Final ID: MDP1313
Additive Prognostic Significance of Vascular Disease in Patients Referred for Exercise Stress Echocardiography
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The presence of carotid plaque (CP) may serve as an indicator of panvascular atherosclerosis. However, the observed incongruity between carotid disease and the presence and severity of coronary artery disease (CAD) suggests differing mechanisms. We investigated the prognostic value of this incongruity, considering both known atherosclerosis and myocardial ischemia.
Methods: In a retrospective analysis, we examined 111 patients (mean age: 64±12 years, 58% women) who underwent exercise stress echocardiography, with recent carotid artery and coronary evaluation. We computed a Vascular Disease (VasD) score, integrating the presence of carotid plaque (CP) on carotid ultrasound, known coronary artery disease (CAD), and myocardial ischemia (MyI). Subsequently, patients were followed for 5.5 years for mortality, coronary revascularization, and cardiac hospitalization.
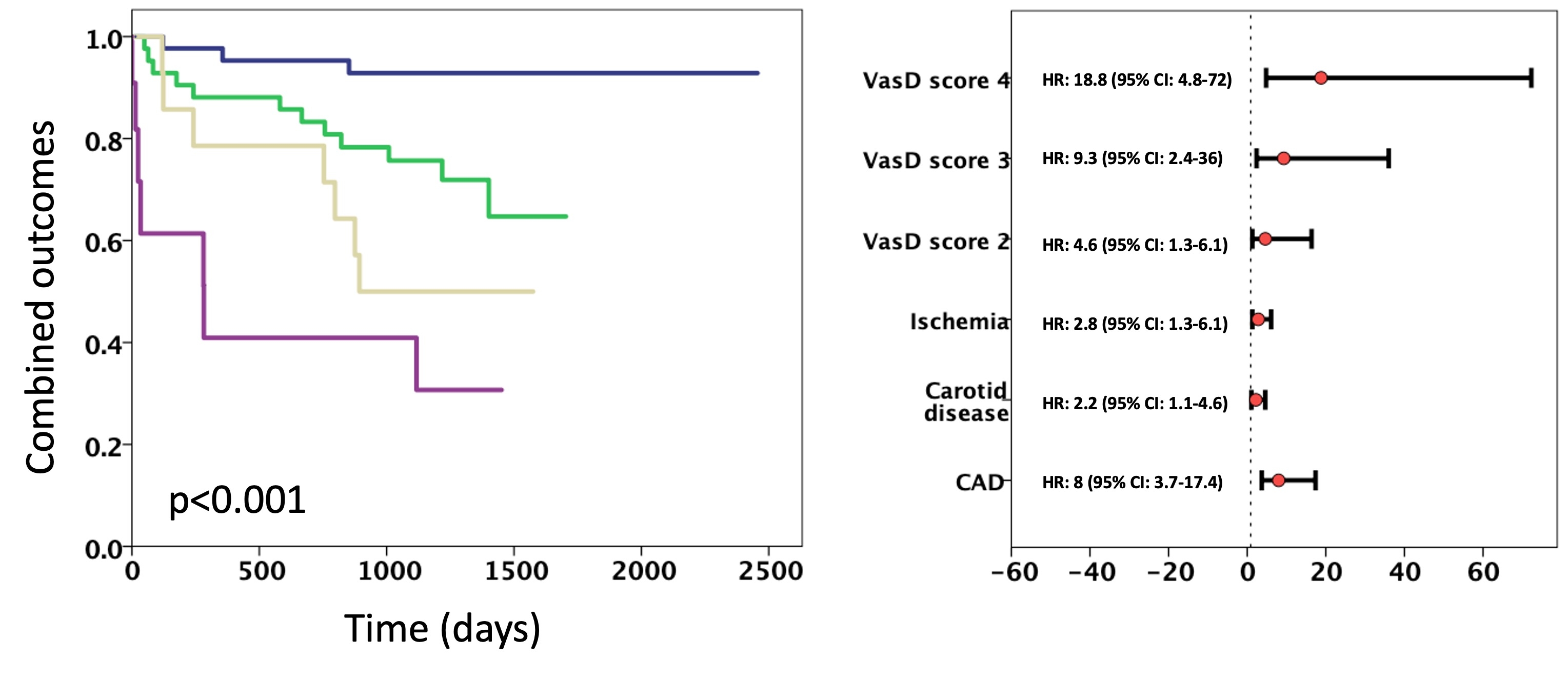
Results: During the follow-up period, 29 patients experienced the combined outcome (4 deaths, 10 revascularizations, and 22 hospitalizations). Among the cohort, 44 patients exhibited no vascular disease, while 67 displayed evidence of vascular disease, categorized as 42 with VasD of 1 (comprising 30 CP, 9 CAD, and 3 MyI), 14 with VasD of 2 (5 CP and CAD, 6 CP and MyI, 3 CAD and MyI), and 11 with VasD of 3. There were no significant differences between patients with and without VasD concerning sex, diabetes, renal function, atrial arrhythmia, baseline LVEF, and baseline diastolic function. However, patients with VasD were older, had higher H2FPEF scores, and lower exercise capacity, as well as elevated baseline and exercise-induced filling pressures. The incidence of the combined outcome showed a progressive increase with higher VasD scores (p<0.001). Survival curves depicted a rising risk of the outcome corresponding to increasing VasD scores (Figure 1).
Conclusions:
The presence of vascular disease as quantified by known CAD, CP as detected by carotid ultrasound, and myocardial ischemia identified during exercise stress echocardiography demonstrates a substantial additive prognostic role in mid-term cardiovascular outcomes.
