Final ID: MDP1573
Long-term Effect of Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Using CT Angiography on Mortality and Cardiac Events in High-risk Patients with Diabetes: the FACTOR-64 Follow-up Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The FACTOR-64 study was a randomized controlled trial designed to assess whether routine screening for CAD by coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) in high-risk patients with diabetes followed by CCTA-directed therapy would reduce the risk of death and nonfatal coronary outcomes. Results at four years showed a lower revascularization rate (3.1% (14) vs. 8.9% (40), p<0.005) among the control group. But there was also a non-significant trend toward a lower incidence of all-cause mortality and nonfatal MI (hazard ratio, 0.82 [95% CI, 0.49-1.32]; p=0.38). Whether screening CCTA might have a more significant effect on the outcomes of patients after longer follow-up is unknown.
Methods: The FACTOR-64 study randomized 900 patients (age = 61.5 years, males = 52%, Type 2 DM = 88%, DM duration = 13 years) with type 1 or type 2 diabetes for at least 3 to 5 years without CAD symptoms to screening with CCTA (n = 452) or standard national guidelines-based optimal diabetes care (n = 448). Standard primary prevention medical therapy or aggressive secondary prevention therapy with invasive coronary angiography was recommended based on CCTA findings. Enrollment occurred between July 2007 and May 2013, and follow-up extended to May 2024.
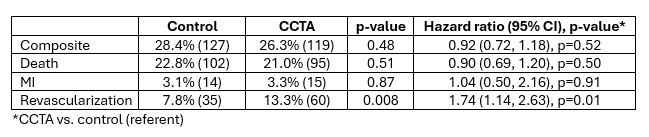
Results: The mean follow-up time was 12.7±3.2 (CCTA=12.8±3.1; control=12.6±3.3, p=0.47) years. During longer-term follow-up after the initial four years, essentially the same numbers of further revascularizations (20 vs. 21) occurred in the CCTA group vs. the control group, thus continuing a significantly higher rate of revascularization among those receiving CCTA (Table). However, the composite and individual outcomes of all-cause mortality and nonfatal MI did not differ between the CCTA and control groups.
Conclusion: Among asymptomatic patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes followed for over twelve years, the use of CCTA to screen for CAD did not significantly affect the rates of all-cause mortality or nonfatal MI. This was despite an overall significantly increased use of revascularization among those receiving CCTA. These definitive findings do not support CCTA screening in this population.
Methods: The FACTOR-64 study randomized 900 patients (age = 61.5 years, males = 52%, Type 2 DM = 88%, DM duration = 13 years) with type 1 or type 2 diabetes for at least 3 to 5 years without CAD symptoms to screening with CCTA (n = 452) or standard national guidelines-based optimal diabetes care (n = 448). Standard primary prevention medical therapy or aggressive secondary prevention therapy with invasive coronary angiography was recommended based on CCTA findings. Enrollment occurred between July 2007 and May 2013, and follow-up extended to May 2024.
Results: The mean follow-up time was 12.7±3.2 (CCTA=12.8±3.1; control=12.6±3.3, p=0.47) years. During longer-term follow-up after the initial four years, essentially the same numbers of further revascularizations (20 vs. 21) occurred in the CCTA group vs. the control group, thus continuing a significantly higher rate of revascularization among those receiving CCTA (Table). However, the composite and individual outcomes of all-cause mortality and nonfatal MI did not differ between the CCTA and control groups.
Conclusion: Among asymptomatic patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes followed for over twelve years, the use of CCTA to screen for CAD did not significantly affect the rates of all-cause mortality or nonfatal MI. This was despite an overall significantly increased use of revascularization among those receiving CCTA. These definitive findings do not support CCTA screening in this population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Electrocardiography For The Prediction of Future Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Pastika Libor, Peters Nicholas, Kramer Daniel, Waks Jonathan, Sau Arunashis, Ng Fu Siong, Patlatzoglou Konstantinos, Sieliwonczyk Ewa, Barker Joseph, Zeidaabadi Boroumand, Mcgurk Kathryn, Khan Sadia, Mandic Danilo, Ware James
A Case of Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Systemic Thromboembolism in a Young Patient on Testosterone Replacement TherapySabri Muhammad, Ijaz Naila, Nadeem Ramsha, Checchio Lucy, Riaz Faiza