Final ID: Su1123
Association of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio with All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients Receiving Peritoneal Dialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a novel inflammatory marker predicting cardiovascular mortality (CVM) and all-cause mortality (ACM) among the general population. We aim to investigate this association in patients who underwent peritoneal dialysis (PD).
Methods: We systematically reviewed articles from PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus until May 2024 on the association of ACM and CVM in patients with NLR following PD. We used a fixed effects model, 95% confidence intervals (CI), and I2 statistics to pool unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratios (HR) and measure heterogeneity. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was employed to study how each study alters the overall effect of the studies. Multivariate meta-regression was utilized to identify influencing confounding factors. Quality assessment of the studies was done through the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) tool. For all results, a P value < 0.05 was considered significant.
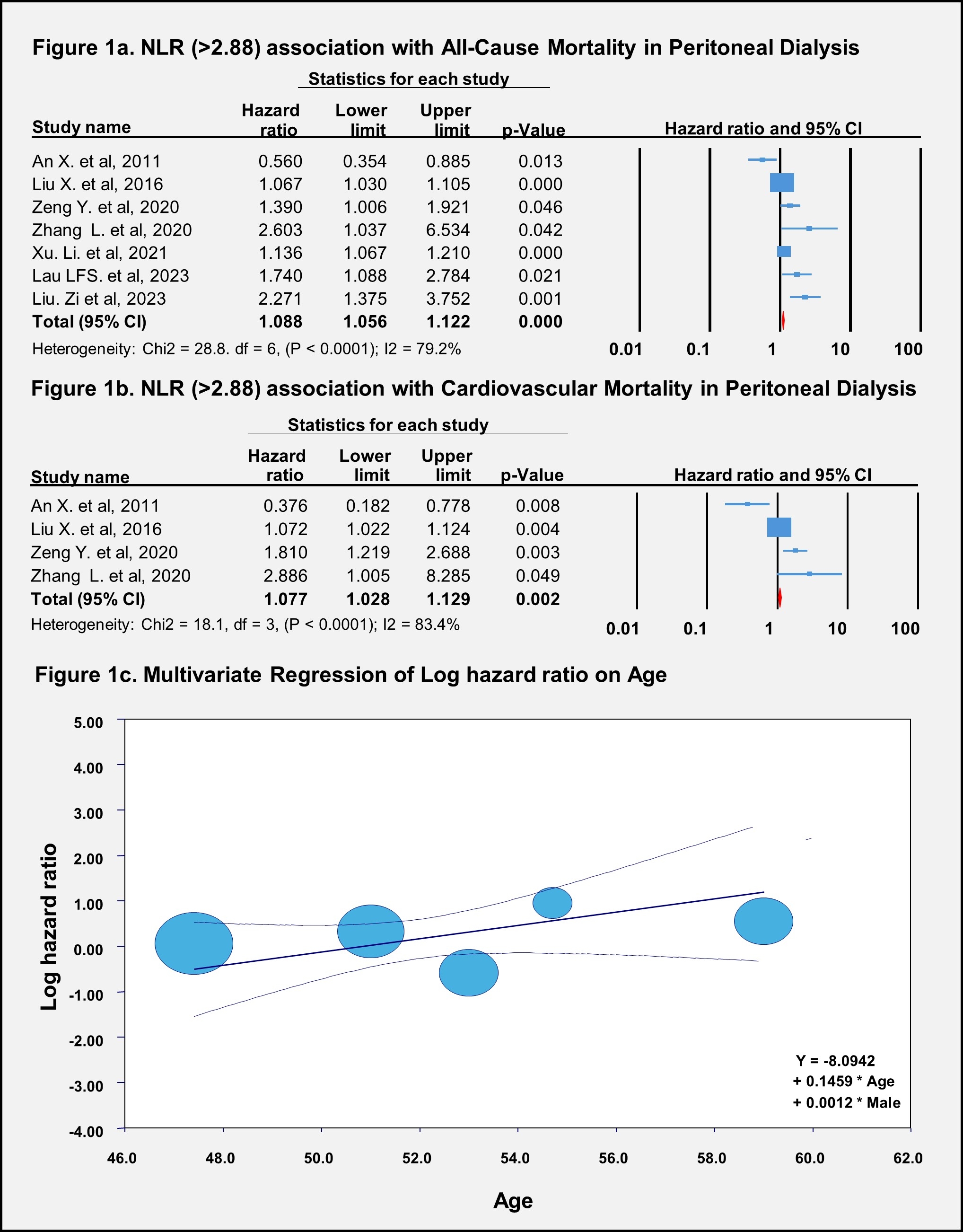
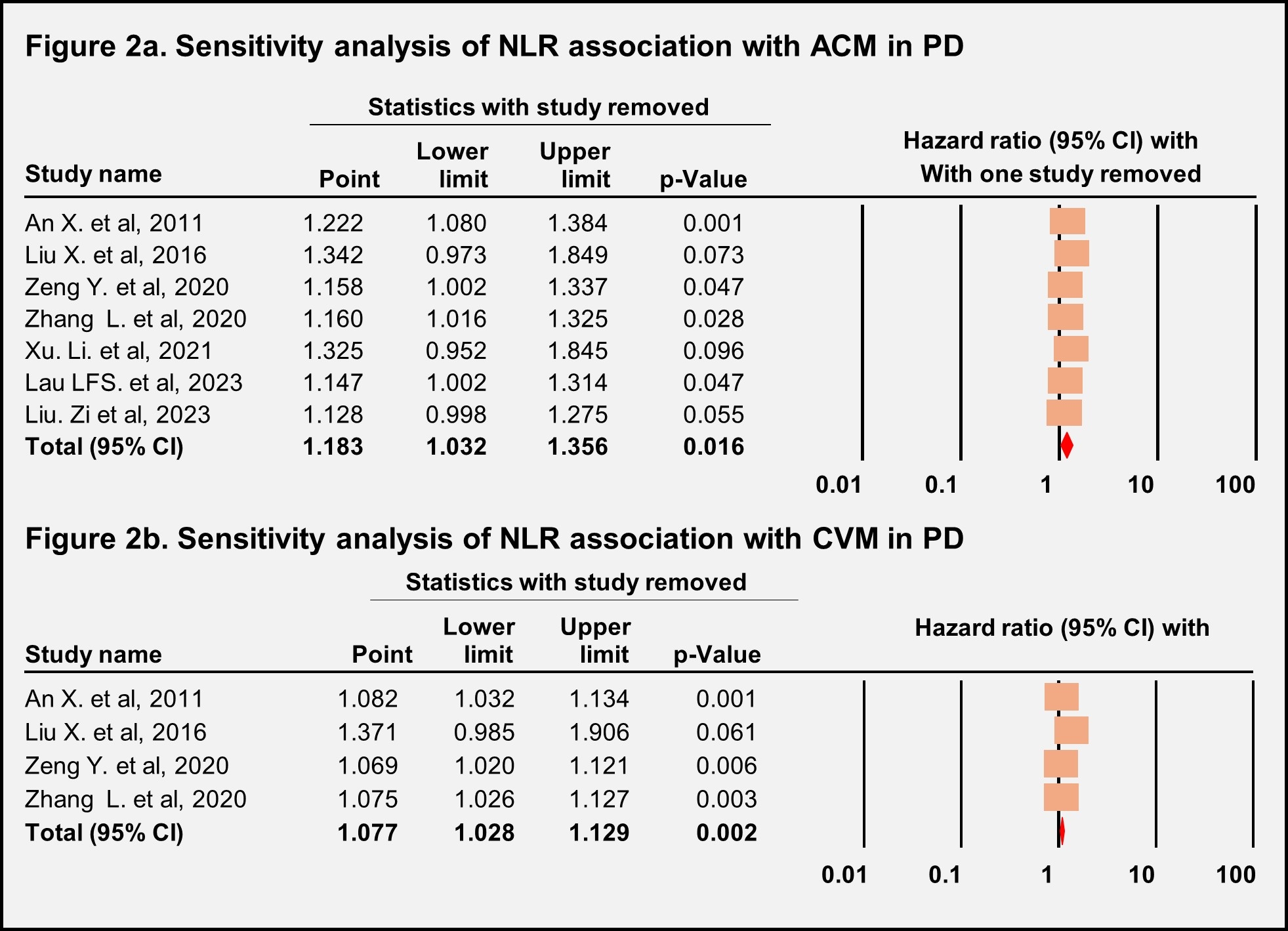
Results: Out of 160 articles screened, seven studies spanning from 2011 to 2023 with 4,350 patients, a mean age of 49.9 ± 15, and a median follow-up of four years were included in our meta-analysis. We found that higher NLR (>2.88) was significantly associated with ACM (aHR: 1.09, 95% CI: 1.05–1.12, p<0.0001) (Fig. 1a) and CVM (aHR: 1.08, 95% CI: 1.03–1.13, p=0.002) (Fig.1b) in patients following PD. Sensitivity