Methods: In a retrospective analysis, we examined 111 patients (mean age: 64±12 years, 58% women) who underwent exercise stress echocardiography, with recent carotid artery and coronary evaluation. We computed a Vascular Disease (VasD) score, integrating the presence of carotid plaque (CP) on carotid ultrasound, known coronary artery disease (CAD), and myocardial ischemia (MyI). Subsequently, patients were followed for 5.5 years for mortality, coronary revascularization, and cardiac hospitalization.
Results: During the follow-up period, 29 patients experienced the combined outcome (4 deaths, 10 revascularizations, and 22 hospitalizations). Among the cohort, 44 patients exhibited no vascular disease, while 67 displayed evidence of vascular disease, categorized as 42 with VasD of 1 (comprising 30 CP, 9 CAD, and 3 MyI), 14 with VasD of 2 (5 CP and CAD, 6 CP and MyI, 3 CAD and MyI), and 11 with VasD of 3. There were no significant differences between patients with and without VasD concerning sex, diabetes, renal function, atrial arrhythmia, baseline LVEF, and baseline diastolic function. However, patients with VasD were older, had higher H2FPEF scores, and lower exercise capacity, as well as elevated baseline and exercise-induced filling pressures. The incidence of the combined outcome showed a progressive increase with higher VasD scores (p<0.001). Survival curves depicted a rising risk of the outcome corresponding to increasing VasD scores (Figure 1).
Conclusions:
The presence of vascular disease as quantified by known CAD, CP as detected by carotid ultrasound, and myocardial ischemia identified during exercise stress echocardiography demonstrates a substantial additive prognostic role in mid-term cardiovascular outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Accumulation of Epicardial Adipose Tissue as a Marker of Diastolic Dysfunction in Patients With Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Undergoing Coronary Computed Tomography Angiograph
Ishikawa Hirotoshi, Kasayuki Noriaki, Fukuda Daiju, Otsuka Kenichiro, Sugiyama Takatoshi, Yamaura Hiroki, Hojo Kana, Kawa Yoshinori, Shintani Ako, Ito Asahiro, Yamazaki Takanori
A Silent Storm: Incidental Discovery of IVC and Right Atrium Thrombus in a Patient with Uterine Stromal SarcomaWasef Natale, Fatima Tehreem, Stys Adam