Final ID: MDP914
Prevalence and Risk Factors of Peripheral Artery Disease Identified by Multimodalities in Hispanics
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: The prevalence of peripheral artery disease (PAD) has been assessed with the ankle-brachial index (ABI), but some studies have raised concerns about its sensitivity.
Aims: Using data from a community-based cohort study, the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos (HCHS/SOL), we estimated the prevalence of PAD in US Hispanics using the toe-brachial index (TBI), pulse volume recordings (PVR), continuous Doppler waveforms, and post-exercise ABI, in addition to resting ABI. We also explored the associations of known risk factors with PAD identified by these methods.
Methods: The HCHS/SOL sampled Hispanics/Latinos from four US regions (CA, IL, FL, and NY). During its third visit, participants aged ≥45 years were invited for a comprehensive evaluation of PAD. PAD was defined as having at least one of the following: 1) resting ABI ≤0.9; 2) post-exercise (heel-raise) drop in ABI ≥20% or drop in ankle blood pressure ≥30 mmHg; or 3) abnormality in at least two of TBI (≤0.6), PVR (mild or greater abnormality), and continuous Doppler waveforms (monophasic/nonpulsatile in either dorsalis pedis or posterior tibial artery or biphasic without good acceleration in both arteries). Certified technicians conducted the measurements using a vascular diagnostic instrument (the Unetixs MultiLab Series II). Major cardiovascular risk factors were measured according to the standard protocol in HCHS/SOL.
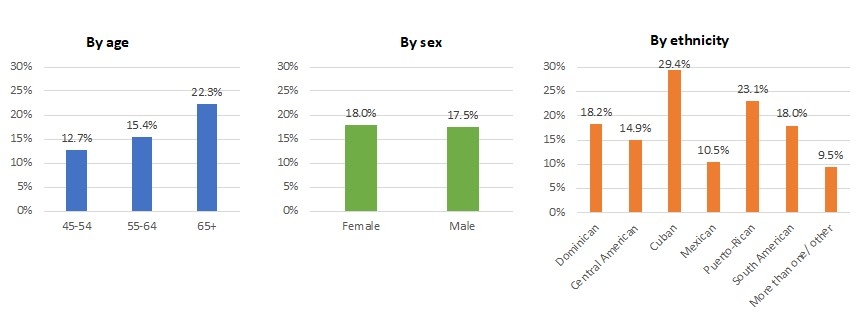
Results: Among 3,130 participants (mean age 62.9 years, 2121 female [67.8%]), the prevalence of PAD was 4.1% with only resting ABI ≤0.9 but 17.8% considering all modalities. The prevalence of PAD exceeded 22% in participants aged 65+ (Figure) and was similar between men and women. PAD prevalence was significantly higher in Cubans, Puerto Ricans, and Central Americans compared to Mexicans (Figure). The higher prevalence in these ethnic groups remained consistent even after adjusting for traditional risk factors. Among traditional risk factors, smoking, diabetes, and systolic blood pressure were robustly associated with the presence of PAD.
Conclusion: In this cohort of US Hispanics/Latinos, the prevalence of PAD is substantially higher when multiple modalities are used to detect PAD. Disparities in the prevalence of PAD across ethnic groups in Hispanics could not be explained by traditional risk factors and should be further investigated.
Aims: Using data from a community-based cohort study, the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos (HCHS/SOL), we estimated the prevalence of PAD in US Hispanics using the toe-brachial index (TBI), pulse volume recordings (PVR), continuous Doppler waveforms, and post-exercise ABI, in addition to resting ABI. We also explored the associations of known risk factors with PAD identified by these methods.
Methods: The HCHS/SOL sampled Hispanics/Latinos from four US regions (CA, IL, FL, and NY). During its third visit, participants aged ≥45 years were invited for a comprehensive evaluation of PAD. PAD was defined as having at least one of the following: 1) resting ABI ≤0.9; 2) post-exercise (heel-raise) drop in ABI ≥20% or drop in ankle blood pressure ≥30 mmHg; or 3) abnormality in at least two of TBI (≤0.6), PVR (mild or greater abnormality), and continuous Doppler waveforms (monophasic/nonpulsatile in either dorsalis pedis or posterior tibial artery or biphasic without good acceleration in both arteries). Certified technicians conducted the measurements using a vascular diagnostic instrument (the Unetixs MultiLab Series II). Major cardiovascular risk factors were measured according to the standard protocol in HCHS/SOL.
Results: Among 3,130 participants (mean age 62.9 years, 2121 female [67.8%]), the prevalence of PAD was 4.1% with only resting ABI ≤0.9 but 17.8% considering all modalities. The prevalence of PAD exceeded 22% in participants aged 65+ (Figure) and was similar between men and women. PAD prevalence was significantly higher in Cubans, Puerto Ricans, and Central Americans compared to Mexicans (Figure). The higher prevalence in these ethnic groups remained consistent even after adjusting for traditional risk factors. Among traditional risk factors, smoking, diabetes, and systolic blood pressure were robustly associated with the presence of PAD.
Conclusion: In this cohort of US Hispanics/Latinos, the prevalence of PAD is substantially higher when multiple modalities are used to detect PAD. Disparities in the prevalence of PAD across ethnic groups in Hispanics could not be explained by traditional risk factors and should be further investigated.
More abstracts on this topic:
Relations Of Inflammatory Biomarkers With Incident Clinical Peripheral Artery Disease In Older Adults
Dosanjh Jagjot, Kizer Jorge, Shitole Sanyog, Garg Parveen, Mukamal Kenneth, Cushman Mary, Sitlani Colleen, Walston Jeremy, Reiner Alex, Tracy Russell, Psaty Bruce
A murine model of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome demonstrates compromised limb function in the ischemic hind limbLotfollahzadeh Saran, Siracuse Jeffrey, Cabral Howard, Malikova Marina, Sayed Nazish, Chitalia Vipul