analysis showed no variations, indicating that no single study influenced the overall results. JBI tool scores revealed low bias among the studies. Multivariate meta-regression revealed a significant relationship between age and ACM outcomes (Coefficient: 0.14, 95% CI: 0.001–0.2905, p=0.04) (Fig.1d).
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis identifies a significant association between higher NLR (>2.88) and outcomes such as ACM and CVM. This association can help prevent deaths in the older population and encourage proper utilization of the elderly resources. Additionally, age was a significant potential confounder for ACM in patients who are receiving PD. Thus, caution should be taken when predicting mortality in the elderly population.
Methods: We systematically reviewed articles from PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus until May 2024 on the association of ACM and CVM in patients with NLR following PD. We used a fixed effects model, 95% confidence intervals (CI), and I2 statistics to pool unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratios (HR) and measure heterogeneity. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was employed to study how each study alters the overall effect of the studies. Multivariate meta-regression was utilized to identify influencing confounding factors. Quality assessment of the studies was done through the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) tool. For all results, a P value < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results: Out of 160 articles screened, seven studies spanning from 2011 to 2023 with 4,350 patients, a mean age of 49.9 ± 15, and a median follow-up of four years were included in our meta-analysis. We found that higher NLR (>2.88) was significantly associated with ACM (aHR: 1.09, 95% CI: 1.05–1.12, p<0.0001) (Fig. 1a) and CVM (aHR: 1.08, 95% CI: 1.03–1.13, p=0.002) (Fig.1b) in patients following PD. Sensitivity analysis showed no variations, indicating that no single study influenced the overall results. JBI tool scores revealed low bias among the studies. Multivariate meta-regression revealed a significant relationship between age and ACM outcomes (Coefficient: 0.14, 95% CI: 0.001–0.2905, p=0.04) (Fig.1d).
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis identifies a significant association between higher NLR (>2.88) and outcomes such as ACM and CVM. This association can help prevent deaths in the older population and encourage proper utilization of the elderly resources. Additionally, age was a significant potential confounder for ACM in patients who are receiving PD. Thus, caution should be taken when predicting mortality in the elderly population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Clearing Senescent Cells Improves Mouse Survival Rate Post Myocardial Infarction through Alteration of Cardiomyocyte and Immune Cell Subpopulations
Mehdizadeh Mozhdeh, Leblanc Francis, Naud Patrice, Lettre Guillaume, Thorin Eric, Ferbeyre Gerardo, Nattel Stanley
Association of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio With Cardiovascular Mortality and All-cause Mortality in Patients Receiving Chronic Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysisVempati Roopeessh, Damarlapally Nanush, Vasudevan Srivatsa Surya, Banda Prathibha, Mourad Denise, Polamarasetty Harshavardhan, Mathur Gaurav, Khan Afrasayab, Desai Rupak