Final ID: MDP648
Short- and Long-Term Outcomes of Antegrade versus Retrograde Approaches in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for Chronic Total Occlusion: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
Chronic total occlusion (CTO) percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a complex procedure to restore blood flow in completely occluded coronary arteries with the aim of improving symptoms and quality of life. While CTO-PCI success rates have increased owing to advancements in antegrade and retrograde techniques, the choice of approach remains crucial. The antegrade approach is often the initial method chosen because of its relative simplicity, whereas the retrograde approach is considered in more complex cases or when the antegrade approach fails.
Aims
The data suggest that the retrograde approach is associated with higher periprocedural complications, although the reports are conflicting. Our meta-analysis aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of the antegrade and retrograde approaches for CTO-PCI.
Methods
A comprehensive literature search was conducted on PubMed, Embase, Google Scholar, and Scopus from inception until June 5, 2024. Pooled risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using Review Manager, with a p-value of <0.05 considered significant. Random-effects models were used for all statistical analyses.
Results
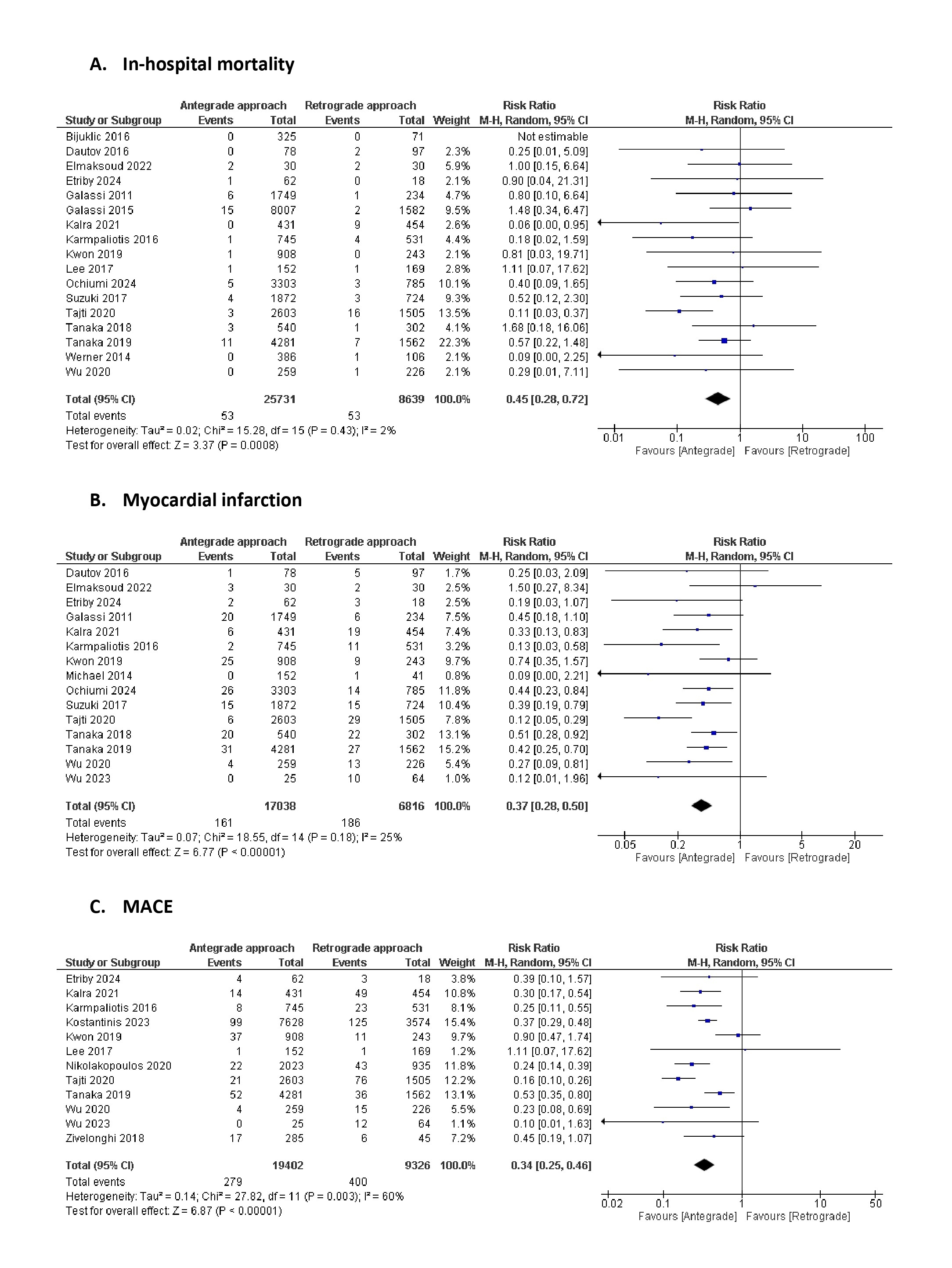
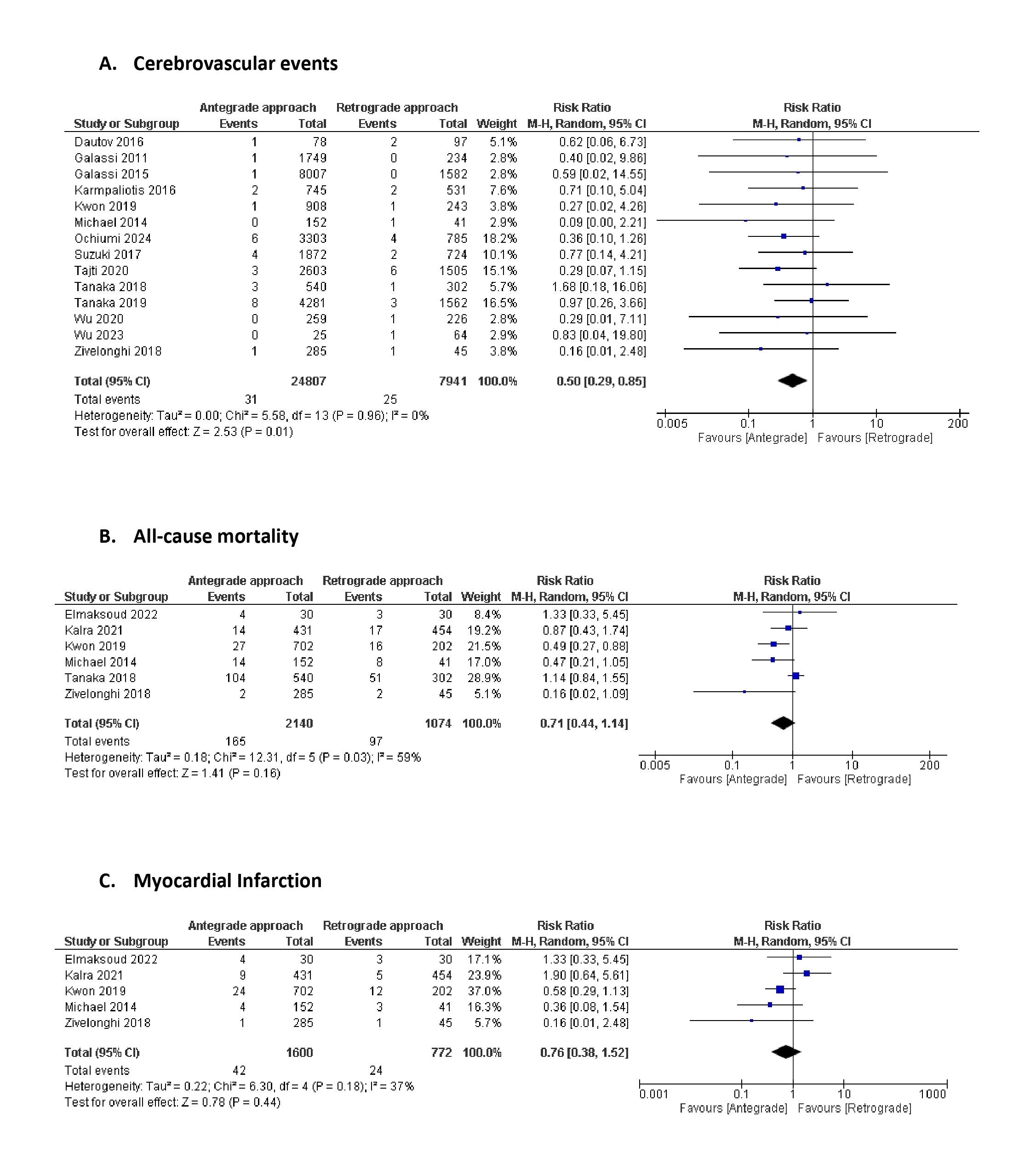
