Final ID: MDP1212
Moderate renal dysfunction is independently associated with increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest but only in males
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Moderate renal dysfunction is independently associated with increased cardiovascular mortality. Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) accounts for at least 25% of chronic kidney disease (CKD) mortality. However, there is a lack of population based studies evaluating a potential association between moderate CKD and SCA.
Hypothesis
Moderate CKD is associated with SCA in the general population.
Methods
We conducted a case-control study from an ongoing, prospective community-based study of SCA in the US Northwest (catchment population ~1 million; 2002-2020). Cases were individuals who suffered SCA aged 40 to 85 years, who had detailed medical records available, and serum creatinine levels measured before their SCA event. Control participants had no history of SCA and were recruited from the same geographical area. Cases and controls were frequency-matched by age and sex in a 3:1 ratio. Moderate CKD was defined as eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 using the CKD-EPI 2021 formula.
Results
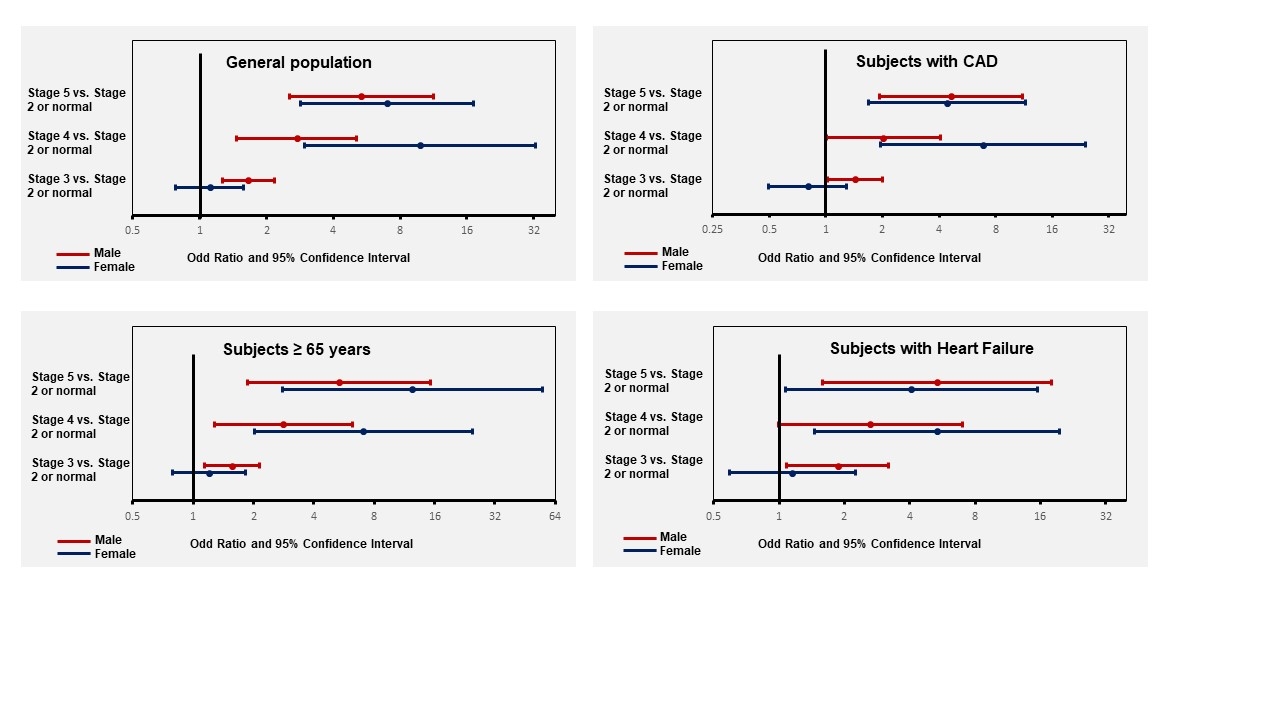
We compared 2729 SCA cases and 1097 controls, with mean ages of 65.9 and 66.4 years, and male percentages of 68.6% and 66.1%, respectively. SCA cases had higher proportion of moderate CKD (22.8 vs. 18.0%, p=0.001) and lower eGFR (69.3 [44.8-89.7] vs. 77.6 [63.6-90.7] mL/min/1.73 m2, p<0.001) than controls. Multivariable regression analysis adjusted for demographics (age, sex, race) and comorbidities showed that both moderate and severe CKD were independent risk factors for SCA with an odds ratio (OR) of 1.43 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.16-1.76) and 4.94 (95% CI 3.29-7.39), respectively. Moderate CKD was associated with SCA in male (OR 1.65, 9% CI 1.26-2.166) but not female individuals (OR 1.11, 95%CI 0.78-1.57) whereas SCA risk was similarly increased for men and women with more severe CKD. These findings were consistent across different high-risk populations (Figure).
Conclusion
Both moderate and severe CKD are associated with SCA in the general population, but females with moderate CKD appear to be protected. These findings of possible renal involvement in SCA, even during early stages of CKD, warrant further investigation.
Moderate renal dysfunction is independently associated with increased cardiovascular mortality. Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) accounts for at least 25% of chronic kidney disease (CKD) mortality. However, there is a lack of population based studies evaluating a potential association between moderate CKD and SCA.
Hypothesis
Moderate CKD is associated with SCA in the general population.
Methods
We conducted a case-control study from an ongoing, prospective community-based study of SCA in the US Northwest (catchment population ~1 million; 2002-2020). Cases were individuals who suffered SCA aged 40 to 85 years, who had detailed medical records available, and serum creatinine levels measured before their SCA event. Control participants had no history of SCA and were recruited from the same geographical area. Cases and controls were frequency-matched by age and sex in a 3:1 ratio. Moderate CKD was defined as eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 using the CKD-EPI 2021 formula.
Results
We compared 2729 SCA cases and 1097 controls, with mean ages of 65.9 and 66.4 years, and male percentages of 68.6% and 66.1%, respectively. SCA cases had higher proportion of moderate CKD (22.8 vs. 18.0%, p=0.001) and lower eGFR (69.3 [44.8-89.7] vs. 77.6 [63.6-90.7] mL/min/1.73 m2, p<0.001) than controls. Multivariable regression analysis adjusted for demographics (age, sex, race) and comorbidities showed that both moderate and severe CKD were independent risk factors for SCA with an odds ratio (OR) of 1.43 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.16-1.76) and 4.94 (95% CI 3.29-7.39), respectively. Moderate CKD was associated with SCA in male (OR 1.65, 9% CI 1.26-2.166) but not female individuals (OR 1.11, 95%CI 0.78-1.57) whereas SCA risk was similarly increased for men and women with more severe CKD. These findings were consistent across different high-risk populations (Figure).
Conclusion
Both moderate and severe CKD are associated with SCA in the general population, but females with moderate CKD appear to be protected. These findings of possible renal involvement in SCA, even during early stages of CKD, warrant further investigation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Buccal epithelium protein map changes precede clinical manifestation of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathies
Jager Joanna, Moscatelli Sara, Bueno Beti Carlos, Field Ella, Luedke Leonie, Behr Elijah, Kaski Juan Pablo, Asimaki Angeliki
Effects of Empagliflozin on diuresis in heart failure: Results from the CINNAMON-study and in-vivo experimentsSinha Frederick, Klatt Susanne, Rietmann Alexander, Schoepperl Anna, Born Sebastian, Maier Lars, Schweda Frank, Wagner Stefan