Final ID: Su3076
Sex Differences in Lipid Measurement, LDL-C Goal Attainment, and Prescribing Practices
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
ASCVD is the leading cause of death in women worldwide. Historically, lipid lowering therapy (LLT) and LDL-C goal attainment have been suboptimal in women.
Aim
We aim to investigate sex differences in lipid measurement, LDL-C goal attainment, and prescribing practices within our health system.
Methods
We performed a retrospective chart review of adult patients with lipid panels performed between 2022 and 2023 in a large health system. We abstracted demographics, comorbidities, lipid levels, LLT, and prescriptions from the electronic health records. Optimal LDL-C was defined as <70 mg/dL for high-risk patients with ASCVD and <100 mg/dL for the rest of the population.
Results
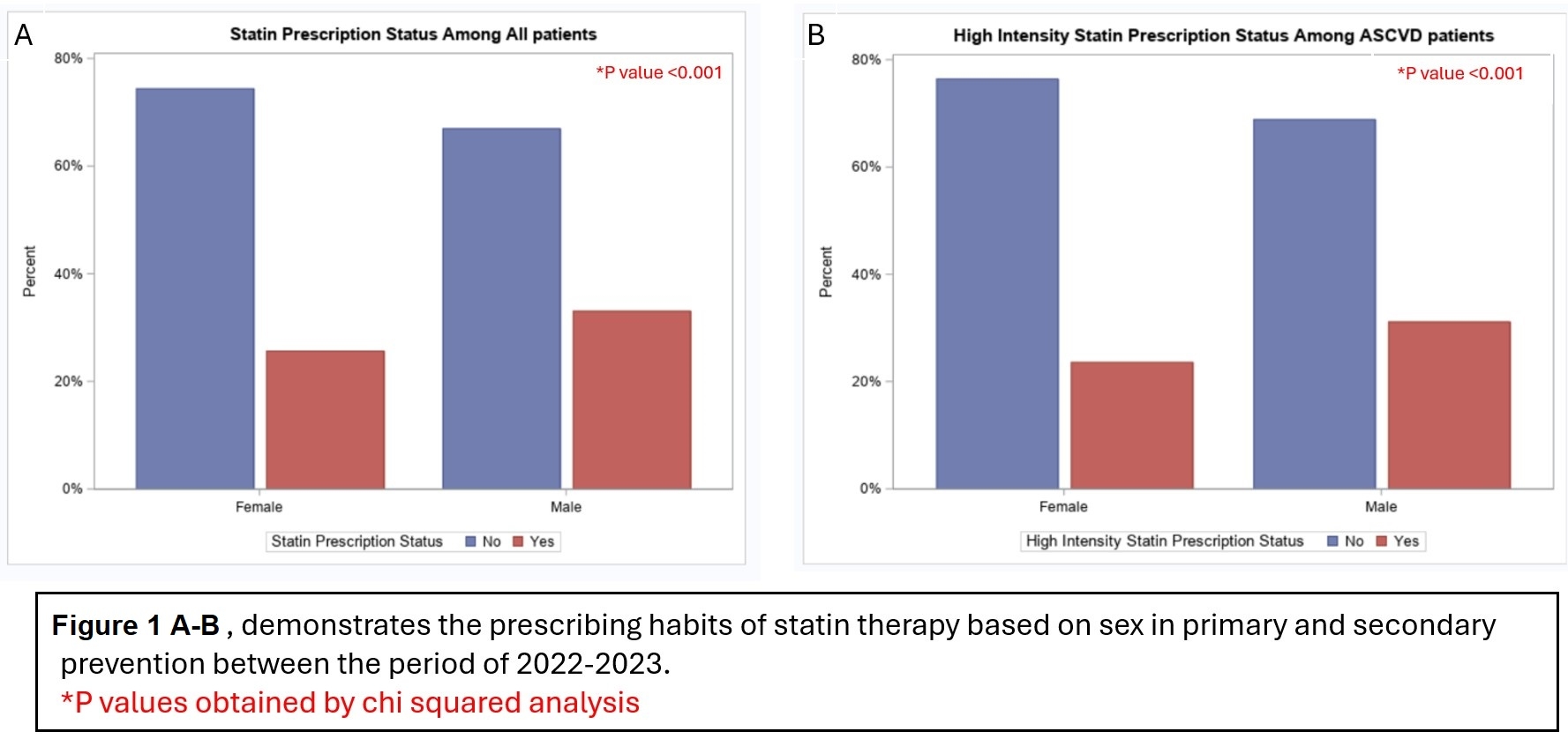
Among 364,021 patients, 57% were female, 60% were White, 10% Black, 6% Asian, 14% Other, and 10% unknown; 12% were Hispanic or Latino with ASCVD noted in 7% of women and 13% of men. Mean LDL-C was 108 mg/dL ± 35 in women vs. 102 mg/dL ± 37 in men. Overall optimal LDL-C was achieved in 41% of women vs. 47% of men; 31% women vs. 47% men with ASCVD achieved goal LDL-C. LDL-C was ordered primarily by primary care (74% and 69%) and cardiology (12% and 17%), in men and women respectively, compared to other specialties.