Twenty-two observational studies involving 49,152 CTO-PCI patients, with 35,844 and 13, 308 patients in the antegrade and retrograde arms, respectively, were included. The antegrade approach was associated with a significantly lower risk of in-hospital outcomes than the retrograde approach, including reduced mortality (RR=0.45, 95% CI: 0.28-0.72, p=0.0008), myocardial infarction (RR=0.37, 95% CI: 0.28-0.50, p<0.00001), major adverse cardiovascular events (RR=0.34, 95% CI: 0.25-0.46, p<0.00001), and cerebrovascular events (RR=0.50, 95% CI: 0.29-0.85, p=0.01) (Figure 1). In terms of long-term outcomes, both approaches had comparable risks for all-cause mortality (RR=0.71, 95% CI: 0.44-1.14, p=0.16) and myocardial infarction (RR=0.76, 95% CI: 0.38-1.52, p=0.44) (Figure 2).
Conclusion
The antegrade approach is associated with significantly reduced risks of several in-hospital outcomes, but both approaches have comparable risks for long-term outcomes. Skillful and judicious use of the retrograde approach for CTO-PCI is recommended.
Background
Chronic total occlusion (CTO) percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a complex procedure to restore blood flow in completely occluded coronary arteries with the aim of improving symptoms and quality of life. While CTO-PCI success rates have increased owing to advancements in antegrade and retrograde techniques, the choice of approach remains crucial. The antegrade approach is often the initial method chosen because of its relative simplicity, whereas the retrograde approach is considered in more complex cases or when the antegrade approach fails.
Aims
The data suggest that the retrograde approach is associated with higher periprocedural complications, although the reports are conflicting. Our meta-analysis aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of the antegrade and retrograde approaches for CTO-PCI.
Methods
