Final ID: Mo2044
Risk Factors for Adverse Outcomes in a Fontan Population
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction/Background
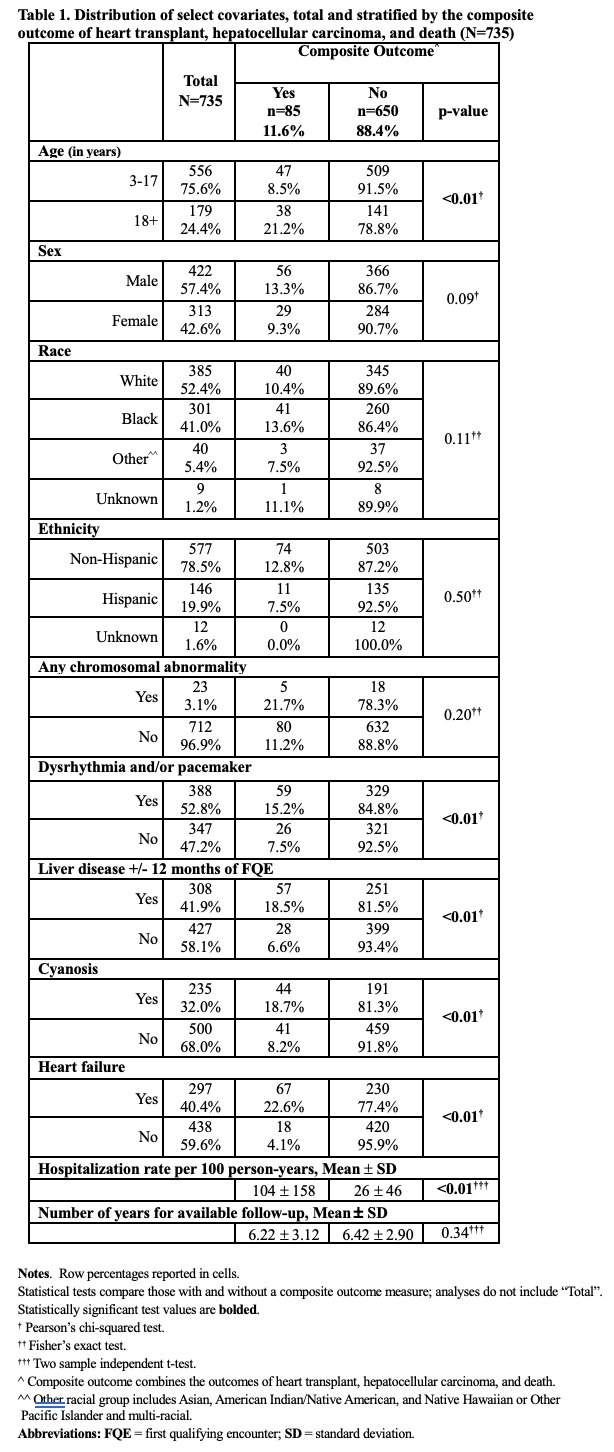
Improved survival following Fontan surgery has been tempered by Fontan failure. Heterogenous multi-organ complications varying over time have limited study of Fontan failure. We sought to identify complications associated with hospitalization.
Methods/Approach
A retrospective cohort of 735 pediatric and adult Fontan patients were identified from two healthcare systems (median age 7yrs, IQR 14, 57.4% male, 41.0% black). The deduplicated cohort was linked to 2010-2019 encounters from both healthcare systems (one pediatric, one adult) and to death certificates to capture vital status. ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM codes were mapped by clinicians to capture variables of interest. Bivariate analyses were conducted to examine select covariates by the composite outcome which includes heart transplant, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and death during the surveillance period; group differences were examined using chi-square, Fisher exact and independent t-tests. Negative binomial regression evaluated the association between select characteristics and hospitalization rates with adjustment.
