Final ID: Sa4043
Association between Congenital Heart Disease and the Risk of Cancer and its subtypes.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
Relationship between congenital heart disease and the risk of cancer and its subtypes is not well understood.
Objective
This study aim to investigate the association between CHD and risk of cancer and its subtypes among adult patients.
Method
The TriNeTX research database was used to identify patients aged ≥18 years of age from January 2000 to January 2021. Patients were categorized into two groups, one with CHD and another without CHD group of patients. Patients were followed for 1 and 3 years respectively. Propensity score-matched analysis (PSM) (1:1) was performed on demographics and comorbidities such as hypertension and diabetes mellitus. The primary outcome was cancer risk, while secondary outcomes were breast cancer, thyroid cancer, skin cancer, gastrointestinal tract cancer (GI), lung cancer, and brain tumors.
Results:
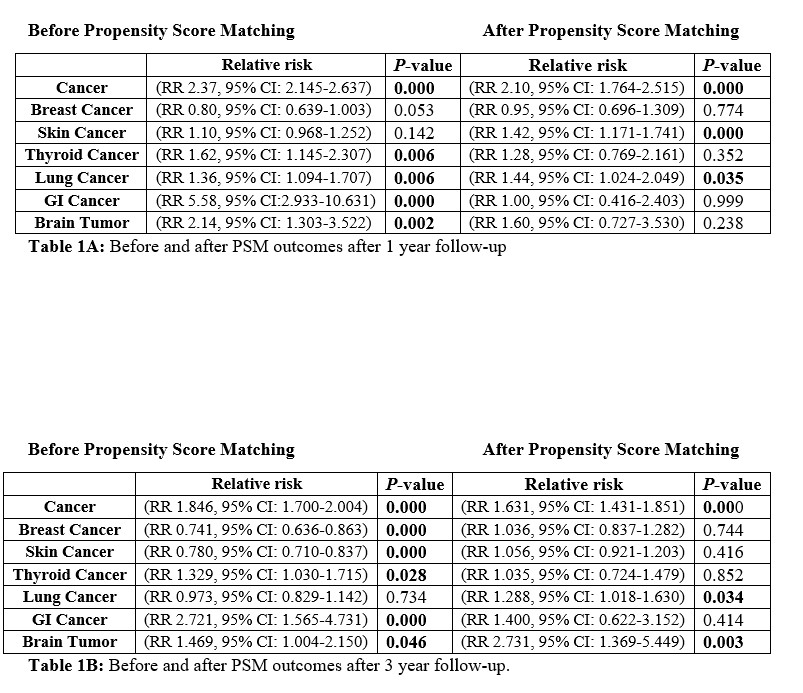
After 1:1 propensity score matching, the study cohort comprised 33,581 CHD patients and 33,581 non CHD patients. CHD patients were having a significantly higher risk of cancer after 1 year of follow-up (RR, 2.10 (95% CI: 1.764-2.515, P<0.001). A similar trend of higher risk of cancer was observed after 3 years of follow-up (RR, 1.63 (95% CI 1.436-1.851, P<0.001) when compared with the non CHD group of patients.
The risk of lung cancer was significantly higher among CHD groups of patients after 1 year of follow-up (RR, 1.44 (95% CI: 1.024-2.049), P=0.035), and after 3 year of follow-up (RR, 1.28 (95% CI: 1.018-1.630, P=0.034). Skin cancer were found significantly higher in CHD patients after 1 year of follow-up (RR, 1.42 (95% CI: 1.171-1.741), P<0.001), however, this became non-significant after 3 years of follow-up (RR, 1.05 (95% CI: 0.926-1.203, P=0.416).
On the other hand, the risk of brain tumors was comparable in both groups after 1 year of follow-up (RR, 1.60 (95%CI: 0.727-3.530), P=238). However, after 3 years of follow-up, the risk of brain tumor became significantly higher in CHD patients (RR, 2.73 (95% CI: 1.369, 5.449), P=0.003) when compared with non CHD group of patients.
In contrast, the risk of breast cancer, GI tumor, and thyroid cancers were comparable both after 1 year follow-up, and after 3 years of follow-up among both groups of patients.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that CHD patients are at higher risk of having Cancer, specifically lung cancer, dermatological cancer, and brain tumors.
Background
Relationship between congenital heart disease and the risk of cancer and its subtypes is not well understood.
Objective
This study aim to investigate the association between CHD and risk of cancer and its subtypes among adult patients.
Method
The TriNeTX research database was used to identify patients aged ≥18 years of age from January 2000 to January 2021. Patients were categorized into two groups, one with CHD and another without CHD group of patients. Patients were followed for 1 and 3 years respectively. Propensity score-matched analysis (PSM) (1:1) was performed on demographics and comorbidities such as hypertension and diabetes mellitus. The primary outcome was cancer risk, while secondary outcomes were breast cancer, thyroid cancer, skin cancer, gastrointestinal tract cancer (GI), lung cancer, and brain tumors.
Results:
After 1:1 propensity score matching, the study cohort comprised 33,581 CHD patients and 33,581 non CHD patients. CHD patients were having a significantly higher risk of cancer after 1 year of follow-up (RR, 2.10 (95% CI: 1.764-2.515, P<0.001). A similar trend of higher risk of cancer was observed after 3 years of follow-up (RR, 1.63 (95% CI 1.436-1.851, P<0.001) when compared with the non CHD group of patients.
The risk of lung cancer was significantly higher among CHD groups of patients after 1 year of follow-up (RR, 1.44 (95% CI: 1.024-2.049), P=0.035), and after 3 year of follow-up (RR, 1.28 (95% CI: 1.018-1.630, P=0.034). Skin cancer were found significantly higher in CHD patients after 1 year of follow-up (RR, 1.42 (95% CI: 1.171-1.741), P<0.001), however, this became non-significant after 3 years of follow-up (RR, 1.05 (95% CI: 0.926-1.203, P=0.416).
On the other hand, the risk of brain tumors was comparable in both groups after 1 year of follow-up (RR, 1.60 (95%CI: 0.727-3.530), P=238). However, after 3 years of follow-up, the risk of brain tumor became significantly higher in CHD patients (RR, 2.73 (95% CI: 1.369, 5.449), P=0.003) when compared with non CHD group of patients.
In contrast, the risk of breast cancer, GI tumor, and thyroid cancers were comparable both after 1 year follow-up, and after 3 years of follow-up among both groups of patients.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that CHD patients are at higher risk of having Cancer, specifically lung cancer, dermatological cancer, and brain tumors.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating Vitamin D Normalization on Major Adverse Cardiovascular-Related Events Among Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients: The TARGET-D Trial
May Heidi, Colipi Dominique, Whiting Tyler, Muhlestein Joseph, Le Viet, Anderson Jeffrey, Babcock Daniel, Wayman Libby, Bair Tami, Knight Stacey, Knowlton Kirk, Iverson Leslie
A Pressure-Volume Loops Approach Predicts Outcomes After Double Switch Operation For Congenitally Corrected Transposition Of The Great Arteries with Intact Ventricular SeptumThatte Nikhil, Del Nido Pedro, Ghelani Sunil, Hammer Peter, Marx Gerald, Beroukhim Rebecca, Gauvreau Kimberlee, Callahan Ryan, Prakash Ashwin, Emani Sitaram, Hoganson David