Final ID: Sa3072
Association of Body Roundness Index and Cardiovascular Disease among US Adults
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Obesity is one of the major risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD), body roundness index (BRI) is more comprehensive in assessing fat distribution than traditional measurements. However, evidence regarding the association between BRI and the risk of CVD was limited, particularly in American people. This current study aimed to investigate the association between BRI and the risk of CVD among US adults.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that higher BRI was associated with a higher risk of CVD.
Methods: A total of 21,852 participants were included in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys from 6 survey cycles (2003-2004, 2005-2006, 2007-2008, 2009-2010, 2011-2012, 2013-2014, 2015-2016 and 2017-2018). Weighted multivariate logistic regression was carried out to examine the relationship between BRI and the risk of CVD. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) curves were employed to analyze nonlinear relationships.
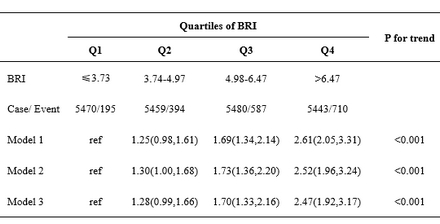
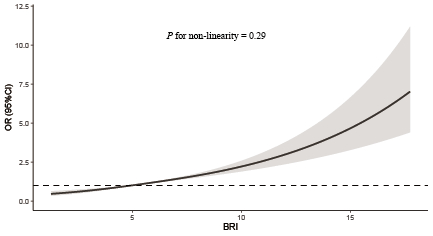
Results: Among 21,852 US adults, the mean (SD) age was 47.5 (17.3) years, 10,669 (48.8%) were female, and 1886 were diagnosed with CVD. In the weighted multi-variable logistic regression model with adjustment for demographics, lifestyle, economic status and dietary factors, higher BRI was significantly associated with a substantially higher risk of CVD. Compared with the participants in the lowest quartile of BRI, those in the highest quartile of BRI had a higher CVD, with OR and 95%CI of 2.47 (1.92-3.17). Furthermore, the RCS demonstrated a linear dose-response relationship between BRI and CVD (Pnon-linearity=0.29).
Conclusion: This national cohort study found a higher BRI was associated with a higher risk of CVD among US adults. BRI may provide a new perspective for CVD prevention among adults.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that higher BRI was associated with a higher risk of CVD.
Methods: A total of 21,852 participants were included in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys from 6 survey cycles (2003-2004, 2005-2006, 2007-2008, 2009-2010, 2011-2012, 2013-2014, 2015-2016 and 2017-2018). Weighted multivariate logistic regression was carried out to examine the relationship between BRI and the risk of CVD. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) curves were employed to analyze nonlinear relationships.
Results: Among 21,852 US adults, the mean (SD) age was 47.5 (17.3) years, 10,669 (48.8%) were female, and 1886 were diagnosed with CVD. In the weighted multi-variable logistic regression model with adjustment for demographics, lifestyle, economic status and dietary factors, higher BRI was significantly associated with a substantially higher risk of CVD. Compared with the participants in the lowest quartile of BRI, those in the highest quartile of BRI had a higher CVD, with OR and 95%CI of 2.47 (1.92-3.17). Furthermore, the RCS demonstrated a linear dose-response relationship between BRI and CVD (Pnon-linearity=0.29).
Conclusion: This national cohort study found a higher BRI was associated with a higher risk of CVD among US adults. BRI may provide a new perspective for CVD prevention among adults.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Multicentre Study for Hands Only CPR (HOCPR) training assessment towards building a ‘Nation of Life Savers” in India
Ravikumar Thanjavur, Sarma Kvs, Ravikumar Thanjavur, Sarkar Manuj, Debnath Dhrubajyoti, Behera Priyamadhaba, Ghate Jayshri, Trikha Divay, Samantaray A, Madhavi K
AI-Derived Retinal Vasculature Features Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Insights from the CRIC StudyDhamdhere Rohan, Modanwal Gourav, Rahman Mahboob, Al-kindi Sadeer, Madabhushi Anant