Final ID: MDP1761
Atrial Function Improves Stroke Prediction in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Stroke contributes to significant morbidity and mortality in atrial fibrillation (AF). Clinical risk scores lack predictive accuracy and mechanistic links to thrombo-embolization.
Hypothesis
Adding MRI-derived parameters to stroke risk calculators improves their predictive accuracy.
Aims
Demonstrate an association between left atrial emptying fraction (LAEF), long axis strain (LAS) and stroke in AF patients.
Incorporating the above-mentioned LARF and LAS into the CHA2DVASc score improves its predictive accuracy.
Methods
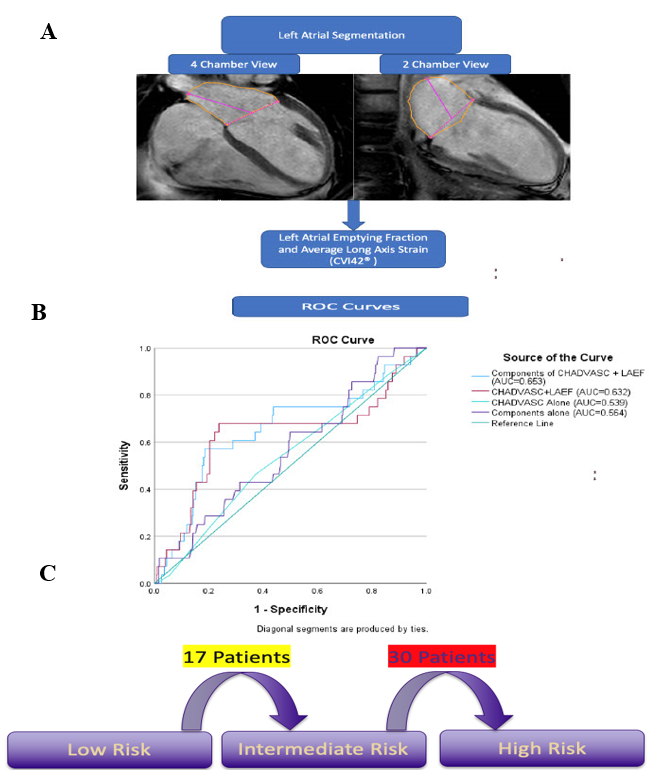
AF patients undergoing cardiac MRI were identified from the University of Washington Cardiac Arrhythmia Data Repository (CADRe). Pts with prior AF ablation were excluded from the study. LAEF and LAS were quantified using a semi-automated contouring of the LA wall was done through image processing software (CVI42®) (Panel A).
Results
417 pts (average age 66±13years; 64% males) were included. The average CHA2DVASc (stroke component removed) score was 2.1±1.4. LAEF was 46.18%±11.64%, and LA LAS was 24.28%±13.45%. Univariate analysis revealed a significant association between stroke/TIA and LAEF (OR= 0.962, p= 0.024); but not with LAS (OR=0.962, p=0.091) or CHA2DVASc (OR=1.084; p=0.553). LAEF remained significantly associated with stroke in multivariate analysis, adjusting for age, gender, congestive heart failure, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and diabetes, (OR= 0.963, p= 0.042). Three other models including composite CHA2DVASc with and without LAEF with their respective ROC curves and AUC are shown in Panel B. Adding LAEF improved the AUC of CHA2DVASc (AUC 0.564 vs 0.653; p=0.048) or its components (AUC 0.539 vs 0.632; p=0.043). Using a cut-off LAEF of 46.53% (AUC: 0.71 CI: 0.61,0.81; Sensitivity: 68%; Specificity: 74%) resulted in the reclassification of 47(11.3%) pts to a higher risk category and none (0%) to lower risk (Panel C).
Conclusion
Left atrial emptying fraction is independently associated with stroke or TIA, and improves the predictive accuracy of clinical risk scores in AF pts.
Stroke contributes to significant morbidity and mortality in atrial fibrillation (AF). Clinical risk scores lack predictive accuracy and mechanistic links to thrombo-embolization.
Hypothesis
Adding MRI-derived parameters to stroke risk calculators improves their predictive accuracy.
Aims
Demonstrate an association between left atrial emptying fraction (LAEF), long axis strain (LAS) and stroke in AF patients.
Incorporating the above-mentioned LARF and LAS into the CHA2DVASc score improves its predictive accuracy.
Methods
AF patients undergoing cardiac MRI were identified from the University of Washington Cardiac Arrhythmia Data Repository (CADRe). Pts with prior AF ablation were excluded from the study. LAEF and LAS were quantified using a semi-automated contouring of the LA wall was done through image processing software (CVI42®) (Panel A).
Results
417 pts (average age 66±13years; 64% males) were included. The average CHA2DVASc (stroke component removed) score was 2.1±1.4. LAEF was 46.18%±11.64%, and LA LAS was 24.28%±13.45%. Univariate analysis revealed a significant association between stroke/TIA and LAEF (OR= 0.962, p= 0.024); but not with LAS (OR=0.962, p=0.091) or CHA2DVASc (OR=1.084; p=0.553). LAEF remained significantly associated with stroke in multivariate analysis, adjusting for age, gender, congestive heart failure, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and diabetes, (OR= 0.963, p= 0.042). Three other models including composite CHA2DVASc with and without LAEF with their respective ROC curves and AUC are shown in Panel B. Adding LAEF improved the AUC of CHA2DVASc (AUC 0.564 vs 0.653; p=0.048) or its components (AUC 0.539 vs 0.632; p=0.043). Using a cut-off LAEF of 46.53% (AUC: 0.71 CI: 0.61,0.81; Sensitivity: 68%; Specificity: 74%) resulted in the reclassification of 47(11.3%) pts to a higher risk category and none (0%) to lower risk (Panel C).
Conclusion
Left atrial emptying fraction is independently associated with stroke or TIA, and improves the predictive accuracy of clinical risk scores in AF pts.
More abstracts on this topic:
A comparison of the efficacy of initial high energy versus initial low energy biphasic shocks for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter – a real-life experience
Alampoondi Venkataramanan Sai Vikram, Vunnam Ramarao, Voruganti Dinesh, Tsai Shane
4D Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Identifies Differences in Regional Strain Patterns Among Pediatric Heart Transplant Patients with Acute Rejection or Cardiac Allograft VasculopathyHenderson Christopher, Starnes Joseph, Samyn Margaret, Damon Bruce, Hernandez Lazaro, Goergen Craig, Soslow Jonathan, Prado Marco Aurélio, Earl Conner, Georgedurrett Kristen, Lee Simon, Nandi Deipanjan, Chan Kak-chen, Shugh Svetlana, Kikano Sandra