis aims to compare the clinical profile and outcomes of IE between males and females.
Hypothesis: The clinical profile and outcomes of IE differ between males and females.
Methods: We conducted a meta-analysis comparing the clinical profile and outcomes of IE in males versus females. Twelve studies were retrieved from PubMed, EMBASE, SCOPUS, and Cochrane databases up to January 1, 2024, with 9 studies reporting on patients admitted for IE and 3 studies reporting on patients who underwent surgery for IE.
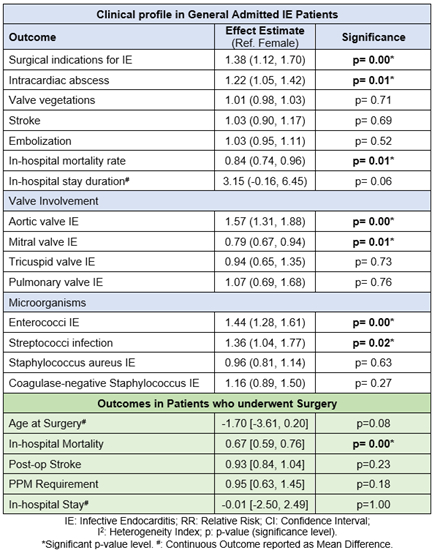
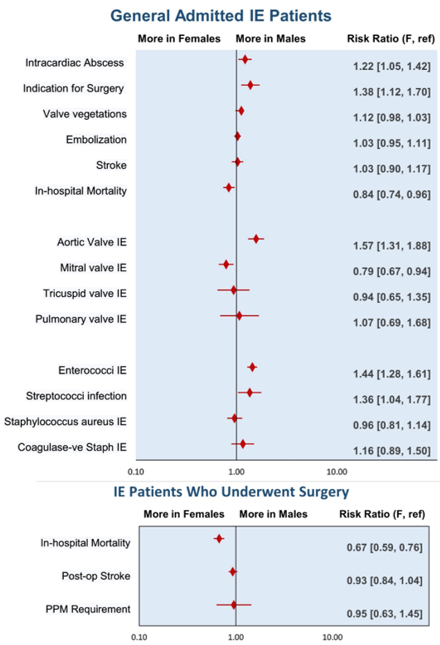
Results: Our meta-analysis revealed notable sex differences in the incidence and complications of IE. Males exhibited a higher incidence of aortic valve IE (RR 1.57; 95% CI [1.31, 1.88]), surgical indications for IE (RR 1.38; [1.12, 1.70]), Streptococci infection (RR 1.36; [1.04, 1.77]), intracardiac abscess (RR 1.22; [1.05, 1.42]), and Enterococci IE (RR 1.44; [1.28, 1.61]). In contrast, females had a higher incidence of mitral valve IE (RR 0.79; [0.67, 0.94]) and a higher in-hospital mortality rate (RR 0.84; [0.74, 0.96]). There were no major sex differences in the occurrence of valve vegetation, tricuspid valve IE, embolization, or Staphylococcus IE. Male patients had a longer in-hospital stay, although this was only marginally significant (RR 3.15; [-0.16, 6.45]; p = 0.06). Among patients who received surgery for IE, male patients had significantly lower mortality rates (RR: 0.67; [0.59, 0.76]; p<0.01).
Conclusions: Compared to females, males exhibit higher rates of aortic valve IE, IE-related surgical indications, intracardiac abscesses, streptococci IE, and enterococci IE. In contrast, females have higher rates of mitral valve IE and in-hospital mortality. Conversely, the incidence of stroke, embolization, and in-hospital stay duration is comparable between both sexes.
Hypothesis: The clinical profile and outcomes of IE differ between males and females.
Methods: We conducted a meta-analysis comparing the clinical profile and outcomes of IE in males versus females. Twelve studies were retrieved from PubMed, EMBASE, SCOPUS, and Cochrane databases up to January 1, 2024, with 9 studies reporting on patients admitted for IE and 3 studies reporting on patients who underwent surgery for IE.
Results: Our meta-analysis revealed notable sex differences in the incidence and complications of IE. Males exhibited a higher incidence of aortic valve IE (RR 1.57; 95% CI [1.31, 1.88]), surgical indications for IE (RR 1.38; [1.12, 1.70]), Streptococci infection (RR 1.36; [1.04, 1.77]), intracardiac abscess (RR 1.22; [1.05, 1.42]), and Enterococci IE (RR 1.44; [1.28, 1.61]). In contrast, females had a higher incidence of mitral valve IE (RR 0.79; [0.67, 0.94]) and a higher in-hospital mortality rate (RR 0.84; [0.74, 0.96]). There were no major sex differences in the occurrence of valve vegetation, tricuspid valve IE, embolization, or Staphylococcus IE. Male patients had a longer in-hospital stay, although this was only marginally significant (RR 3.15; [-0.16, 6.45]; p = 0.06). Among patients who received surgery for IE, male patients had significantly lower mortality rates (RR: 0.67; [0.59, 0.76]; p<0.01).
Conclusions: Compared to females, males exhibit higher rates of aortic valve IE, IE-related surgical indications, intracardiac abscesses, streptococci IE, and enterococci IE. In contrast, females have higher rates of mitral valve IE and in-hospital mortality. Conversely, the incidence of stroke, embolization, and in-hospital stay duration is comparable between both sexes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A sex-specific CD4+ T cell response limits Coxsackievirus B pathogenesis in mice.
Robinson Christopher, Pattnaik Aryamav, Dhalech Adeeba, Condotta Stephanie, Corn Caleb, Richer Martin, Snell Laura
Demographic and socio-economic differences in the co-occurrence of Obesity and Chronic Kidney Disease – A Population-Based StudyArora Komal, Shah Anand, Goyal Ritik, Rana Chirag