Final ID: MDP123
Efficacy of Mavacamten on Echocardiographic Parameters and Cardiac Biomarkers in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Mavacamten, a cardiac myosin inhibitor, distinguishes from other pharmacological interventions by addressing not only symptomatic treatment but also targeting the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM). Therefore, we aimed in our meta-analysis to evaluate the impact of mavacamten on echocardiographic parameters and cardiac biomarkers in HCM patients.
Methods: We searched different databases such as PubMed, SCOPUS, WOS, and Cochrane from inception until February 20, 2023, for any randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compare mavacamten to placebo in HCM patients and report the echocardiographic parameters. Our outcomes of interest were diastolic function parameters [lateral and septal early diastolic mitral annular velocity (lateral e’ and septal e’), lateral and septal ratio of early diastolic mitral inflow velocity to early diastolic mitral annulus velocity of the septum (E/e’ lateral and septal ratio)], left ventricular parameters [left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) valsalva gradient ], as well as cardiac biomarkers [NT-proBNP and troponin]. We used the mean difference (MD) for continuous outcomes with the corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI).
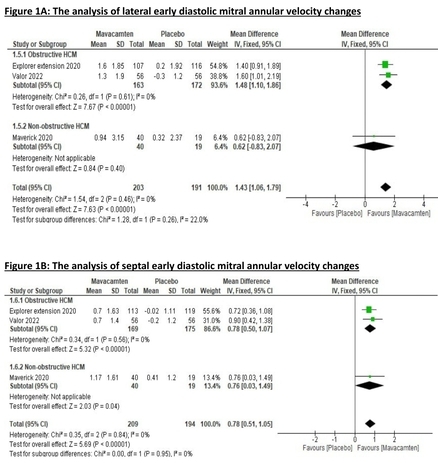
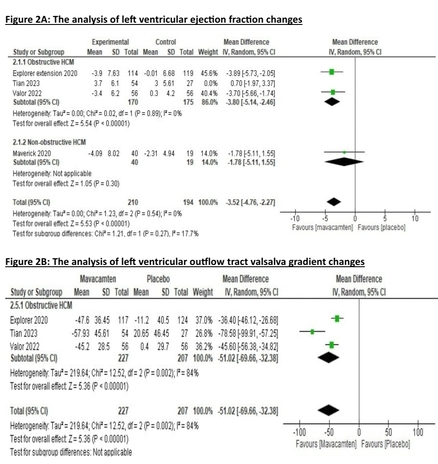
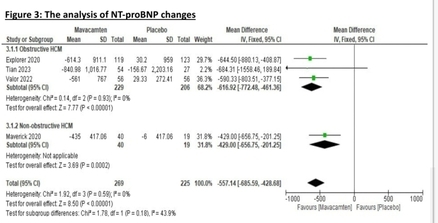
Results: Four RCTs with a total of 503 patients were included. Mavacamten led to a significant improvement in lateral e’ and septal e’, (MD=1.43, 95% CI [1.06, 1.79]), (MD=0.78, 95% CI [0.51, 1.05]) respectively compared to placebo. Furthermore, mavacamten was superior to placebo in reducing E/e’ lateral ratio, (MD=-3.05, 95% CI [-5.05, -1.05]) E/e' septal ratio (MD=-3.38, 95% CI [-4.50, -2.25]), LVEF, and LVOT valsalva gradient, (MD=-3.52, 95% CI [-4.76, -2.27]), (MD=-51.02, 95% CI [-69.66, -32.38]), respectively. Regarding to cardiac biomarkers, mavacamten demonstrated substantial efficacy in reducing NT-proBNP (MD=-557.14, 95% CI [-685.59, -428.68]), and troponin (MD=-8.47, 95% CI [-12.73, -4.21]).
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis reveals that mavacamten significantly enhanced echocardiographic outcomes for diastolic function and left ventricular parameters. Also, mavacamten led to a significant reduction in cardiac biomarkers.
Methods: We searched different databases such as PubMed, SCOPUS, WOS, and Cochrane from inception until February 20, 2023, for any randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compare mavacamten to placebo in HCM patients and report the echocardiographic parameters. Our outcomes of interest were diastolic function parameters [lateral and septal early diastolic mitral annular velocity (lateral e’ and septal e’), lateral and septal ratio of early diastolic mitral inflow velocity to early diastolic mitral annulus velocity of the septum (E/e’ lateral and septal ratio)], left ventricular parameters [left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) valsalva gradient ], as well as cardiac biomarkers [NT-proBNP and troponin]. We used the mean difference (MD) for continuous outcomes with the corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results: Four RCTs with a total of 503 patients were included. Mavacamten led to a significant improvement in lateral e’ and septal e’, (MD=1.43, 95% CI [1.06, 1.79]), (MD=0.78, 95% CI [0.51, 1.05]) respectively compared to placebo. Furthermore, mavacamten was superior to placebo in reducing E/e’ lateral ratio, (MD=-3.05, 95% CI [-5.05, -1.05]) E/e' septal ratio (MD=-3.38, 95% CI [-4.50, -2.25]), LVEF, and LVOT valsalva gradient, (MD=-3.52, 95% CI [-4.76, -2.27]), (MD=-51.02, 95% CI [-69.66, -32.38]), respectively. Regarding to cardiac biomarkers, mavacamten demonstrated substantial efficacy in reducing NT-proBNP (MD=-557.14, 95% CI [-685.59, -428.68]), and troponin (MD=-8.47, 95% CI [-12.73, -4.21]).
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis reveals that mavacamten significantly enhanced echocardiographic outcomes for diastolic function and left ventricular parameters. Also, mavacamten led to a significant reduction in cardiac biomarkers.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel JAK Activity Reporter for Live Cell Screening and Drug Discovery
Lopez-cecetaite Gabriel, Song Qianxiao, Severino Alex, Reyes Gaido Oscar, Luczak Elizabeth
2 Dimensional Echocardiography versus 3 Dimentional Echocardiography to Assess Right Ventricular Function in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic ReviewChaudhry Waleed Razzaq, Hajj Fatima, Bathula Satyamedha, Meghji Mohammed Askari, Pasupuleti Hemalatha, Kiyani Madiha, Shah Syeda Simrah, Neelakantan Ramaswamy Sanathanan, Mirzaeidizaji Nakisa, St. Jacques Jahnoy, Khan Khalil Ullah, Veluchamy Elakkiya, Jesse Joshanna