Final ID: MDP229
Sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy – what is the role of coronary artery disease?
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Myocardial ischemia is a potential trigger for sudden cardiac death (SCD) in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) but significant coronary artery disease (CAD) is not considered in clinical risk stratification calculators. The overlap between HCM and CAD needs further investigation, especially in the general population.
Hypothesis: A large proportion of patients with HCM who suffer SCD, have associated significant CAD.
Methods: From an ongoing prospective, population-based study of SCD in the Northwestern US (catchment pop. ≈1 M, 2002-2020), we performed a case-case analysis. Comparisons of the lifetime clinical history and available autopsy findings were made between SCD cases with HCM and CAD(HCM-CAD) vs. HCM without CAD(HCM-NCAD). HCM was defined as left ventricle (LV) wall thickness ≥15mm in the absence of any other cause for LVH. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted.
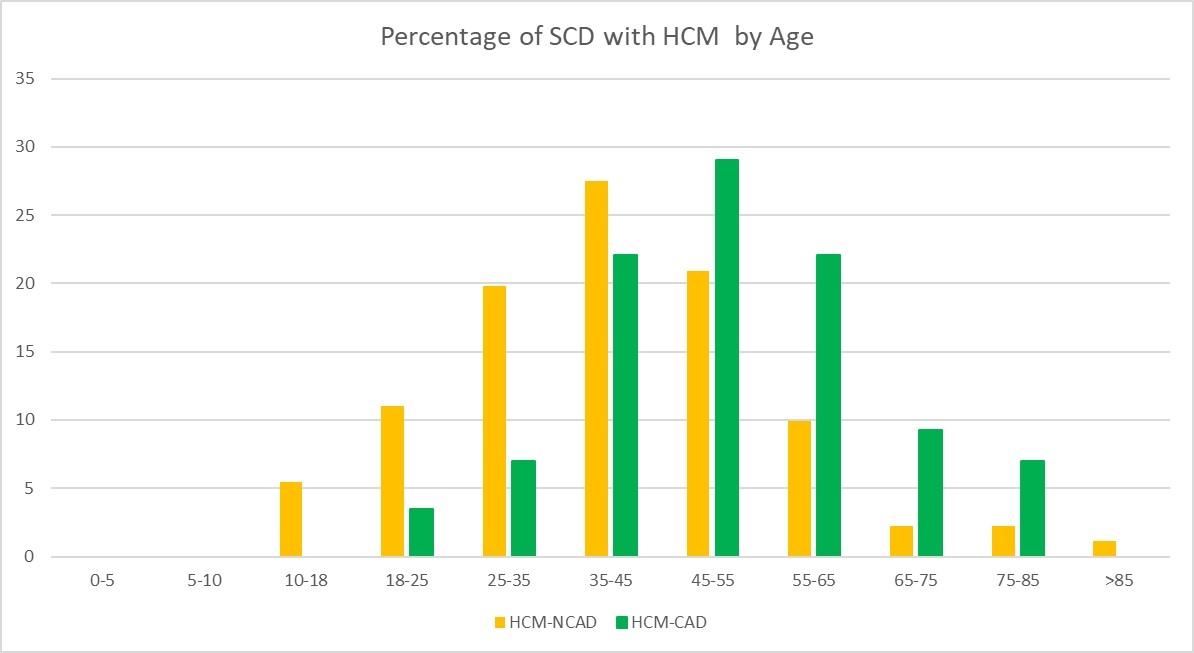
Results: A total of 5962 (male 67%, age 64±19yr, black 9%) SCD cases with detailed clinical data were evaluated and 2.9% (n=177, male 84%, age 46±16yr, black 12%) met criteria for HCM. HCM-CAD was observed in 86 (48.6%). When compared to HCM-NCAD (n=91), HCM-CAD were more likely to be male (93% vs 75.8%, p =0.002) and older (51±15 vs 41±16 years, p<0.0001) (Figure). The multivariable model showed that HCM-CAD were older (OR :1.1 [1.0-1.1]) and male (OR 5.9 [2.0-18.0]). Heart failure (OR 0.18 [0.05-0.68]) and asthma (OR 0.19 [0.05-0.71]) were more common in HCM-NCAD. Out of those with symptom data available (n=152), chest pain as a warning symptom was more common in HCM-CAD vs HCM-NCAD (20.8% vs 8%, p =0.03).
Conclusion: Approximately 50% of HCM who suffered SCD had associated significant CAD, suggesting that myocardial ischemia could be an important trigger of SCD in HCM. These findings highlight the importance of CAD as a risk modifier for SCD in HCM and should be investigated further.
Hypothesis: A large proportion of patients with HCM who suffer SCD, have associated significant CAD.
Methods: From an ongoing prospective, population-based study of SCD in the Northwestern US (catchment pop. ≈1 M, 2002-2020), we performed a case-case analysis. Comparisons of the lifetime clinical history and available autopsy findings were made between SCD cases with HCM and CAD(HCM-CAD) vs. HCM without CAD(HCM-NCAD). HCM was defined as left ventricle (LV) wall thickness ≥15mm in the absence of any other cause for LVH. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted.
Results: A total of 5962 (male 67%, age 64±19yr, black 9%) SCD cases with detailed clinical data were evaluated and 2.9% (n=177, male 84%, age 46±16yr, black 12%) met criteria for HCM. HCM-CAD was observed in 86 (48.6%). When compared to HCM-NCAD (n=91), HCM-CAD were more likely to be male (93% vs 75.8%, p =0.002) and older (51±15 vs 41±16 years, p<0.0001) (Figure). The multivariable model showed that HCM-CAD were older (OR :1.1 [1.0-1.1]) and male (OR 5.9 [2.0-18.0]). Heart failure (OR 0.18 [0.05-0.68]) and asthma (OR 0.19 [0.05-0.71]) were more common in HCM-NCAD. Out of those with symptom data available (n=152), chest pain as a warning symptom was more common in HCM-CAD vs HCM-NCAD (20.8% vs 8%, p =0.03).
Conclusion: Approximately 50% of HCM who suffered SCD had associated significant CAD, suggesting that myocardial ischemia could be an important trigger of SCD in HCM. These findings highlight the importance of CAD as a risk modifier for SCD in HCM and should be investigated further.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Polygenic Score Modifies Penetrance of Pathogenic Hypertrophic and Dilated Cardiomyopathy Variants in Opposite Directions
Abramowitz Sarah, Hoffman-andrews Lily, Depaolo John, Judy Renae, Owens Anjali, Damrauer Scott, Levin Michael
Acute Severe Mitral Regurgitation Due to Flail Posterior Leaflet without Chordal Rupture Following Myosin Inhibitor Treatment of Hypertrophic Obstructive CardiomyopathyPatel Shreyan, Taha Israa, Elmi Daniel, Shirani Jamshid