Final ID: Su1125
Association of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio With Cardiovascular Mortality and All-cause Mortality in Patients Receiving Chronic Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been proposed as a potential prognostic marker for mortality outcomes in various conditions, yet its association with chronic hemodialysis (HD) remains underexplored. We aim to study its utility by conducting a meta-analysis of this specific population.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive systematic search from PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus to identify studies showing the association between NLR and mortality outcomes in patients with chronic HD. Random-effects model with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were employed to pool adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) and odds ratios (OR), I2 statistics for evaluating heterogeneity for all-cause mortality (ACM) and cardiovascular mortality (CVM) outcomes. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis and meta-regression analyses assessed changes in overall effects and identified confounders, respectively. The Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) tool was used to assess the quality of the studies.
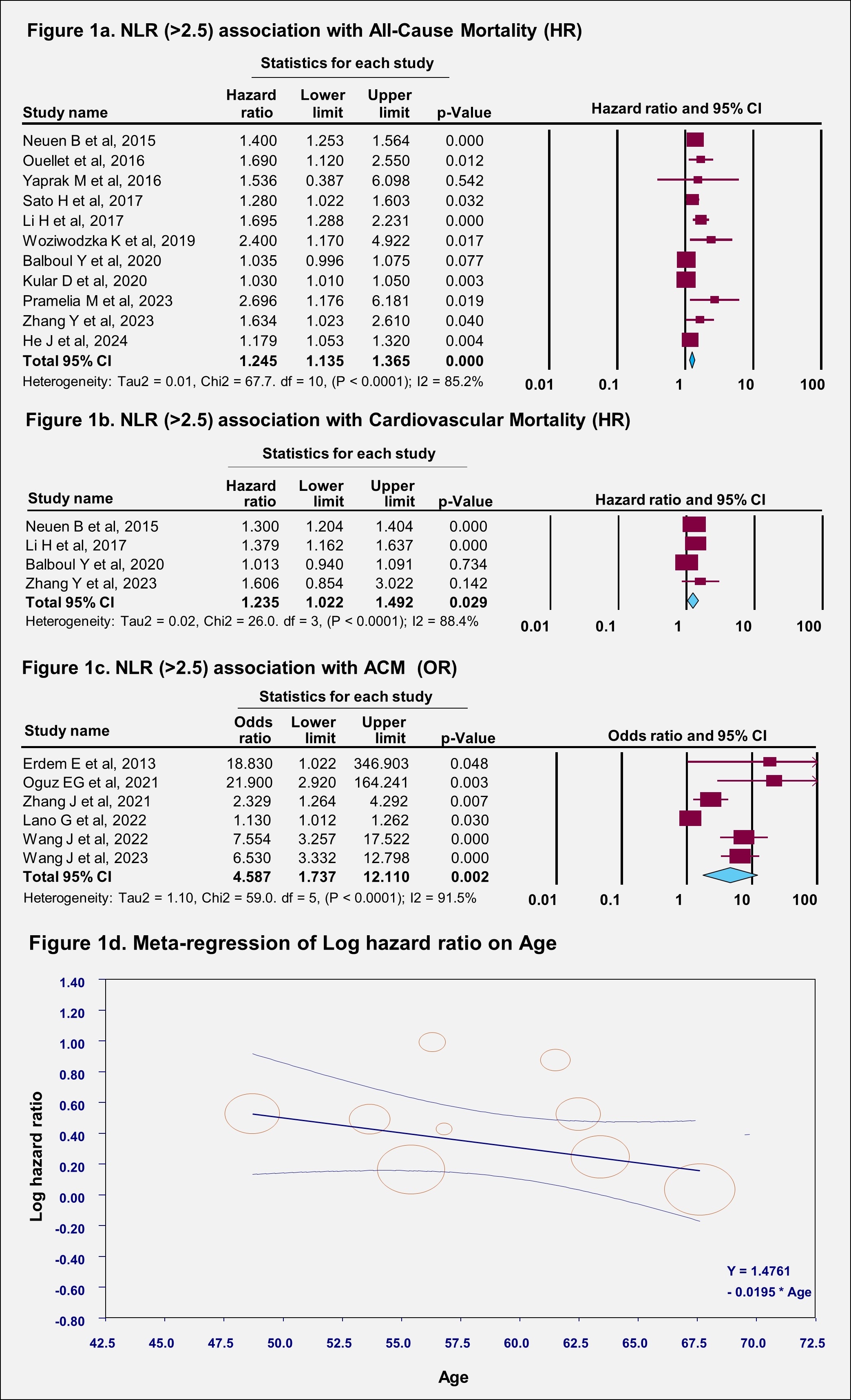
Results: Out of 180 articles analyzed, nineteen studies comprising 9,047 patients with a mean age of 59.5 ± 5.86 years and a mean follow-up duration of 46.7 months were included in our meta-analysis. The majority of the sample had a smoking history, hypertension, diabetes, and cerebrovascular diseases. Our meta-analysis revealed a significant association between higher NLR (>2.5) and increased risks of both ACM (aHR: 1.24, 95% CI: 1.13-1.36, P < 0.0001) (Figure 1a) and CVM (aHR: 1.23, 95% CI: 1.02-1.49, P = 0.03). (Figure 1b) Studies reporting outcomes in OR also reported similar findings for ACM (OR: 4.58, 95% CI: 1.73 - 12.1, p = 0.002) (Figure 1c) and CVM (OR: 1.11, 95% CI: 1.01 - 1.23, p = 0.03). Sensitivity analysis revealed no variations. The pooled AUC was 0.711 (95% CI: 0.63 - 0.80, p < 0.0001). JBI tool revealed higher scores indicating higher quality studies. Meta-regression analysis did not identify significant associations between NLR and confounding variables such as age. (Figure 1d)
