Final ID: Sa3160
Peak METs vs. Peak VO2: When is it not predictive?
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Metabolic equivalents (METs), a measure of energy use during a specified exercise intensity, and volume of oxygen consumed (VO2) are key measurements in cardiopulmonary exercise tests (CPETs). METs are traditionally converted to VO2 via multiplying METs by 3.5 ml/kg/min when VO2 data is not available, due to the fact that the latter requires more-expensive, accurate measurements of volume of inspired and expired oxygen and CO2. However, it is unclear which populations have significant variation between peak METs and peak VO2.
Research Question:
In a general cardiology population, do older women have a weaker relationship between peak METs and peak VO2?
Methods:
We present a retrospective study analyzing the relationship of peak METs and peak VO2 achieved on a CPET. Patients presenting to the cardiology clinic who received a CPET from 2017-2022 were included. Patients with severe valvular dysfunction, congenital heart disease, prior coronary artery bypass grafting, or ejection fraction < 50% were removed to limit confounding. A Spearman correlation coefficient was calculated for the whole sample comparing peak METs and peak VO2. Subsequently, a subgroup of women age 65 or greater were compared to the general sample by a fisher’s z transformation.
Results:
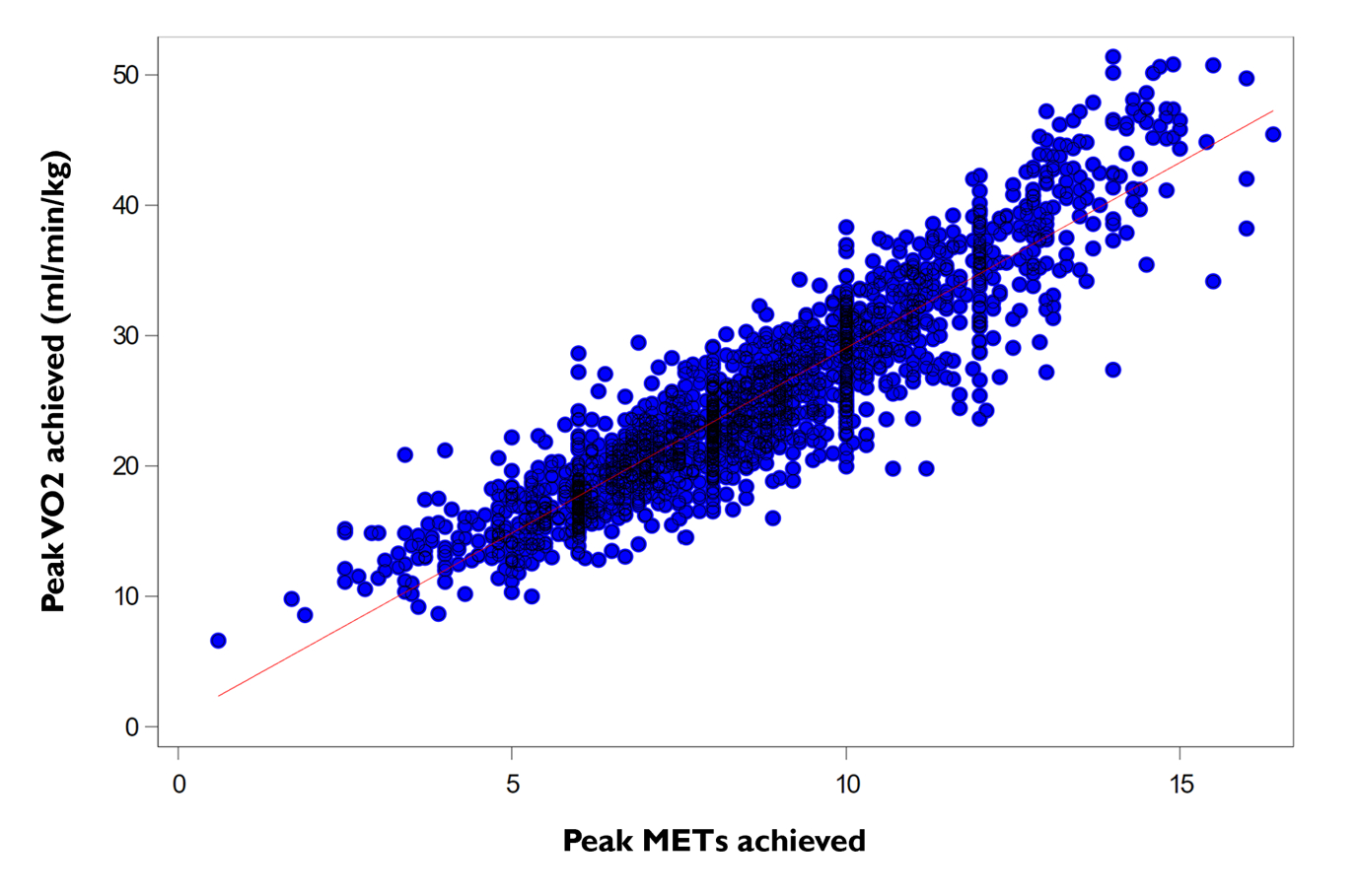
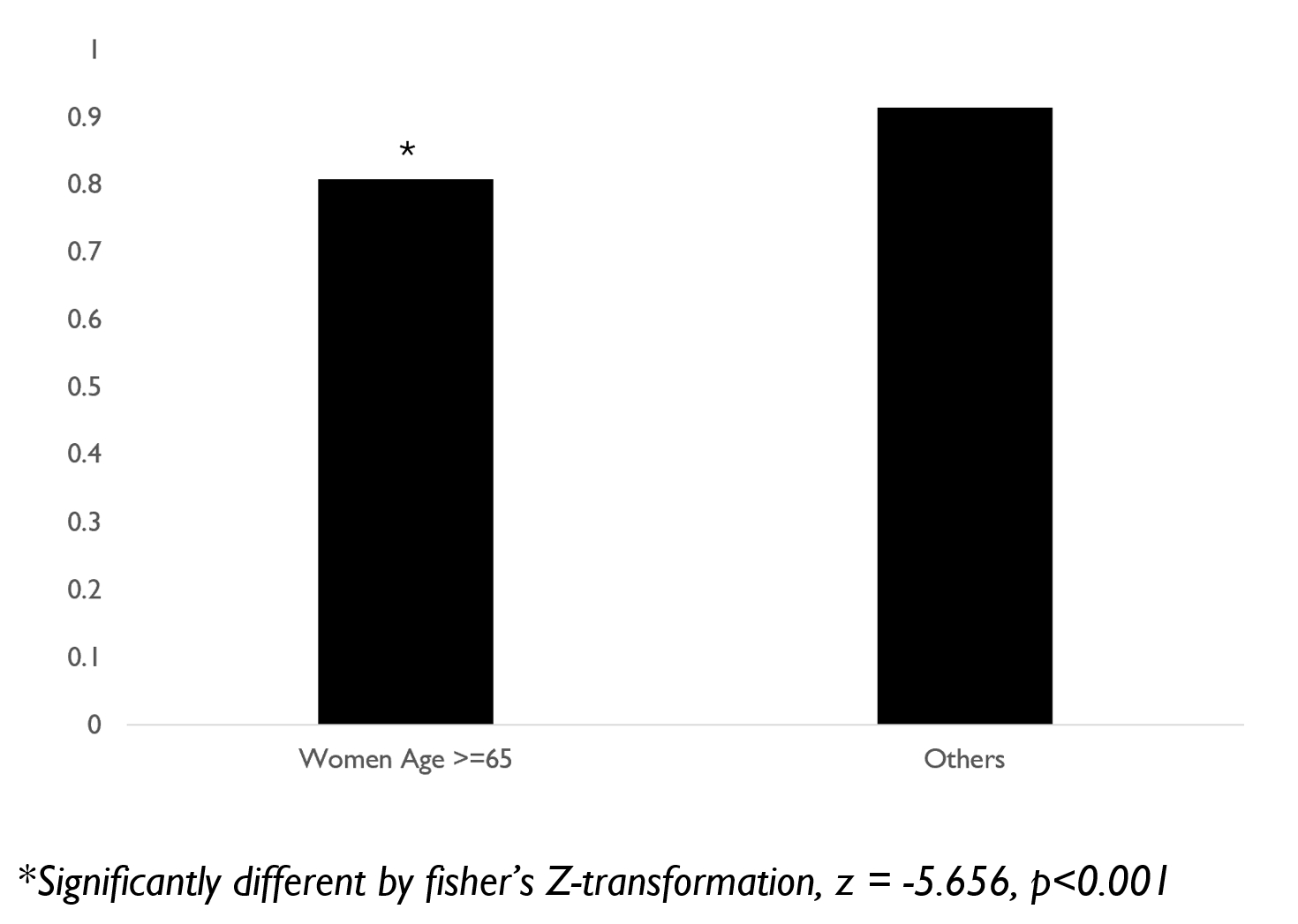