A comprehensive literature search was conducted on PubMed, Embase, Google Scholar, and Scopus from inception until June 5, 2024. Pooled risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using Review Manager, with a p-value of <0.05 considered significant. Random-effects models were used for all statistical analyses.
Results
Twenty-two observational studies involving 49,152 CTO-PCI patients, with 35,844 and 13, 308 patients in the antegrade and retrograde arms, respectively, were included. The antegrade approach was associated with a significantly lower risk of in-hospital outcomes than the retrograde approach, including reduced mortality (RR=0.45, 95% CI: 0.28-0.72, p=0.0008), myocardial infarction (RR=0.37, 95% CI: 0.28-0.50, p<0.00001), major adverse cardiovascular events (RR=0.34, 95% CI: 0.25-0.46, p<0.00001), and cerebrovascular events (RR=0.50, 95% CI: 0.29-0.85, p=0.01) (Figure 1). In terms of long-term outcomes, both approaches had comparable risks for all-cause mortality (RR=0.71, 95% CI: 0.44-1.14, p=0.16) and myocardial infarction (RR=0.76, 95% CI: 0.38-1.52, p=0.44) (Figure 2).
Conclusion
The antegrade approach is associated with significantly reduced risks of several in-hospital outcomes, but both approaches have comparable risks for long-term outcomes. Skillful and judicious use of the retrograde approach for CTO-PCI is recommended.
More abstracts on this topic:
Angiographic and Clinical Outcomes with Drug-Coated Balloon Versus Drug-Eluting Stents for In-Stent Restenosis: A Meta-Analysis
Jain Hritvik, Passey Siddhant, Odat Ramez, Pervez Neha, Goyal Aman, Jain Jyoti, Patel Nandan, Yadav Ashish, Shah Janhvi, Jha Jagriti
Left Ventricular Thrombus and Occluded Coronary Artery in a Patient with JAK2 V617F MutationAlawneh Omar, Khayata Mohamed