Final ID: Su1079
Torsemide versus furosemide for hospitalization in patients with heart failure: a meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background: Furosemide is the most commonly used loop diuretic in patients with heart failure (HF). However, recent studies suggest that torsemide might be a better option, potentially reducing hospitalization rates. This meta-analysis aimed to compare the effectiveness of torsemide versus furosemide in patients with HF.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing torsemide versus furosemide in HF patients. We pooled risk ratios (RR) for binary outcomes, and mean differences (MD) for continuous outcomes with 95% confidence intervals (CI) with a random-effects model. We performed a trial sequential analysis (TSA) to assess the random risk of HF-related hospitalizations. We used R version 4.3.2 and TSA version 0.9.5.10 for statistical analyses.
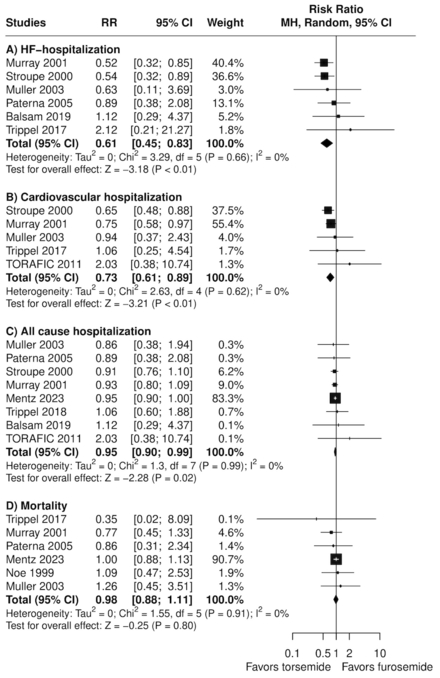
Results: Our meta-analysis included 9 RCTs comprising 4077 patients, of whom 2014 (49.4%) were randomized to torsemide. The mean age was 65.9 years old. Torsemide significant reduced the HF-related hospitalizations (RR 0.61; 95% CI: 0.45 to 0.83; p<0.05; Figure A), cardiovascular hospitalization (RR 0.73; 95% CI: 0.61 to 0.89; p<0.05; Figure B), and all-cause hospitalization (RR 0.95; 95% CI: 0.90 to 0.99; p<0.05; Figure C). However, there were no significant differences in all-cause mortality (RR 0.98; 95% CI: 0.88 to 1.11; Figure D) between groups. Additionally, for the primary endpoint, TSA suggested a low risk of type 1 error; therefore, this result may be conclusive (Figure E).
Conclusion: In patients with heart failure, torsemide significantly reduced the incidence of hospitalizations. However, it appears not to have significant benefits in mortality rates.
Background: Furosemide is the most commonly used loop diuretic in patients with heart failure (HF). However, recent studies suggest that torsemide might be a better option, potentially reducing hospitalization rates. This meta-analysis aimed to compare the effectiveness of torsemide versus furosemide in patients with HF.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing torsemide versus furosemide in HF patients. We pooled risk ratios (RR) for binary outcomes, and mean differences (MD) for continuous outcomes with 95% confidence intervals (CI) with a random-effects model. We performed a trial sequential analysis (TSA) to assess the random risk of HF-related hospitalizations. We used R version 4.3.2 and TSA version 0.9.5.10 for statistical analyses.
Results: Our meta-analysis included 9 RCTs comprising 4077 patients, of whom 2014 (49.4%) were randomized to torsemide. The mean age was 65.9 years old. Torsemide significant reduced the HF-related hospitalizations (RR 0.61; 95% CI: 0.45 to 0.83; p<0.05; Figure A), cardiovascular hospitalization (RR 0.73; 95% CI: 0.61 to 0.89; p<0.05; Figure B), and all-cause hospitalization (RR 0.95; 95% CI: 0.90 to 0.99; p<0.05; Figure C). However, there were no significant differences in all-cause mortality (RR 0.98; 95% CI: 0.88 to 1.11; Figure D) between groups. Additionally, for the primary endpoint, TSA suggested a low risk of type 1 error; therefore, this result may be conclusive (Figure E).
Conclusion: In patients with heart failure, torsemide significantly reduced the incidence of hospitalizations. However, it appears not to have significant benefits in mortality rates.
More abstracts on this topic:
Finerenone Reduces Loop Diuretic Requirement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and CKD: Participant-Level Pooled Analysis of FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD
Chatur Safia, Bakris George, Brinker Meike, Scalise Andrea, Schloemer Patrick, Rohwedder Katja, Solomon Scott, Filippatos Gerasimos, Vaduganathan Muthiah, Claggett Brian, Neuen Brendon, Pitt Bertram, Anker Stefan, Rossing Peter, Joseph Amer, Ruilope Luis
β1 Adrenergic Receptor Autoantibodies Promote Heart Failure Though Activation of Prostaglandin E2 Receptor EP1/Phosphodiesterase 4B PathwayCao Ning, Qiu Hui, Li Hongwei