Statins were most often prescribed by primary care (61%) and cardiology (31%). Cardiology prescribed more frequently to men compared to women (55% vs. 45%); primary care prescribed more often to women compared to men (53% vs. 47%). Non-statin prescriptions were more common by cardiology (57%) and primary care (34%). Overall, men were more frequently prescribed statins than women (33% vs 26%) and amongst ASCVD patients, men had higher prescriptions rates of high intensity statins compared to women (31% vs. 24%) (Figure 1A-D). Results were statistically significant (p<0.01) for all comparisons between men and women.
Conclusions
In our study, women had higher mean LDL-C and suboptimal LDL-C levels compared to men. Women with ASCVD were less frequently prescribed high intensity statins. Most LDL-C orders and statin prescriptions were by primary care, but women experienced treatment disparities even when treated by cardiologists, highlighting the need for increased awareness and education around sex disparities in lipid management.
ASCVD is the leading cause of death in women worldwide. Historically, lipid lowering therapy (LLT) and LDL-C goal attainment have been suboptimal in women.
Aim
We aim to investigate sex differences in lipid measurement, LDL-C goal attainment, and prescribing practices within our health system.
Methods
We performed a retrospective chart review of adult patients with lipid panels performed between 2022 and 2023 in a large health system. We abstracted demographics, comorbidities, lipid levels, LLT, and prescriptions from the electronic health records. Optimal LDL-C was defined as <70 mg/dL for high-risk patients with ASCVD and <100 mg/dL for the rest of the population.
Results
Among 364,021 patients, 57% were female, 60% were White, 10% Black, 6% Asian, 14% Other, and 10% unknown; 12% were Hispanic or Latino with ASCVD noted in 7% of women and 13% of men. Mean LDL-C was 108 mg/dL ± 35 in women vs. 102 mg/dL ± 37 in men. Overall optimal LDL-C was achieved in 41% of women vs. 47% of men; 31% women vs. 47% men with ASCVD achieved goal LDL-C. LDL-C was ordered primarily by primary care (74% and 69%) and cardiology (12% and 17%), in men and women respectively, compared to other specialties.
Statins were most often prescribed by primary care (61%) and cardiology (31%). Cardiology prescribed more frequently to men compared to women (55% vs. 45%); primary care prescribed more often to women compared to men (53% vs. 47%). Non-statin prescriptions were more common by cardiology (57%) and primary care (34%). Overall, men were more frequently prescribed statins than women (33% vs 26%) and amongst ASCVD patients, men had higher prescriptions rates of high intensity statins compared to women (31% vs. 24%) (Figure 1A-D). Results were statistically significant (p<0.01) for all comparisons between men and women.
Conclusions
In our study, women had higher mean LDL-C and suboptimal LDL-C levels compared to men. Women with ASCVD were less frequently prescribed high intensity statins. Most LDL-C orders and statin prescriptions were by primary care, but women experienced treatment disparities even when treated by cardiologists, highlighting the need for increased awareness and education around sex disparities in lipid management.
More abstracts on this topic:
A drug target Mendelian randomization study of triglyceride lowering therapies for aortic stenosis
Ciofani Jonathan, Han Daniel, Gill Dipender, Rao Karan, Allahwala Usaid, Bhindi Ravinay
Ang II i.c.v. is Associated with Cognitive Impairment and Tau Phosphorylation in Male Mice in the Absence of HypertensionZarate Sara, Vissa Udaykiran, Santner Ava, Kelly Olivia, Reasonover Samantha, Santisteban Monica