Final ID: Mo1138
Efficacy and Safety of Rivaroxaban and Lower Molecular Weight Heparin in Preventing Venous Thromboembolism in Cancer Patients; A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
As per current guidelines, low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) has been commonly used as prophylaxis for venous thromboembolism in cancer patients. Directly acting anticoagulants (DOACs) having ease of administration, oral availability despite renal dysfunction, and possibly higher adherence, are also being used as an alternative to prevent venous thromboembolism Events (VTE) recently. In addition, rivaroxaban is among the first DOACs used in the prophylaxis for VTE.
Hypothesis:
This study intends to compare the efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban and LMWH (enoxaparin, dalteparin, and nadroparin) in preventing VTE in cancer patients.
Methods:
A comprehensive literature search was performed on PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and Cochrane libraries from inception until March 2024, with suitable Mesh terms. The random effects model was used to calculate the pooled Odds Ratio (OR) with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI). A p-value of <0.005 was considered statistically significant.
Results:
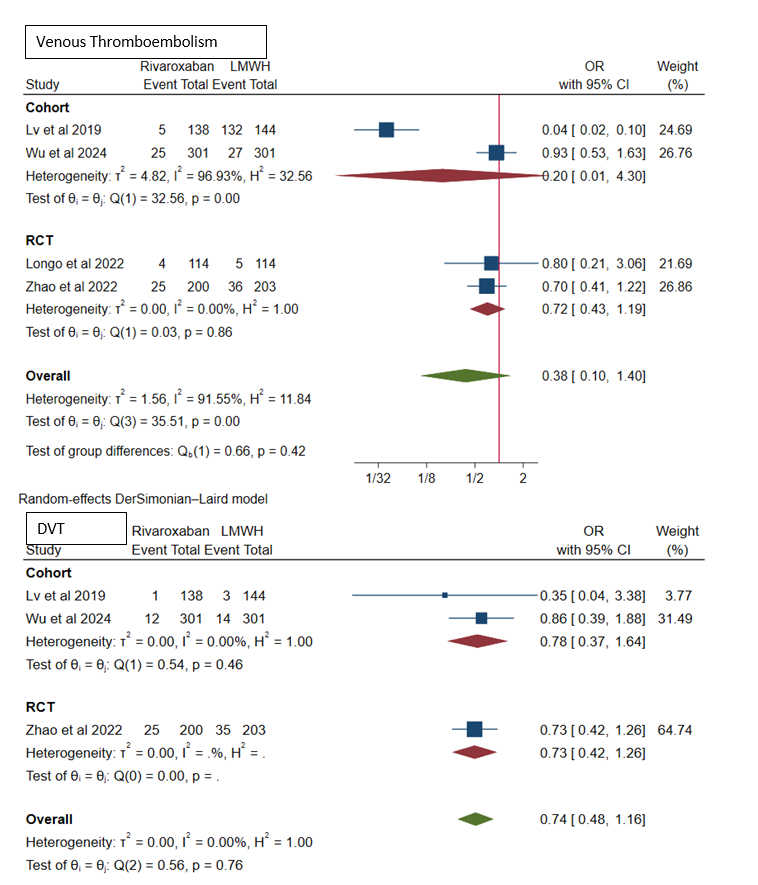
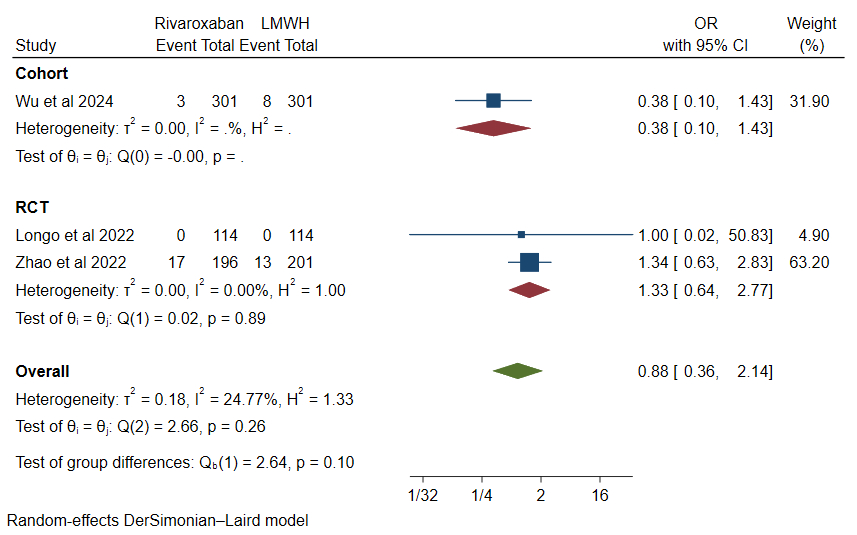
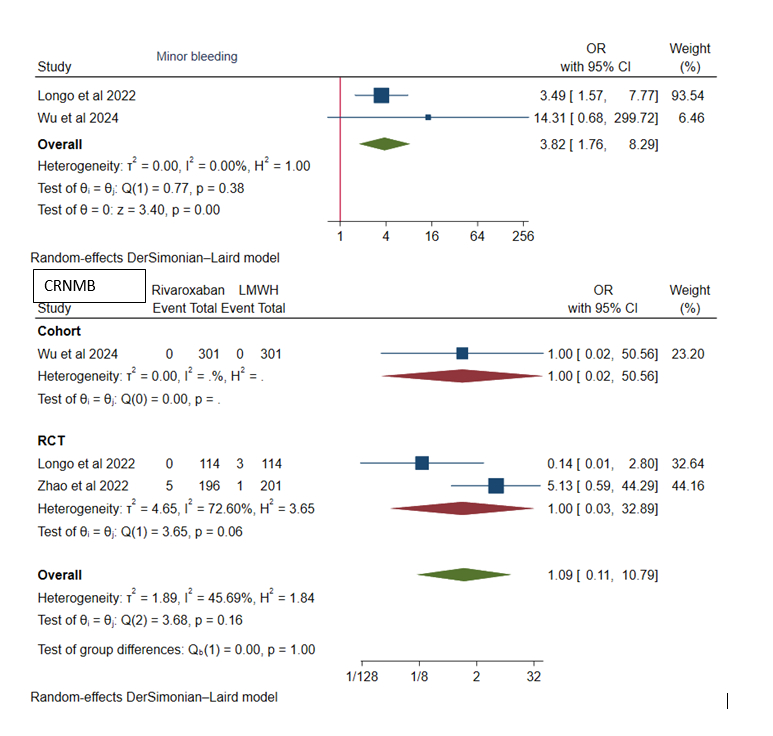
Four studies including two cohort studies and two Randomized Controlled trials (RCTs) with 1515 patients (rivaroxaban: 753 and LMWH: 762) with mean ages of 58.15 and 58.6 years respectively were included in the analysis. Up to 30 days after follow-up, the rates of VTE (OR, 0.38, 95% CI: 0.10 – 1.40, p=0.42), DVT (OR, 0.74, 95% CI: 0.48 – 1.16, p= 0.76) and major bleed (OR, 0.88, 95% CI: 0.36 – 2.14, p=0.26) were lower with rivaroxaban compared to LMWH. But, the minor bleeds (OR, 3.82, 95% CI: 1.76 – 8.29, p=0.38), clinically relevant non-major bleeding (CRNMB) (OR, 1.09, 95% CI: 0.11 – 10.79, p=0.16), bleeding (major + CRNMB) (OR, 1.47, 95% CI: 0.82 – 2.61, p=0.27), all-cause mortality (OR, 1.17, 95% CI: 0.70 – 1.96, p=0.54) were higher with rivaroxaban compared to LMWH.
Conclusion: In cancer patients for the prevention of venous thromboembolism, rivaroxaban shows non-inferior efficacy and questionable safety profile as compared to LMWH. Further research needs to be done to confirm the above findings.