Results/Data
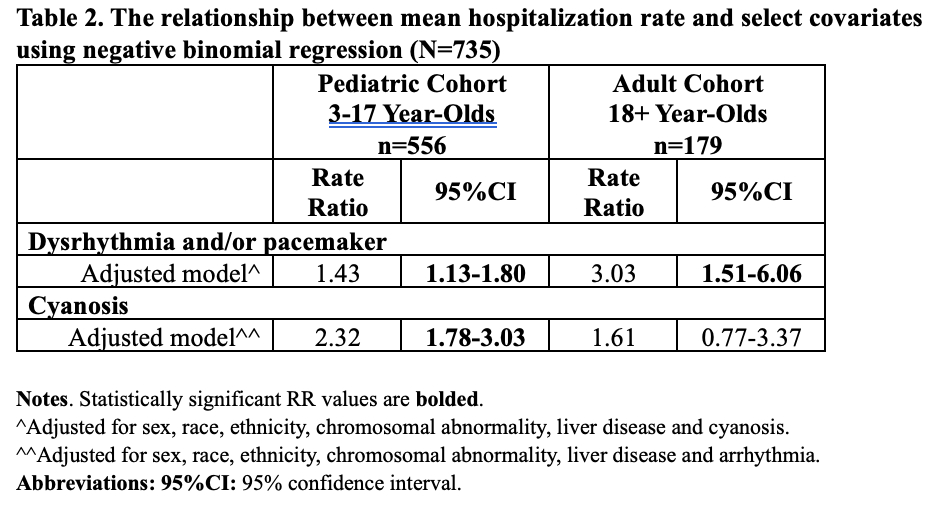
Of 735 Fontan patients,11.6% experienced the primary outcomes (median age 14yrs, IQR 17). Characteristics significantly associated with the composite outcome included older age, dysrhythmia, liver disease, cyanosis and heart failure (Table 1). Modeling showed increased rates of hospitalization for children with dysrhythmia (RR=1.43, 95%CI 1.13-1.80) and cyanosis (RR=2.32, 95%CI 1.78-3.03) adjusting for potential confounders (Table 2). This association remained for adults, however, after adjustment, the association of cyanosis and hospitalization rate was attenuated.
Conclusion
Fontan patients with dysrhythmia, liver disease, cyanosis and heart failure are at an increased risk for heart transplant, HCC, and death, and have higher hospitalization rates. Incorporation of these factors into the definition of Fontan failure may help early identification and intervention.
Improved survival following Fontan surgery has been tempered by Fontan failure. Heterogenous multi-organ complications varying over time have limited study of Fontan failure. We sought to identify complications associated with hospitalization.
Methods/Approach
A retrospective cohort of 735 pediatric and adult Fontan patients were identified from two healthcare systems (median age 7yrs, IQR 14, 57.4% male, 41.0% black). The deduplicated cohort was linked to 2010-2019 encounters from both healthcare systems (one pediatric, one adult) and to death certificates to capture vital status. ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM codes were mapped by clinicians to capture variables of interest. Bivariate analyses were conducted to examine select covariates by the composite outcome which includes heart transplant, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and death during the surveillance period; group differences were examined using chi-square, Fisher exact and independent t-tests. Negative binomial regression evaluated the association between select characteristics and hospitalization rates with adjustment.
Results/Data
Of 735 Fontan patients,11.6% experienced the primary outcomes (median age 14yrs, IQR 17). Characteristics significantly associated with the composite outcome included older age, dysrhythmia, liver disease, cyanosis and heart failure (Table 1). Modeling showed increased rates of hospitalization for children with dysrhythmia (RR=1.43, 95%CI 1.13-1.80) and cyanosis (RR=2.32, 95%CI 1.78-3.03) adjusting for potential confounders (Table 2). This association remained for adults, however, after adjustment, the association of cyanosis and hospitalization rate was attenuated.
Conclusion
Fontan patients with dysrhythmia, liver disease, cyanosis and heart failure are at an increased risk for heart transplant, HCC, and death, and have higher hospitalization rates. Incorporation of these factors into the definition of Fontan failure may help early identification and intervention.
More abstracts on this topic:
Aerobic Capacity of Adults with Fontan Palliation: Disease-specific Reference Values and Relationship to Outcomes
Ali Ahmed, Goda Ahmed, Abozied Omar, Egbe Alexander
A Novel Cardiac Simulator "ped UT-Heart" to Support Decision-Making in Surgical Procedures for Complex Congenital Heart DiseaseShiraishi Isao, Kurosaki Kenichi, Iwai Shigemitsu, Washio Takumi, Sugiura Seiryo, Hisada Toshiaki