Final ID: MDP437
Cardiometabolic Risk during the Venezuelan Humanitarian Crisis: Insights from the EVESCAM Study on Crisis Indicators.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Social vulnerability is linked to increased cardiovascular morbimortality. Venezuela faces a severe humanitarian crisis –rated 4.2/5 on the INFORM Severity Index-, marked by hyperinflation, healthcare collapse, and mass migration (>7.2 million by 2023), with poverty escalating from 48% in 2014 to 96.2% by 2020. This study aims to examine the association between crisis indicators—food insecurity, stressful life events (SLEs), and family separation—and cardiometabolic risk factors (CMRF).
Methods: This analysis uses follow-up data (2018-2020) from 1,257 individuals in the Venezuelan Study of Cardiometabolic Health (EVESCAM,2014-2017). The distribution of CMRF (adiposity, dysglycemia, dyslipidemia, anxiety/depression symptoms, diet, physical activity, alcohol intake, and smoking) by three crisis indicators (food insecurity, SLEs—including financial difficulties, accidents, family deaths, health issues, and violence—and family separation) was analyzed. Logistic regression determined the associations.
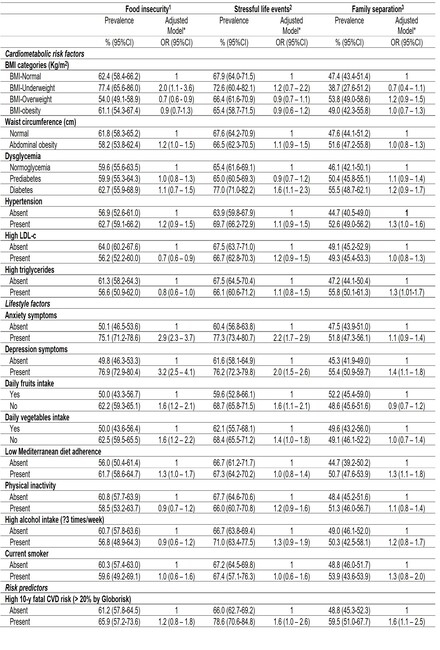
Results: Table 1 illustrates the relationship between crisis indicators and CMRF. Food insecurity was prevalent in 60.2% of participants, especially those with low SES, and was associated with higher odds of being underweight (OR:2.0[1.1-3.6]), anxiety (OR:2.9[2.3-3.7]), depression (OR=3.2[2.5-4.1]), and reduced fruit/vegetable intake. SLEs affected 67.2% of participants, linked to higher odds of diabetes (OR:1.6[1.1-2.3]), anxiety (OR: 2.2[1.7- 2.9]), depression (OR: 2.0[1.5- 2.6]), and poor dietary habits. Family separation, with a prevalence of 49.2%, was more common in older adults and females and linked to depression (OR: 1.4[1.1- 1.8]), low adherence to the Mediterranean diet, high triglycerides (OR:1.3[1.01-1.7]), and high risk of a fatal cardiovascular event (OR: 1.6 [1.1 – 2.5]).
Conclusion: The Venezuelan humanitarian crisis has severely impacted adults, with high prevalence rates of food insecurity, SLEs, and family separation, while increasing CMRF, especially among vulnerable groups. Food insecurity rates in Venezuela were aligned with crisis-hit countries like Yemen. This study underscores the urgent need for targeted interventions to support the most affected populations.
Methods: This analysis uses follow-up data (2018-2020) from 1,257 individuals in the Venezuelan Study of Cardiometabolic Health (EVESCAM,2014-2017). The distribution of CMRF (adiposity, dysglycemia, dyslipidemia, anxiety/depression symptoms, diet, physical activity, alcohol intake, and smoking) by three crisis indicators (food insecurity, SLEs—including financial difficulties, accidents, family deaths, health issues, and violence—and family separation) was analyzed. Logistic regression determined the associations.
Results: Table 1 illustrates the relationship between crisis indicators and CMRF. Food insecurity was prevalent in 60.2% of participants, especially those with low SES, and was associated with higher odds of being underweight (OR:2.0[1.1-3.6]), anxiety (OR:2.9[2.3-3.7]), depression (OR=3.2[2.5-4.1]), and reduced fruit/vegetable intake. SLEs affected 67.2% of participants, linked to higher odds of diabetes (OR:1.6[1.1-2.3]), anxiety (OR: 2.2[1.7- 2.9]), depression (OR: 2.0[1.5- 2.6]), and poor dietary habits. Family separation, with a prevalence of 49.2%, was more common in older adults and females and linked to depression (OR: 1.4[1.1- 1.8]), low adherence to the Mediterranean diet, high triglycerides (OR:1.3[1.01-1.7]), and high risk of a fatal cardiovascular event (OR: 1.6 [1.1 – 2.5]).
Conclusion: The Venezuelan humanitarian crisis has severely impacted adults, with high prevalence rates of food insecurity, SLEs, and family separation, while increasing CMRF, especially among vulnerable groups. Food insecurity rates in Venezuela were aligned with crisis-hit countries like Yemen. This study underscores the urgent need for targeted interventions to support the most affected populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
BMI Thresholds and Incident ASCVD in Disaggregated Asian American, Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander Men and Women: The PANACHE Study
Go Alan, Parikh Rishi, Tan Thida, Ambrosy Andrew, Alexeeff Stacey, Howick Connor, Daida Yihe, Lo Joan
Dietary patterns, serum metabolites and risk of cardiovascular disease in the US Hispanic/Latino adults: the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of LatinosYang Hongbo, Daviglus Martha, Yu Bing, Hu Frank, Kaplan Robert, Qi Qibin, Wang Yi, Luo Kai, Mossavar-rahmani Yasmin, Cordero Christina, Ostfeld Robert, Martinez Claudia, Maldonado Luis, Pirzada Amber