Conclusion: This meta-analysis strongly concludes that NLR (>2.5) is significantly associated with ACM and CVM in patients with chronic HD and can be useful in planning for the prevention of mortality-related strategies.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive systematic search from PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus to identify studies showing the association between NLR and mortality outcomes in patients with chronic HD. Random-effects model with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were employed to pool adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) and odds ratios (OR), I2 statistics for evaluating heterogeneity for all-cause mortality (ACM) and cardiovascular mortality (CVM) outcomes. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis and meta-regression analyses assessed changes in overall effects and identified confounders, respectively. The Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) tool was used to assess the quality of the studies.
Results: Out of 180 articles analyzed, nineteen studies comprising 9,047 patients with a mean age of 59.5 ± 5.86 years and a mean follow-up duration of 46.7 months were included in our meta-analysis. The majority of the sample had a smoking history, hypertension, diabetes, and cerebrovascular diseases. Our meta-analysis revealed a significant association between higher NLR (>2.5) and increased risks of both ACM (aHR: 1.24, 95% CI: 1.13-1.36, P < 0.0001) (Figure 1a) and CVM (aHR: 1.23, 95% CI: 1.02-1.49, P = 0.03). (Figure 1b) Studies reporting outcomes in OR also reported similar findings for ACM (OR: 4.58, 95% CI: 1.73 - 12.1, p = 0.002) (Figure 1c) and CVM (OR: 1.11, 95% CI: 1.01 - 1.23, p = 0.03). Sensitivity analysis revealed no variations. The pooled AUC was 0.711 (95% CI: 0.63 - 0.80, p < 0.0001). JBI tool revealed higher scores indicating higher quality studies. Meta-regression analysis did not identify significant associations between NLR and confounding variables such as age. (Figure 1d)
Conclusion: This meta-analysis strongly concludes that NLR (>2.5) is significantly associated with ACM and CVM in patients with chronic HD and can be useful in planning for the prevention of mortality-related strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Geographic and Social Disparities Predict Worse Cardiac Outcomes Among U.S. Dialysis Patients: A ZIP Code–Level Analysis of Rurality, Race, and Social Determinants of Health
Tayag Nicole, Liu George
Angiopoeitin-2 and Mortality in an End-Stage Renal Disease, Heart Failure PopulationRobbin Vanessa, Bansal Vinod, Siddiqui Fakiha, Fareed Jawed, Syed Mushabbar