1907 patients were included. There was a strong positive correlation between peak VO2 and peak METs in the whole sample (r(1860) = 0.914), p<0,001), shown in Figure 1. Women age 65 or greater had a weaker correlation (r(190)=0.808, p<0.0001) compared to the those who were not (r(1668) = 0.915, p<0.0001; z = -5.656, p<0.001), shown in Figure 2.
Conclusions:
Peak METs and peak VO2 have an extremely strong positive correlation in a general cardiology population. However, these relationships weaken for women age 65 or greater. METs are an accurate, cost-effective proxy measurement of VO2 in a general population, however may lack reliability for certain demographics.
Metabolic equivalents (METs), a measure of energy use during a specified exercise intensity, and volume of oxygen consumed (VO2) are key measurements in cardiopulmonary exercise tests (CPETs). METs are traditionally converted to VO2 via multiplying METs by 3.5 ml/kg/min when VO2 data is not available, due to the fact that the latter requires more-expensive, accurate measurements of volume of inspired and expired oxygen and CO2. However, it is unclear which populations have significant variation between peak METs and peak VO2.
Research Question:
In a general cardiology population, do older women have a weaker relationship between peak METs and peak VO2?
Methods:
We present a retrospective study analyzing the relationship of peak METs and peak VO2 achieved on a CPET. Patients presenting to the cardiology clinic who received a CPET from 2017-2022 were included. Patients with severe valvular