Final ID: MDP1626
Enhanced Cardiovascular Risk Prediction of Calcium Scoring Computed Tomography Scans by Incorporating Pericardial Fat Characteristics: A Machine Learning Gradient Boost Analysis of Data Derived from a Deep Learning Segmentation Model of a Community-Based Cohort
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Calcium scoring computed tomography (CAC) is a widely available and inexpensive modality of screening for atherosclerosis. This study aims to improve the predictive value of CAC by incorporating pericardial fat characteristics in a CatBoost model.
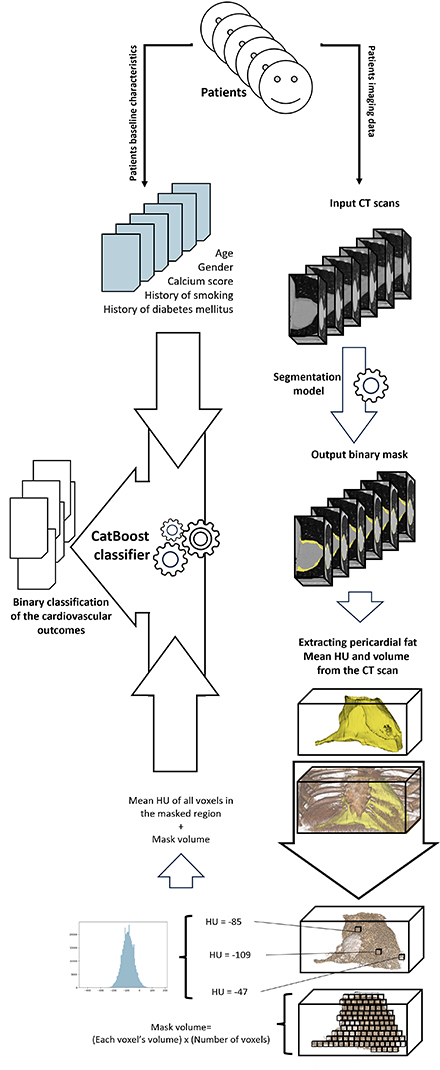
Methods: A sample of 7,000 non-contrast clinically indicated CAC scans were randomly selected from a cohort of consecutive Olmsted County MN residents. Known history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or impaired images were excluded. A pericardial fat segmentation model, trained on 191 images of the same dataset with a dice similarity score of 94%, was applied to 6,194 CT scans; Volume and mean Hounsfield unit (mHU) of the output masks were added to age at imaging, radiologist-measured calcium score, male gender, diabetes, and smoking (Figure 1). A 70,20 and 10% split was used to produce the training, validation and test set, respectively. Features were inputted to CatBoost classifier, as the best model tested, to predict four outcomes: acute coronary syndrome (ACS), heart failure (HF), ischemic stroke, and all-cause mortality. Model was evaluated by area under the ROC curve (AUC) on the unseen test set.
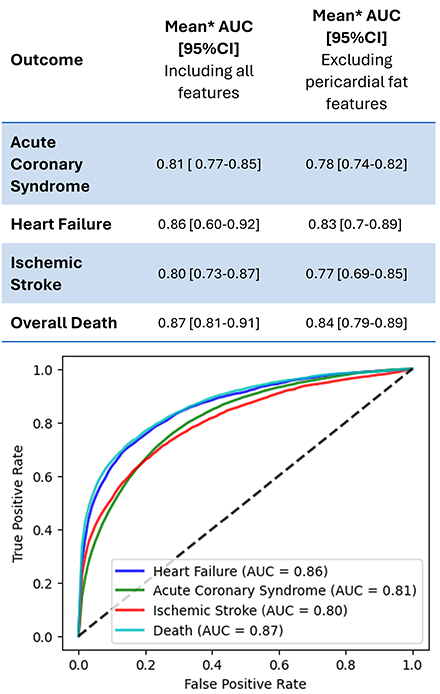
Results: Mean age was 55.2 (8.8), 55.2 (8.8) and 54.8 (8.5) years in the training, validation and test sets, respectively, and 65%, 67% and 66% of the populations were male. The mean AUC, obtained through bootstrapping with 100 iterations, was 0.81 [0.77-0.85], 0.86 [0.60-0.92], 0.80 [0.73-0.87] and 0.87 [0.81-0.91] for HF, ACS, stroke and death, respectively; The same analysis excluding pericardial fat measurements showed a 3% reduction in the AUC for all of the investigated outcomes (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Our study presents a robust risk prediction model for ACS, HF, stroke, and mortality based on CAC scans. The improved performance of the model by incorporating pericardial fat characteristics, highlights the potentials of deep learning in timely inexpensive risk prediction in large populations.
Methods: A sample of 7,000 non-contrast clinically indicated CAC scans were randomly selected from a cohort of consecutive Olmsted County MN residents. Known history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or impaired images were excluded. A pericardial fat segmentation model, trained on 191 images of the same dataset with a dice similarity score of 94%, was applied to 6,194 CT scans; Volume and mean Hounsfield unit (mHU) of the output masks were added to age at imaging, radiologist-measured calcium score, male gender, diabetes, and smoking (Figure 1). A 70,20 and 10% split was used to produce the training, validation and test set, respectively. Features were inputted to CatBoost classifier, as the best model tested, to predict four outcomes: acute coronary syndrome (ACS), heart failure (HF), ischemic stroke, and all-cause mortality. Model was evaluated by area under the ROC curve (AUC) on the unseen test set.
Results: Mean age was 55.2 (8.8), 55.2 (8.8) and 54.8 (8.5) years in the training, validation and test sets, respectively, and 65%, 67% and 66% of the populations were male. The mean AUC, obtained through bootstrapping with 100 iterations, was 0.81 [0.77-0.85], 0.86 [0.60-0.92], 0.80 [0.73-0.87] and 0.87 [0.81-0.91] for HF, ACS, stroke and death, respectively; The same analysis excluding pericardial fat measurements showed a 3% reduction in the AUC for all of the investigated outcomes (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Our study presents a robust risk prediction model for ACS, HF, stroke, and mortality based on CAC scans. The improved performance of the model by incorporating pericardial fat characteristics, highlights the potentials of deep learning in timely inexpensive risk prediction in large populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel EMR-Based Algorithm with the Virtual Echocardiography Screening Tool (VEST) to Screen Patients for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Narowska Gabriela, Anand Suneesh, Gangireddy Chethan, Enevoldsen John, Keane Martin, Edmundowicz Daniel, Forfia Paul, Vaidya Anjali
3D Statistical Shape Analysis Predicts Type A Aortic Dissection Better Than Aortic DiametersMarway Prabhvir, Campello Jorge Carlos Alberto, Wagner Catherine, Baker Timothy, Burris Nicholas