Final ID: MDP524
DOACs versus Aspirin for Secondary Prevention of Stroke after ESUS: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS) is a nonlacunar ischemic stroke with no clear cause, having a 4%-5% annual recurrence rate. The potential benefits of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) relative to aspirin in patients with ESUS remain unclear.
Objective: We aimed to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the efficacy of the DOACs in secondary prevention for patients with ESUS compared with aspirin.
Methods: MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane, and ClinicalTrias.gov were searched for RCTs comparing DOACs versus aspirin for secondary stroke prevention after ESUS. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review (PRISMA) and Cochrane guidelines. Statistical analysis was performed using R software 4.3.2. A random-effects model was employed to measure mean differences and hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
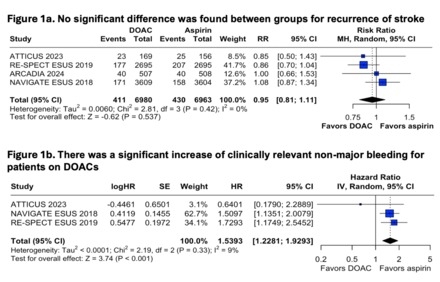
Results: We included 4 RCTs comprising 13,970 patients. The median age was 67 years (IQR 65.5-68.2), 61% were male, 76% had hypertension, and 51% had diabetes. DOACs were administered to 50% of the participants. No significant difference was found between groups for stroke recurrence [RR 0.95 (95% CI 0.8-1.11) p=0.52; I2=0%]. Death from any cause [HR 1.11 (95% CI 0.87-1.42) p=0.38; I2=0%], cardiovascular death [HR 1.08 (95% CI 0.61-1.94) p=0.77; I2=18%] and myocardial infarction [HR 0.92 (95% CI 0.54-1.54) p=0.76; I2=16%] were also similar between groups. However, there was a significant increase in clinically relevant non-major bleeding for patients treated with DOACs [HR 1.53 (95% CI 1.22-1.92) p<0.001; I2=9%].
Conclusion: In patients with ESUS, DOACs were not superior to aspirin for the secondary prevention of stroke. However, there was a significant increase in clinically relevant non-major bleeding among patients treated with DOACs. These findings suggest that aspirin remains a viable option for secondary prevention in ESUS patients.
Objective: We aimed to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the efficacy of the DOACs in secondary prevention for patients with ESUS compared with aspirin.
Methods: MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane, and ClinicalTrias.gov were searched for RCTs comparing DOACs versus aspirin for secondary stroke prevention after ESUS. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review (PRISMA) and Cochrane guidelines. Statistical analysis was performed using R software 4.3.2. A random-effects model was employed to measure mean differences and hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results: We included 4 RCTs comprising 13,970 patients. The median age was 67 years (IQR 65.5-68.2), 61% were male, 76% had hypertension, and 51% had diabetes. DOACs were administered to 50% of the participants. No significant difference was found between groups for stroke recurrence [RR 0.95 (95% CI 0.8-1.11) p=0.52; I2=0%]. Death from any cause [HR 1.11 (95% CI 0.87-1.42) p=0.38; I2=0%], cardiovascular death [HR 1.08 (95% CI 0.61-1.94) p=0.77; I2=18%] and myocardial infarction [HR 0.92 (95% CI 0.54-1.54) p=0.76; I2=16%] were also similar between groups. However, there was a significant increase in clinically relevant non-major bleeding for patients treated with DOACs [HR 1.53 (95% CI 1.22-1.92) p<0.001; I2=9%].
Conclusion: In patients with ESUS, DOACs were not superior to aspirin for the secondary prevention of stroke. However, there was a significant increase in clinically relevant non-major bleeding among patients treated with DOACs. These findings suggest that aspirin remains a viable option for secondary prevention in ESUS patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
Antithrombotic Strategies for Stroke Prevention in Elderly Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis of Contemporary Evidence
Farooq Talha, Pandit Maleeha, Ali Mohammad Eisa, Ahsan Muhammad, Khan Abdul Moiz, Qasim Muhammad, Qayyum Mahhum, Akram Anusha, Kamel Mohammed, Naseem Ali
Among Older Adults With Atrial Fibrillation, First Anticoagulant Prescription Is Not Associated with Reduced Hazard of Ischemic Stroke but Is Associated with Increased Hazard of Major Bleeding: A Nationwide StudyLusk Jay, Li Fan, Mac Grory Brian, Nalawade Vinit, Wilson Lauren, Yarnell Stephanie, Song Ailin, Schrag Matthew, Poli Sven, Hammill Bradley, Xian Ying