As per current guidelines, low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) has been commonly used as prophylaxis for venous thromboembolism in cancer patients. Directly acting anticoagulants (DOACs) having ease of administration, oral availability despite renal dysfunction, and possibly higher adherence, are also being used as an alternative to prevent venous thromboembolism Events (VTE) recently. In addition, rivaroxaban is among the first DOACs used in the prophylaxis for VTE.
Hypothesis:
This study intends to compare the efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban and LMWH (enoxaparin, dalteparin, and nadroparin) in preventing VTE in cancer patients.
Methods:
A comprehensive literature search was performed on PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and Cochrane libraries from inception until March 2024, with suitable Mesh terms. The random effects model was used to calculate the pooled Odds Ratio (OR) with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI). A p-value of <0.005 was considered statistically significant.
Results:
Four studies including two cohort studies and two Randomized Controlled trials (RCTs) with 1515 patients (rivaroxaban: 753 and LMWH: 762) with mean ages of 58.15 and 58.6 years respectively were included in the analysis. Up to 30 days after follow-up, the rates of VTE (OR, 0.38, 95% CI: 0.10 – 1.40, p=0.42), DVT (OR, 0.74, 95% CI: 0.48 – 1.16, p= 0.76) and major bleed (OR, 0.88, 95% CI: 0.36 – 2.14, p=0.26) were lower with rivaroxaban compared to LMWH. But, the minor bleeds (OR, 3.82, 95% CI: 1.76 – 8.29, p=0.38), clinically relevant non-major bleeding (CRNMB) (OR, 1.09, 95% CI: 0.11 – 10.79, p=0.16), bleeding (major + CRNMB) (OR, 1.47, 95% CI: 0.82 – 2.61, p=0.27), all-cause mortality (OR, 1.17, 95% CI: 0.70 – 1.96, p=0.54) were higher with rivaroxaban compared to LMWH.
Conclusion: In cancer patients for the prevention of venous thromboembolism, rivaroxaban shows non-inferior efficacy and questionable safety profile as compared to LMWH. Further research needs to be done to confirm the above findings.
More abstracts on this topic:
4D Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Identifies Differences in Regional Strain Patterns Among Pediatric Heart Transplant Patients with Acute Rejection or Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy
Henderson Christopher, Starnes Joseph, Samyn Margaret, Damon Bruce, Hernandez Lazaro, Goergen Craig, Soslow Jonathan, Prado Marco Aurélio, Earl Conner, Georgedurrett Kristen, Lee Simon, Nandi Deipanjan, Chan Kak-chen, Shugh Svetlana, Kikano Sandra
A Novel Missense Mutation in TNNT2 Gene in a Lebanese Pedigree With Ebstein Anomaly And Wolf-Parkinson-White Syndrome: A Case ReportAtasi Montaser, Dankar Razan, Barakat Salim, Wehbi Jad, Refaat Marwan