dysfunction, congenital heart disease, prior coronary artery bypass grafting, or ejection fraction < 50% were removed to limit confounding. A Spearman correlation coefficient was calculated for the whole sample comparing peak METs and peak VO2. Subsequently, a subgroup of women age 65 or greater were compared to the general sample by a fisher’s z transformation.
Results:
1907 patients were included. There was a strong positive correlation between peak VO2 and peak METs in the whole sample (r(1860) = 0.914), p<0,001), shown in Figure 1. Women age 65 or greater had a weaker correlation (r(190)=0.808, p<0.0001) compared to the those who were not (r(1668) = 0.915, p<0.0001; z = -5.656, p<0.001), shown in Figure 2.
Conclusions:
Peak METs and peak VO2 have an extremely strong positive correlation in a general cardiology population. However, these relationships weaken for women age 65 or greater. METs are an accurate, cost-effective proxy measurement of VO2 in a general population, however may lack reliability for certain demographics.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Quantitative Echocardiographic Parameters with Peak VO2, Heart Rate Recovery, and VE/VCO2 from Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing
Sharma Arundhati, Sharma Anubhuti, Chaliki Kalyan, Viggiano Taylor, Chaliki Hari, Reddy Satyajit
Effect of Medical-Grade Mask Use on Exercise Physiology in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Crossover StudyLee Ju-hee, Lee Goo Joo, Kang Mingyu, Eom Sang Yong