Final ID: Mo2041
Women with Severe Congenital Heart Disease Have Increased Risk of Fetal/Neonatal Death
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Women with congenital heart defects (CHD) now routinely survive to reproductive age. Offspring of these women have more complications, including but not limited to inherited CHD, prematurity, small for gestational age (SGA), and fetal/neonatal death. In the United States, pregnancy-related complications and death are more common in Black women and their offspring compared to White women and their offspring, and in those residing in rural areas compared to urban areas.
Aims: This study evaluates fetal/neonatal outcomes among women with CHD covered by Georgia Medicaid at the time of pregnancy, looking for differences among racial, geographic, and CHD severity groups.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study identified 4581 women with CHD aged 11-50 with 6522 pregnancies (28.5% with severe CHD, 50.9% Black, 23.2% rural) covered by Georgia Medicaid between 2008-2019. Fetal/neonatal death, defined as fetal death after 20 weeks gestation, stillbirth, or neonatal death, was examined by CHD severity, race, and rurality using chi-square analysis. Multivariate logistic regression models were conducted adjusting for age at first documented pregnancy, social deprivation index (SDI), number of pregnancies, and multiple gestations.
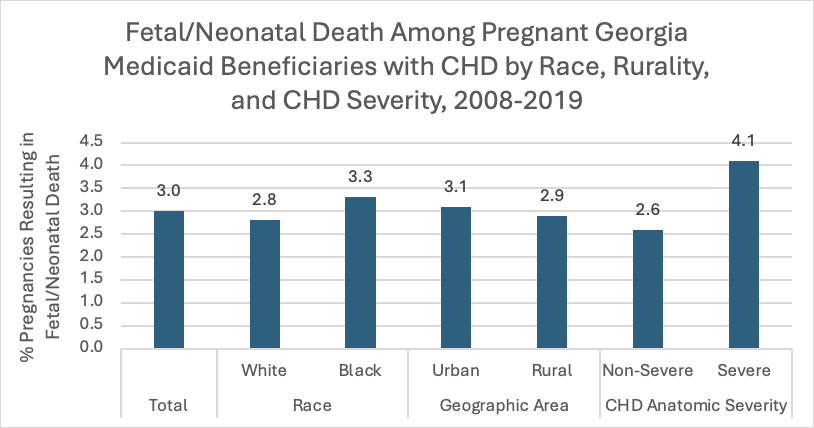
Results: Of 6522 pregnancies, 3.0% resulted in fetal/neonatal death. Fetal/neonatal death was more common in women with severe CHD compared to those with non-severe CHD (4.1% severe vs. 2.6% non-severe [aOR 1.39, 95% CI 1.02-1.85, p = 0.0018]). No significant differences were revealed in fetal/neonatal death between racial (3.3% Black vs. 2.8% White) or geographic (2.9% rural vs. 3.1% urban) groups after controlling for other variables.
Conclusions: Compared to reported fetal and neonatal death rates among all U.S. pregnancies in 2019, women with CHD experienced a higher rate of fetal/neonatal death. Fetal/neonatal death was even more prevalent for women with severe CHD (4.1%) versus women with non-severe CHD (2.6%). Women with CHD, especially those with severe disease, have a high risk of fetal/neonatal death and should be monitored closely throughout the course of pregnancy.
Aims: This study evaluates fetal/neonatal outcomes among women with CHD covered by Georgia Medicaid at the time of pregnancy, looking for differences among racial, geographic, and CHD severity groups.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study identified 4581 women with CHD aged 11-50 with 6522 pregnancies (28.5% with severe CHD, 50.9% Black, 23.2% rural) covered by Georgia Medicaid between 2008-2019. Fetal/neonatal death, defined as fetal death after 20 weeks gestation, stillbirth, or neonatal death, was examined by CHD severity, race, and rurality using chi-square analysis. Multivariate logistic regression models were conducted adjusting for age at first documented pregnancy, social deprivation index (SDI), number of pregnancies, and multiple gestations.
Results: Of 6522 pregnancies, 3.0% resulted in fetal/neonatal death. Fetal/neonatal death was more common in women with severe CHD compared to those with non-severe CHD (4.1% severe vs. 2.6% non-severe [aOR 1.39, 95% CI 1.02-1.85, p = 0.0018]). No significant differences were revealed in fetal/neonatal death between racial (3.3% Black vs. 2.8% White) or geographic (2.9% rural vs. 3.1% urban) groups after controlling for other variables.
Conclusions: Compared to reported fetal and neonatal death rates among all U.S. pregnancies in 2019, women with CHD experienced a higher rate of fetal/neonatal death. Fetal/neonatal death was even more prevalent for women with severe CHD (4.1%) versus women with non-severe CHD (2.6%). Women with CHD, especially those with severe disease, have a high risk of fetal/neonatal death and should be monitored closely throughout the course of pregnancy.
More abstracts on this topic:
β1 integrins regulate cellular behavior and cardiomyocyte organization during ventricular wall formation
Miao Lianjie, Schwartz Robert, R Burns Alan, Kumar Ashok, Dipersio C. Michael, Wu Mingfu, Lu Yangyang, Nusrat Anika, Zhao Luqi, Castillo Micah, Xiao Yongqi, Guo Hongyan, Liu Yu, Gunaratne Preethi
A Failure to Increase Glomerular Filtration Rate during Pregnancy Results in a Greater Susceptibility to Kidney Damage and Renal Impairment in Response to a Postpartum High Salt DietRittmeyer William, Murders Evan, Tchangwa Marvin, Engelbrecht Evan, Humphrey Riley, Mantilla Katherine, Nist Kayla, Brooks Heddwen, Dasinger John Henry